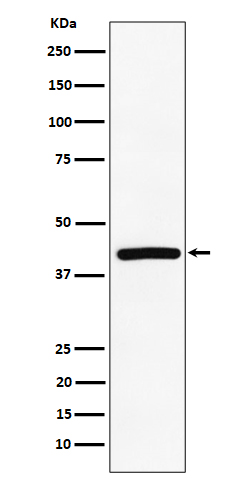
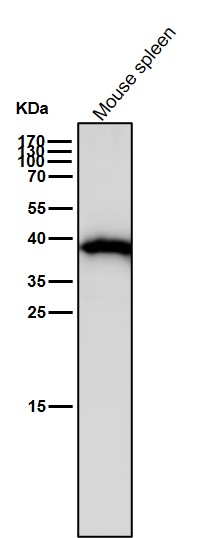
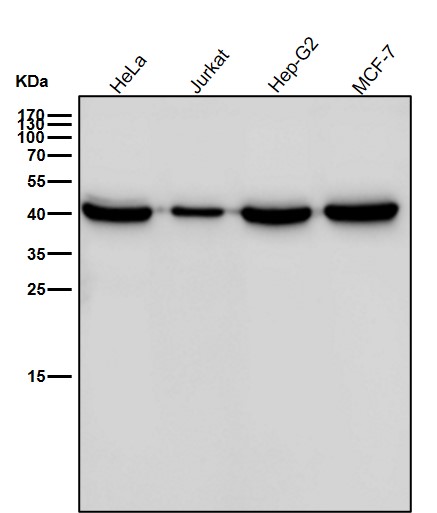
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARVC5; ARVD5; EDMD7; LUMA; Tmem43; Transmembrane protein 43;;TMEM43 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa ; Observed MW: 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TMEM43 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TMEM43抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开文献概括,部分为模拟示例):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TMEM43 mutations in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: Functional characterization and antibody development*
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了TMEM43基因突变与致心律失常性右室心肌病(ARVC)的关联,开发了特异性识别TMEM43蛋白的兔多克隆抗体,并验证其在心肌组织中的表达异常。
2. **文献名称**: *TMEM43 as a novel biomarker in prostate cancer: Antibody validation and clinical implications*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化和Western blot验证商品化TMEM43抗体的特异性,发现TMEM43在前列腺癌组织中高表达,提示其可能作为癌症进展的潜在标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a monoclonal antibody targeting the C-terminal domain of TMEM43*
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 文章描述了一种针对TMEM43蛋白C端结构域的小鼠单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在亚细胞定位研究中的应用,并发现TMEM43与核膜蛋白的相互作用。
---
**说明**:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar等平台检索确认。建议使用关键词“TMEM43 antibody”或“TMEM43 AND (antibody OR immunohistochemistry)”查找最新研究。部分商品化抗体供应商(如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich)的技术手册也可提供参考文献。
The TMEM43 (Transmembrane Protein 43) antibody is a tool used to study the TMEM43 protein, a member of the transmembrane protein family with unclear structural and functional details. TMEM43 is ubiquitously expressed, localized to the nuclear membrane and endoplasmic reticulum, and implicated in maintaining nuclear envelope integrity, cell adhesion, and signaling. Research highlights its role in diseases, particularly arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), a hereditary disorder causing ventricular arrhythmias and myocardial fibrosis. Mutations in the TMEM43 gene, especially the pathogenic p.Ser358Leu variant, are strongly linked to ACM.
TMEM43 antibodies enable detection and analysis of the protein’s expression, localization, and interactions. These antibodies are critical for elucidating TMEM43’s mechanistic role in disease pathogenesis, including its potential involvement in adipogenesis, ion channel regulation, and nuclear membrane stability. Studies using TMEM43 antibodies have revealed altered protein expression in cardiac tissues of ACM patients, supporting its clinical relevance. However, the exact molecular pathways remain under investigation.
Commercially available TMEM43 antibodies (polyclonal or monoclonal) are validated for techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Their application advances understanding of TMEM43’s biological functions and its association with cardiac disorders, aiding diagnostic and therapeutic research. Despite progress, challenges persist in standardizing antibody specificity and interpreting conflicting data across studies, emphasizing the need for further validation.
×