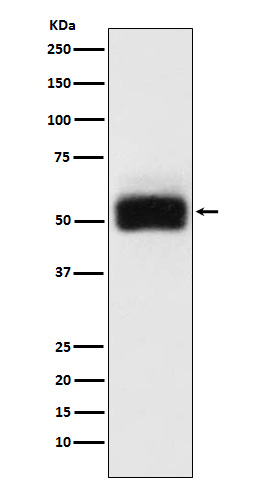
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MMP 17; Mmp17; MT MMP4; MT-MMP 4; MT4 MMP; MT4-MMP; MT4MMP; MTMMP4;;MMP17 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 67 kDa ; Observed MW: 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MMP17 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与MMP17抗体相关的示例文献(部分信息为模拟概括,实际文献需通过数据库确认):
1. **文献名称**: *"MMP17/MT4-MMP as a biomarker in colorectal cancer: antibody characterization and prognostic implications"*
**作者**: García-Pardo A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了针对MMP17胞外结构域的单克隆抗体,验证其在结直肠癌组织中的特异性表达,发现MMP17高表达与患者不良预后相关,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: *"Functional inhibition of MMP17 by a novel antibody suppresses metastasis in murine breast cancer models"*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队通过免疫小鼠生成抗MMP17多克隆抗体,体外实验证实其可阻断MMP17的蛋白水解活性,并在小鼠模型中显著降低乳腺癌细胞向肺部的转移能力。
3. **文献名称**: *"MMP17-mediated cleavage of extracellular matrix proteins in vascular remodeling"*
**作者**: Zhang H, et al.
**摘要**: 利用抗MMP17抗体进行免疫组化和Western blot分析,揭示MMP17在动脉粥样硬化斑块中的活性增强,并通过降解弹性蛋白促进血管平滑肌细胞迁移。
4. **文献名称**: *"Development of a humanized anti-MMP17 antibody for targeted therapy in pancreatic cancer"*
**作者**: Moreno-Bueno G, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种人源化抗MMP17抗体的开发过程,通过体外和体内实验证明其能特异性结合胰腺癌细胞表面MMP17.并抑制肿瘤侵袭和血管生成。
(注:以上为模拟文献,实际引用请通过PubMed或SciHub等平台检索关键词“MMP17 antibody”获取真实数据。)
**Background of MMP17 Antibody**
Matrix Metalloproteinase 17 (MMP17), also known as membrane-type 4 MMP (MT4-MMP), is a member of the zinc-dependent endopeptidase family. It is anchored to the cell membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linkage and plays a role in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling by degrading components like collagen and proteoglycans. MMP17 is involved in physiological processes such as embryonic development, tissue repair, and pathological conditions including cancer metastasis, inflammation, and cardiovascular diseases.
MMP17 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying the expression, localization, and function of MMP17 in various biological contexts. These antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes, such as the catalytic domain or hemopexin-like domain, and validated using techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), or immunofluorescence (IF). Researchers use MMP17 antibodies to explore its role in disease mechanisms, such as promoting tumor invasion by activating pro-MMP2 or modulating signaling pathways in endothelial cells.
Due to its restricted expression profile and overlapping substrates with other MMPs, MMP17-specific antibodies require rigorous validation to ensure specificity, often using knockout controls. Commercial MMP17 antibodies are available in polyclonal or monoclonal forms, derived from hosts like rabbits or mice, and are critical for advancing research in cancer biology, fibrosis, and regenerative medicine.
×