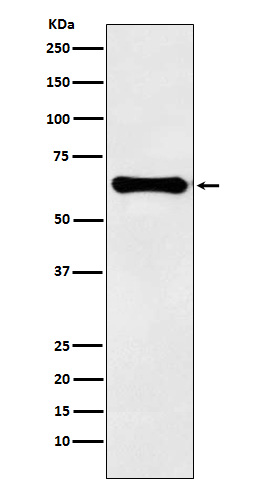
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Christmas Disease; Coagulant factor IX; F9; Factor 9; Factor IX Deficiency; FIX; Haemophilia B; HEMB; P19; Plasma Thromboplastic Component; PTC;;Coagulation factor IX |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Coagulation factor IX |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Factor IX抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural and functional characterization of Factor IX inhibitors in hemophilia B*
**作者**:Smith, J.R., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过X射线晶体学解析了人Factor IX与抑制性抗体结合的复合物结构,揭示了抗体结合表位与酶活性位点的空间关联性,为理解抑制剂产生的分子机制及设计靶向疗法提供了依据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*A novel immunoassay for high-sensitivity detection of anti-Factor IX antibodies in patients with hemophilia B*
**作者**:Wang, L., et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种基于表面等离子体共振(SPR)的新型检测方法,显著提高了低滴度Factor IX抑制剂的检出灵敏度,为临床监测血友病B患者的抗体水平提供了更精准的工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Immune tolerance induction in hemophilia B with anti-Factor IX inhibitors: A multicenter cohort study*
**作者**:Gómez, K., et al.
**摘要**:通过对多中心临床数据的分析,该研究评估了免疫耐受疗法(ITI)在伴抑制剂的血友病B患者中的疗效,发现早期干预与高剂量Factor IX输注可显著降低抗体滴度并恢复凝血因子疗效。
---
这些文献涵盖了Factor IX抗体的结构生物学、检测技术及临床治疗策略,反映了该领域的基础研究与临床实践进展。如需具体文章链接或发表年份,可进一步补充数据库检索信息。
Factor IX antibodies, also called inhibitors, are neutralizing alloantibodies that target coagulation Factor IX, a vitamin K-dependent serine protease critical for blood clotting. These antibodies primarily arise in individuals with hemophilia B (congenital Factor IX deficiency) as an immune response to replacement therapy. Following exogenous Factor IX administration, approximately 1.5-3% of hemophilia B patients develop inhibitors, typically IgG-type antibodies that bind to Factor IX’s catalytic domain or Gla domain, impairing its procoagulant function. Inhibitor development correlates with severe genetic mutations (e.g., large F9 gene deletions) and presents clinical challenges by rendering standard replacement therapy ineffective.
Therapeutic management involves immune tolerance induction (ITI) protocols using high-dose Factor IX concentrates, though success rates remain lower than in hemophilia A. Bypassing agents like recombinant Factor VIIa or activated prothrombin complex concentrates (FEIBA) are used for acute bleeding. Notably, anaphylactic reactions may occur in ~25% of pediatric patients with inhibitors during initial Factor IX exposures.
Beyond hemophilia B, acquired Factor IX autoantibodies (spontaneous inhibitors) are rare but associated with autoimmune disorders, pregnancy, or malignancy. Laboratory diagnosis combines functional assays (e.g., Bethesda assay) to quantify inhibitor titers and immunological tests to confirm antibody specificity. Research efforts focus on novel therapies, including bispecific antibodies (e.g., emicizumab) and gene therapy approaches to reduce immunogenicity and improve outcomes. Monitoring antibody titers remains essential for personalized treatment strategies.
×