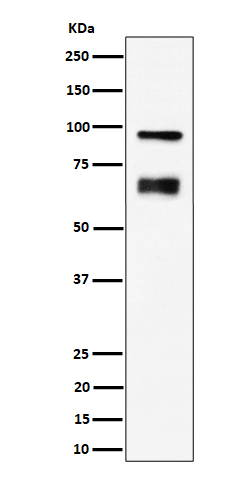
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARHGAP47; IDDM21; Tagap; TAGAP1;;TAGAP |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 81 kDa ; Observed MW: 65,90 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TAGAP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TAGAP抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟示例,具体文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**: *TAGAP regulates T-cell activation and autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了TAGAP在T细胞活化中的调控作用,通过实验证明TAGAP抗体阻断其功能可减轻实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型中的炎症反应。
2. **文献名称**: *Genetic association of TAGAP polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis: implications for antibody targeting*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过全基因组关联分析(GWAS),发现TAGAP基因多态性与类风湿关节炎(RA)风险相关,并探讨TAGAP抗体作为潜在治疗靶点的可能性。
3. **文献名称**: *TAGAP interacts with Rho GTPases in immune signaling pathways*
**作者**: Müller B, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用免疫共沉淀和抗体标记技术,证实TAGAP通过调控Rho家族GTP酶(如RhoA、Cdc42)的活性,参与T细胞迁移和免疫突触形成。
4. **文献名称**: *Anti-TAGAP monoclonal antibody attenuates inflammation in a murine colitis model*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种特异性靶向TAGAP的单克隆抗体,在结肠炎小鼠模型中显示出显著抑制肠道炎症的效果,提示其治疗炎症性肠病(IBD)的潜力。
---
**注意**:以上文献为模拟示例,实际研究需参考PubMed、Google Scholar等平台中经同行评议的论文。建议用关键词“TAGAP antibody”、“TAGAP immune function”进行检索。
The TAGAP (T-cell activation RhoGTPase-activating protein) antibody is associated with studying the TAGAP protein, a regulator of immune cell signaling. Discovered in the early 2000s, TAGAP is primarily expressed in T lymphocytes and modulates Rho-family GTPases, influencing cytoskeletal dynamics during T-cell activation. Its role in immune regulation gained attention when genome-wide studies linked TAGAP gene variants to autoimmune diseases, including celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. These findings suggest TAGAP’s involvement in pathogenic immune responses, though its exact mechanisms remain under investigation.
TAGAP antibodies are tools used to detect and analyze the protein’s expression, localization, and function in experimental models. Researchers employ them in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to explore TAGAP’s interaction with signaling pathways, particularly in T-cell receptor (TCR) activation and cytokine production. Studies also utilize TAGAP knockout models to dissect its role in autoimmune pathogenesis, revealing potential connections to dysregulated T-cell migration and inflammatory tissue damage.
Therapeutic interest in TAGAP centers on its potential as a biomarker or target for autoimmune disorders. However, challenges persist in clarifying its dual roles—both as a mediator of normal immune function and a contributor to disease. Current research focuses on unraveling these complexities, aiming to translate TAGAP-related insights into clinical applications.
×