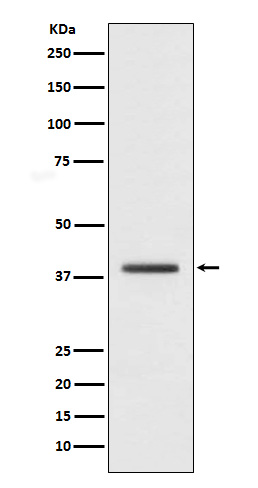
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | H2A.y; H2A/y; H2AF12M; H2AFJ; H2afy; Histone H2A.Y; Histone macroH2A1; Histone macroH2A1.1; Histone macroH2A1.2; mH2a;mH2A1;;Histone mH2A1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Histone mH2A1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于macroH2A.1抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: "MacroH2A1 associates with nuclear lamina and regulates chromatin organization in melanoma cells"
**作者**: Kapoor A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用macroH2A.1特异性抗体,发现其在黑色素瘤细胞中通过与核纤层相互作用调控染色质空间构象,抑制肿瘤转移相关基因的表达。
---
2. **文献名称**: "The histone variant macroH2A1.1 regulates stem cell pluripotency through modulation of chromatin states"
**作者**: Pasque V, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和ChIP-seq实验(使用macroH2A.1抗体),证明该组蛋白变体通过维持分化相关基因的沉默状态,在多能干细胞重编程中起关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Antibody-specific validation for macroH2A1 isoforms reveals distinct roles in cellular senescence"
**作者**: Gialitakis M, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发并验证了针对macroH2A1不同亚型(如macroH2A1.1和1.2)的特异性抗体,揭示其在细胞衰老过程中对DNA损伤应答的差异性调控机制。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Age-dependent loss of macroH2A1 in human fibroblasts correlates with disrupted senescence-associated chromatin reorganization"
**作者**: Chouliaras L, et al.
**摘要**: 使用macroH2A.1抗体检测发现,衰老的人类成纤维细胞中该组蛋白表达显著降低,提示其参与维持衰老相关的异染色质稳定性。
---
以上文献均涉及macroH2A.1抗体的实验应用,涵盖癌症、干细胞及衰老研究领域。
The macroH2A.1 antibody is a critical tool for studying the unique histone variant macroH2A.1. which plays a role in epigenetic regulation. MacroH2A is a conserved H2A variant characterized by a large C-terminal macrodomain, a feature absent in canonical histones. MacroH2A.1. one of two major splice isoforms (macroH2A.1 and macroH2A.2), is involved in chromatin compaction, transcriptional repression, and X-chromosome inactivation. Its macrodomain can bind metabolites like NAD+-derived ligands, linking chromatin dynamics to cellular metabolism.
Antibodies targeting macroH2A.1 are widely used to investigate its localization and function in heterochromatin formation, cellular differentiation, and senescence. These antibodies enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and ChIP-seq to assess macroH2A.1's association with silenced genes, retrotransposons, or specific genomic regions. Researchers also utilize them to explore its tumor-suppressive roles, as macroH2A.1 is often downregulated in cancers, influencing metastasis and proliferation.
Commercial macroH2A.1 antibodies are typically raised against epitopes within the macrodomain or isoform-specific regions, with validation across species like humans and mice. Specificity remains a consideration due to homology between macroH2A isoforms. Studies employing these antibodies have advanced understanding of epigenetic aging, stem cell plasticity, and metabolic diseases, highlighting macroH2A.1's multifaceted role in health and disease.
×