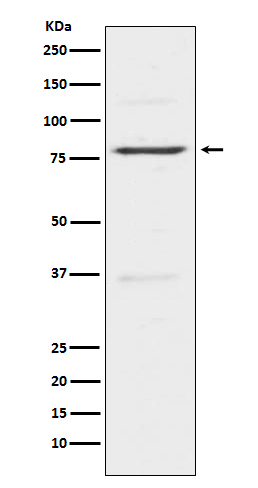
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | INSRR; Insulin receptor related receptor precursor; IR related receptor; IRR; Sirr;;Insulin receptor related protein |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 144 kDa ; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Insulin receptor related protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与胰岛素受体抗体(Insulin Receptor Antibodies)相关的文献摘要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies to the insulin receptor in human disease*
**作者**: C. Ronald Kahn, Jeffrey S. Flier, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了抗胰岛素受体自身抗体与严重胰岛素抵抗综合征(如B型胰岛素抵抗)的关联。抗体通过阻断胰岛素与受体结合或加速受体降解,导致高血糖和黑棘皮症。部分患者出现低血糖,提示抗体可能具有激动剂样作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Insulin receptor autoantibodies in hypoglycemia: Mechanism and clinical significance*
**作者**: Y. Hirata, K. Ishizu, et al.
**摘要**: 描述了某些自身免疫性疾病患者体内存在激动型胰岛素受体抗体,这些抗体模拟胰岛素作用,激活受体下游信号,导致空腹低血糖(Hirata病)。研究揭示了抗体功能异质性及其与代谢异常的复杂关系。
3. **文献名称**: *Structural and functional characterization of anti-insulin receptor monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**: Simeon I. Taylor, Barbara Marcus-Samuels, et al.
**摘要**: 通过单克隆抗体研究胰岛素受体表位,发现不同抗体可拮抗或激活受体功能。拮抗型抗体抑制胰岛素信号传导,而激动型抗体可独立激活受体,为理解抗体介导的病理机制提供了分子基础。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对原文准确性。若需具体论文链接或更多文献,可进一步说明。
×