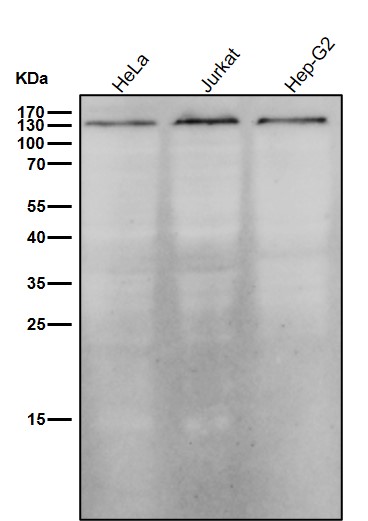

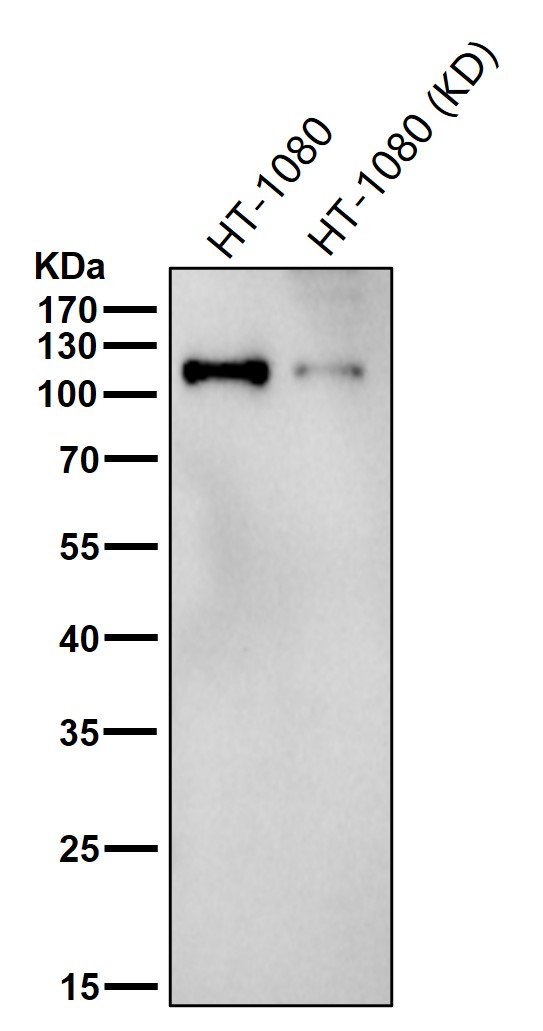
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Helicard; Hlcd; IDDM19; IFIH1; MDA-5; RH116; RIG I like receptor 2; RLR 2; RNA helicase DEAD box protein 116;;MDA5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 117 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MDA5 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MDA5抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against MDA5 and clinical phenotypes in patients with dermatomyositis*
**作者**:Sato S, Hirakata M.
**摘要**:该研究分析了MDA5抗体在皮肌炎患者中的临床意义,发现其阳性与快速进展性间质性肺病(RP-ILD)显著相关,提示MDA5抗体可作为预后不良的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Distinctive cutaneous and systemic features associated with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibodies in adults with dermatomyositis*
**作者**:Hall JC, Casciola-Rosen L.
**摘要**:研究揭示了MDA5抗体阳性皮肌炎患者的独特皮肤表现(如手掌丘疹、溃疡)和系统性特征(如ILD高发),并强调其与低肌炎活性但高ILD死亡率的关联。
3. **文献名称**:*Myositis autoantibodies in clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis*
**作者**:Fiorentino D, Chung L.
**摘要**:探讨了无肌病性皮肌炎(CADM)中MDA5抗体的高阳性率,及其与急性/亚急性ILD的强相关性,提出早期抗体检测对ILD风险分层的重要性。
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-MDA5 antibody as a predictor of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in juvenile dermatomyositis*
**作者**:Gono T, Kawaguchi Y.
**摘要**:针对儿童皮肌炎的研究发现,MDA5抗体阳性患者更易发生快速进展性ILD,且对传统免疫治疗反应差,提示需早期强化干预。
以上文献均聚焦于MDA5抗体在自身免疫性肌炎中的诊断、临床表型及预后价值,尤其强调其对ILD风险的预警作用。
MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5), encoded by the *IFIH1* gene, is a cytosolic RNA helicase belonging to the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) family. It functions as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) that detects long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) from viral infections or endogenous sources, triggering innate immune responses via the MAVS/IPS-1 signaling pathway. This activates transcription factors (IRF3/7. NF-κB) to induce type I interferons (IFNs) and proinflammatory cytokines.
Anti-MDA5 autoantibodies are primarily associated with autoimmune conditions, notably dermatomyositis (DM), particularly in clinically amyopathic DM (CADM). These autoantibodies target the MDA5 protein, disrupting its normal antiviral signaling and correlating with distinct clinical features, such as skin ulcers, palmar papules, and rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD), a life-threatening complication.
First identified in 2005. anti-MDA5 antibodies are detected via immunoprecipitation or ELISA. Their presence is a critical biomarker for diagnosing MDA5-associated DM and stratifying disease severity, especially in Asian populations. RP-ILD linked to anti-MDA5 antibodies has a high mortality rate, necessitating aggressive immunosuppressive therapies (e.g., glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, rituximab). Research continues to explore their pathogenic role, including potential interference with viral RNA sensing or induction of proapoptotic pathways. Early detection improves prognosis, highlighting their clinical relevance in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
×