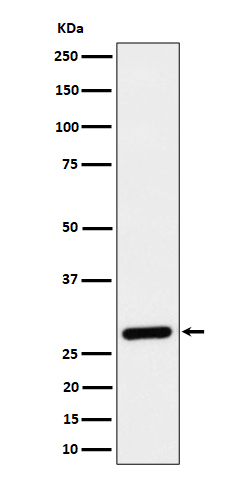
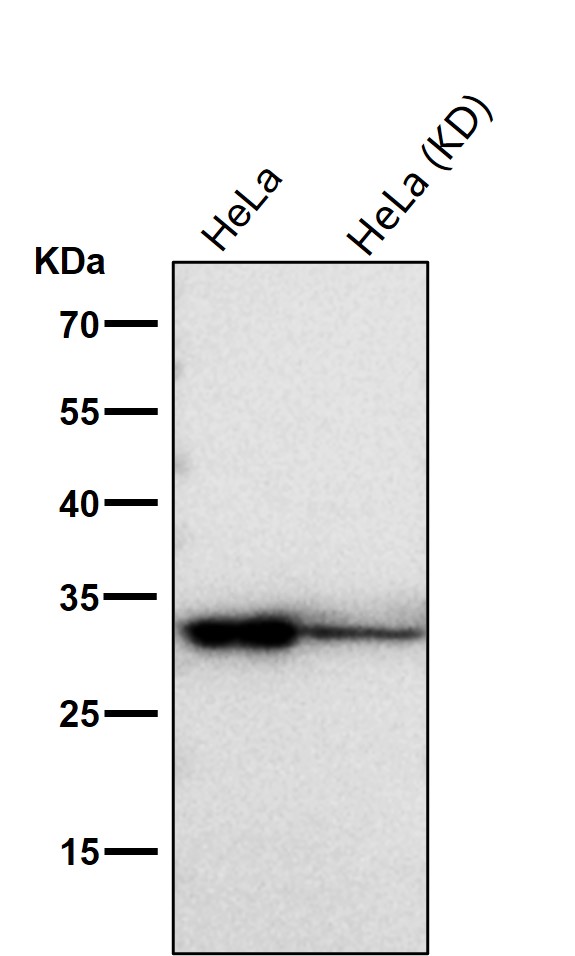
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Chloride intracellular channel 4; Clic4; CLIC4L; HUH1; MC3S5; mtCLIC; p64H1;;CLIC4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CLIC4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于 **CLIC4抗体** 的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"CLIC4 regulates TGF-β-dependent myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix production"*
**作者**: Suh KS, Crutchley JM, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用CLIC4抗体检测其在转化生长因子β(TGF-β)信号通路中的作用,发现CLIC4通过调节细胞骨架重组和胶原分泌,促进成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞分化,与纤维化疾病及肿瘤微环境相关。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"CLIC4 mediates cell migration and invasion by regulating Rac1 activity in breast cancer cells"*
**作者**: Argenzio E, Moolenaar WH, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过CLIC4抗体的免疫沉淀和免疫荧光技术,揭示CLIC4通过与Rac1 GTP酶相互作用调控乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Mitochondrial targeting of CLIC4 modulates autophagy and promotes cell survival under oxidative stress"*
**作者**: Tung JJ, Kitajewski J, et al.
**摘要**: 利用CLIC4抗体进行亚细胞定位分析,发现氧化应激下CLIC4易位至线粒体,通过调控自噬通路影响细胞存活,为氧化损伤相关疾病机制提供新见解。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Antibody-based profiling of CLIC4 expression in human tumors reveals stromal-specific upregulation"*
**作者**: Valenzuela SM, Martin DK, et al.
**摘要**: 通过多种CLIC4抗体的免疫组化验证,发现CLIC4在多种癌症(如乳腺癌、胰腺癌)的肿瘤间质中高表达,提示其作为肿瘤微环境生物标志物的潜力。
---
以上文献聚焦于CLIC4抗体在疾病机制、细胞行为调控及临床诊断中的应用,涵盖分子机制、亚细胞定位及临床相关性研究。
CLIC4 (Chloride Intracellular Channel 4) is a member of the CLIC protein family, which exhibits dual functionality as both soluble cytoplasmic proteins and integral membrane chloride ion channels. It plays diverse roles in cellular processes such as apoptosis, autophagy, cell cycle regulation, and differentiation. Structurally, CLIC4 contains conserved glutathione S-transferase-like domains and undergoes redox-dependent conformational changes, enabling its translocation to cellular membranes under stress conditions. This dynamic behavior allows CLIC4 to interact with various signaling molecules, including TGF-β, p53. and NF-κB pathways, influencing cellular responses to oxidative stress, DNA damage, and extracellular cues.
CLIC4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate CLIC4's involvement in pathological conditions. Research has linked CLIC4 dysregulation to cancer progression (showing both tumor-suppressive and oncogenic roles depending on context), fibrosis, angiogenesis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Its subcellular redistribution during apoptosis—from cytoplasm to nucleus or mitochondria—has made it a biomarker of cellular stress. However, CLIC4's pleiotropic effects and tissue-specific expression patterns complicate its functional characterization, driving continued interest in developing high-specificity antibodies. These reagents help clarify CLIC4's paradoxical roles, particularly its dual impact on tumor growth versus suppression, and its potential as a therapeutic target or diagnostic marker in diseases like breast cancer and pulmonary fibrosis.
×