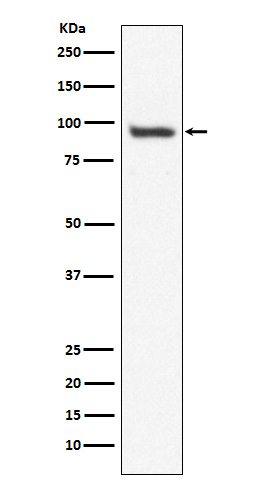
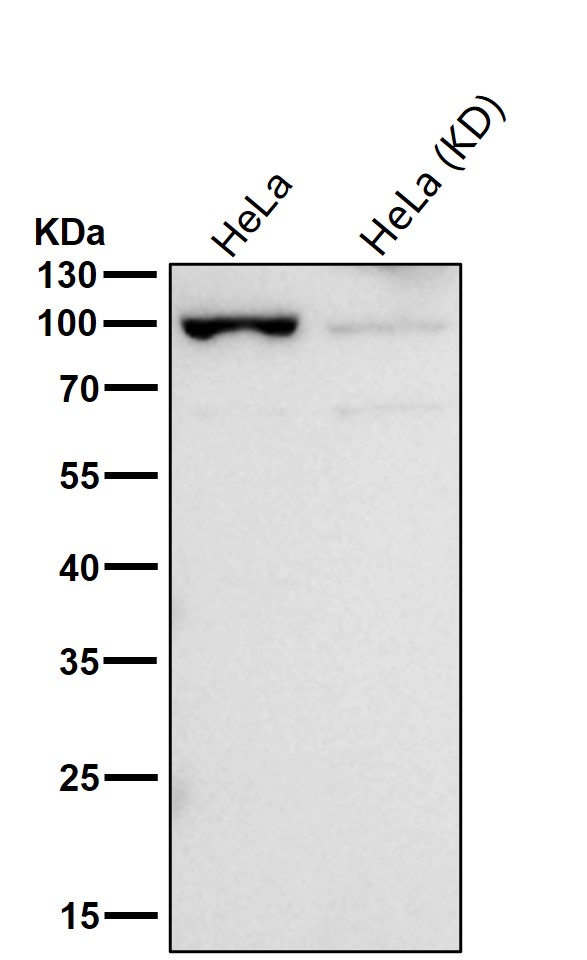
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Deubiquitinating enzyme 13; Isopeptidase T3; ISOT3; UBP13; USP13;;USP13 |
| WB Predicted band size | 97 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human USP13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于USP13抗体的3篇参考文献摘要,涵盖其在不同研究中的应用和功能分析:
---
1. **文献名称**:*USP13 regulates the RAP80-BRCA1 complex dependent DNA damage response*
**作者**:Lu et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用USP13特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示USP13通过去泛素化RAP80调控BRCA1复合体功能,影响DNA损伤修复过程,尤其在乳腺癌细胞中作用显著。
---
2. **文献名称**:*USP13 deubiquitinates and stabilizes the E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin*
**作者**:Liu et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用USP13抗体),研究发现USP13通过稳定Parkin蛋白调控线粒体自噬,其异常表达可能导致帕金森病相关神经退行性病变。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting USP13-mediated deubiquitination of CDC25A as a therapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Wang et al.
**摘要**:该研究使用USP13抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现USP13通过去泛素化CDC25A促进肝癌细胞增殖,提示其作为肝癌治疗靶点的潜力。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需核对期刊名称、年份等完整信息。如需更多文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“USP13 antibody application”为关键词检索。
USP13 (Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 13) is a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) belonging to the USP family, which regulates protein stability and function by removing ubiquitin chains from target substrates. It plays critical roles in diverse cellular processes, including protein quality control, DNA repair, autophagy, and immune signaling. USP13 is implicated in cancer progression, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic diseases, with studies highlighting its involvement in modulating key substrates like p53. PTEN, MITF, and Parkin. For instance, USP13 stabilizes oncoproteins (e.g., MITF in melanoma) or tumor suppressors (e.g., PTEN in breast cancer), depending on cellular context, making it a potential therapeutic target.
Antibodies against USP13 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Researchers often validate USP13 antibodies using knockout cell lines or tissues to ensure specificity, as cross-reactivity with other USP family members (e.g., USP5 or USP10) can occur. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised against epitopes within the N-terminal or catalytic domains. Recent studies also employ USP13 antibodies to explore its role in diseases, such as its interaction with α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease or regulation of PD-L1 in cancer immunotherapy. Proper validation and application-specific optimization remain crucial for reliable experimental outcomes.
×