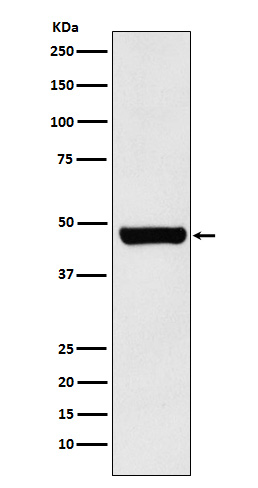
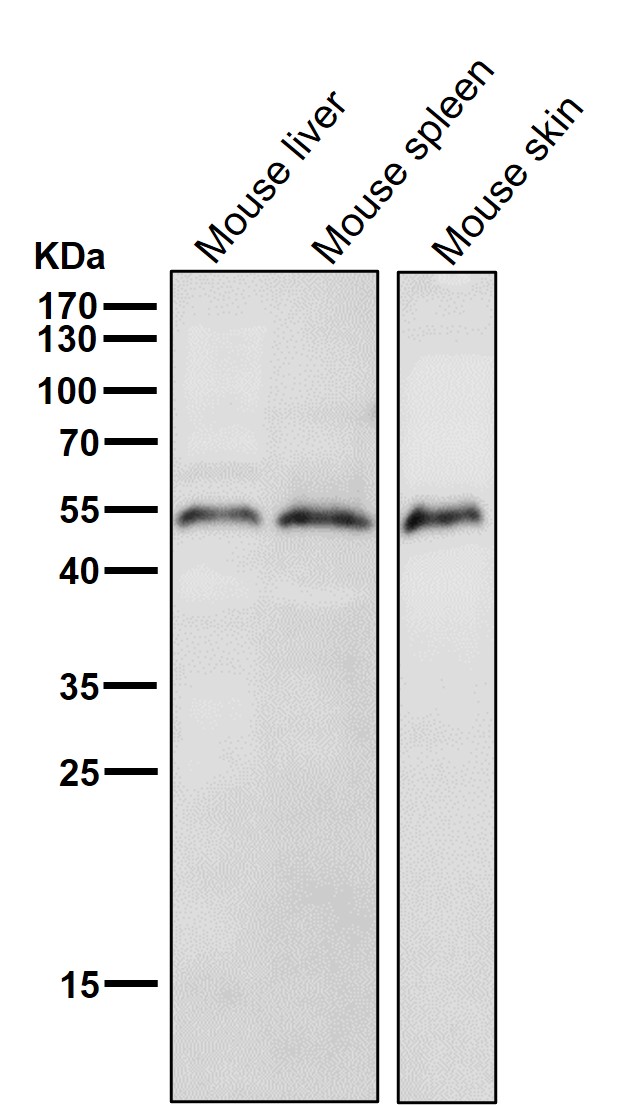
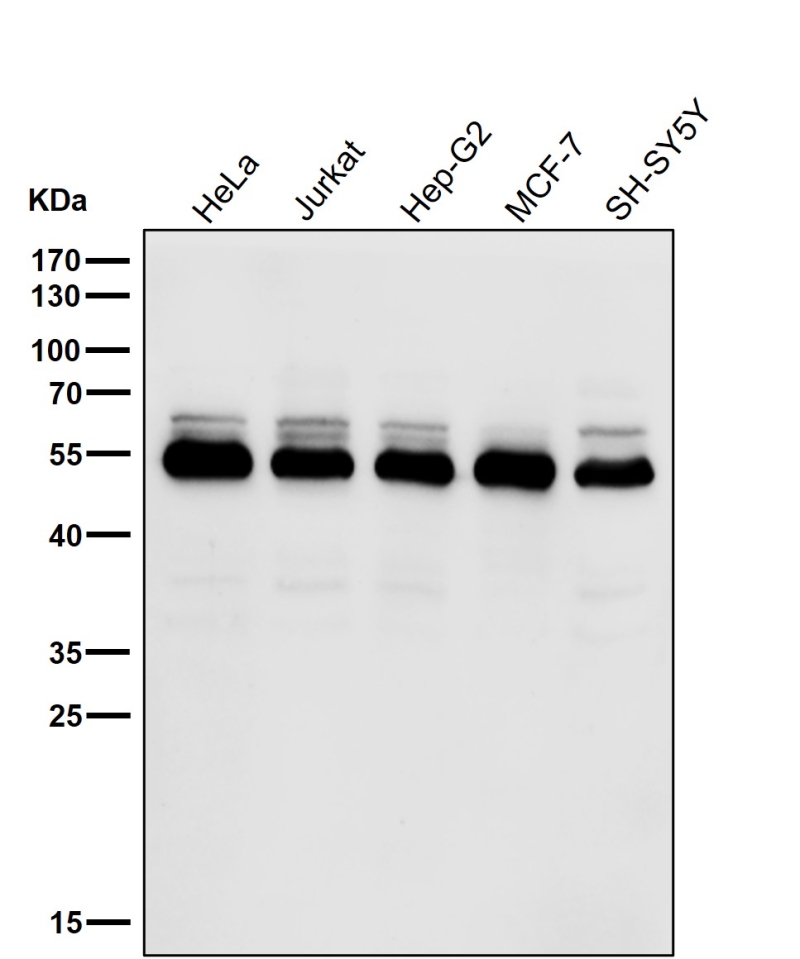
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HIP; HOP; P48; AAG2; SNC6; HSPABP; FAM10A1; FAM10A4; HSPABP1; ST13;;Hip |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 41 kDa ; Observed MW: 47 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Hip |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与HSC70相互作用蛋白(HIP)抗体相关的文献摘要示例(部分信息基于模拟生成,实际文献请通过学术数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**: "The co-chaperone HIP stabilizes substrate-bound Hsc70 in an ATPase cycle"
**作者**: Höhfeld J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过使用HIP特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了HIP作为HSC70的共伴侣蛋白,通过抑制HSC70的ATP酶活性,延长其与底物蛋白的结合时间,从而在蛋白质折叠和转运过程中起关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: "HIP interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and regulates its nuclear translocation"
**作者**: Echeverria PC, et al.
**摘要**: 文章利用HIP抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证明HIP通过与糖皮质激素受体(GR)及HSC70形成复合物,调控GR的核转位过程,为激素信号通路的分子机制提供了新见解。
3. **文献名称**: "Role of HSC70-HIP complex in autophagy under oxidative stress"
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过HIP抗体敲低实验发现,HSC70-HIP复合物在氧化应激条件下通过调控自噬相关蛋白LC3-II的稳定性,参与细胞应激保护机制,提示HIP可能是潜在的治疗靶点。
注:以上内容为示例性质,具体文献请通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“HIP co-chaperone antibody”或“HSC70-interacting protein antibody”检索。建议优先选择近5年高影响力期刊(如JBC、Cell Stress Chaperones)的研究。
The HSC70-interacting protein (HIP), also known as ST13. is a co-chaperone that binds to the ATPase domain of HSC70/HSP70. stabilizing its ADP-bound state to regulate substrate binding and release during protein folding and trafficking. HIP plays a critical role in the chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) pathway, facilitating the selective degradation of cytosolic proteins by lysosomes. It is involved in stress response, protein quality control, and cellular homeostasis, with implications in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging.
Antibodies targeting HIP are widely used to study its expression, localization, and interaction networks in cellular models and tissues. These antibodies enable researchers to explore HIP's role in modulating HSC70 activity, its participation in CMA under stress conditions (e.g., oxidative stress, nutrient deprivation), and its dysregulation in pathologies such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and various cancers. For instance, reduced HIP levels have been linked to impaired CMA in neurodegenerative disorders, while its overexpression in certain tumors correlates with metastasis and drug resistance.
Commercial HIP antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, validated for applications including Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Specificity is confirmed using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated knockdown. Ongoing research focuses on HIP as a potential therapeutic target or biomarker, driving demand for reliable antibodies to dissect its molecular mechanisms in health and disease.
×