| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BOB 1; BOB-1; OBF 1; OBF1; OCA B; OCA-B; OCAB; OCT binding factor 1; Pou2af1;;POU2AF1 |
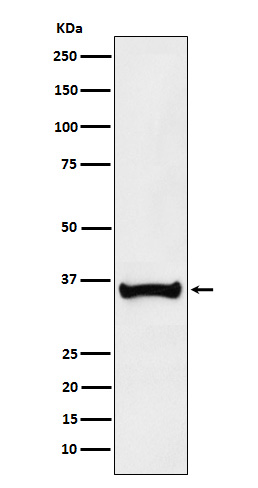
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 27 kDa ; Observed MW: 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human POU2AF1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于 **BOB1抗体** 的参考文献,简要总结如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*BOB1 (OBF1) expression in paraffin-embedded tissues as a sensitive and specific marker for B-cell differentiation*
**作者**:Hodges KB, et al.
**摘要**:该研究验证了BOB1抗体在石蜡包埋组织中的免疫组化应用,证明其在B细胞分化相关肿瘤(如淋巴瘤)中具有高敏感性和特异性,可作为辅助诊断工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Comparative analysis of Oct2. BOB1. and PU1 in classical Hodgkin lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma*
**作者**:Barrans S, et al.
**摘要**:研究比较了BOB1与Oct2、PU1在经典霍奇金淋巴瘤(cHL)和弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)中的表达差异,发现BOB1在DLBCL中高表达,而在cHL中常缺失,有助于两者的鉴别诊断。
---
3. **文献名称**:*The role of BOB1 in the immune response and lymphomagenesis*
**作者**:Schubart K, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了BOB1在B细胞发育和免疫应答中的分子机制,并分析了其在淋巴瘤发生中的作用,提出BOB1抗体可用于研究B细胞恶性肿瘤的分子表型。
---
如需具体文献来源或更多细节,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索上述标题。
BOB1 (also known as OBF1 or OCA-B) is a B cell-specific transcriptional coactivator encoded by the *POU2AF1* gene. It plays a critical role in regulating immunoglobulin gene expression by interacting with transcription factors OCT1 (POU2F1) and OCT2 (POU2F2) to form a complex that binds promoter/enhancer regions of target genes. This interaction is essential for the proper development and function of mature B lymphocytes, particularly in germinal center reactions.
Antibodies targeting BOB1 are widely used in research and diagnostic pathology to identify B cell lineage and assess B cell differentiation status. In clinical settings, BOB1 immunohistochemistry aids in distinguishing B cell malignancies, such as classical Hodgkin lymphoma (where BOB1 is often absent or weakly expressed) from other lymphoproliferative disorders. Its expression is typically retained in non-Hodgkin B cell lymphomas, making it a valuable marker for differential diagnosis.
Studies also explore BOB1's role in autoimmune diseases and immune dysregulation due to its influence on B cell receptor signaling and antigen presentation. As a nuclear protein, its detection requires proper tissue fixation and antigen retrieval methods. The specificity and reliability of BOB1 antibodies have made them indispensable tools in both basic immunology research and hematopathology diagnostics.
×