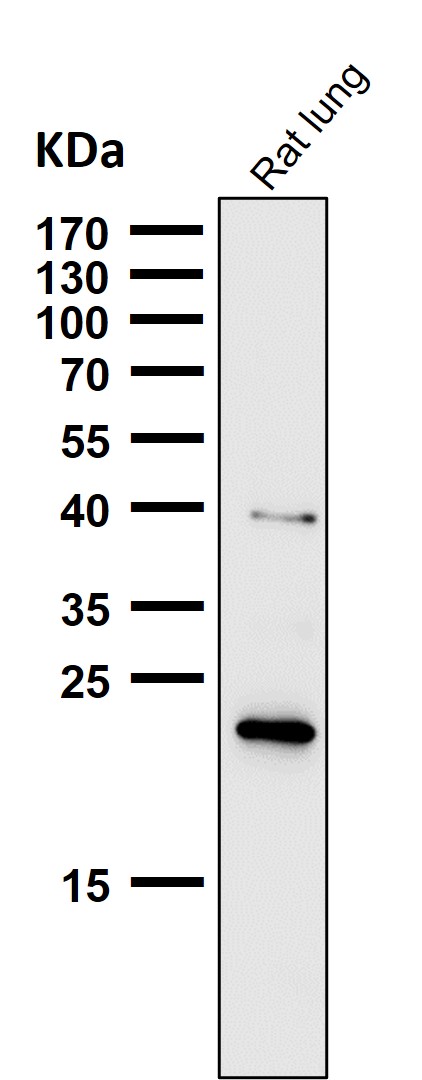
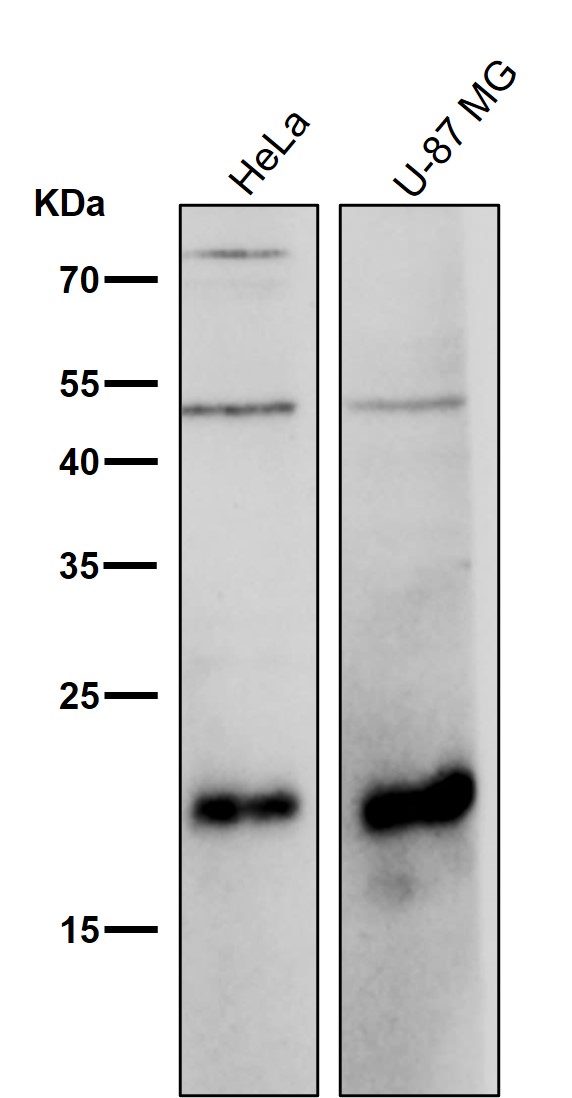
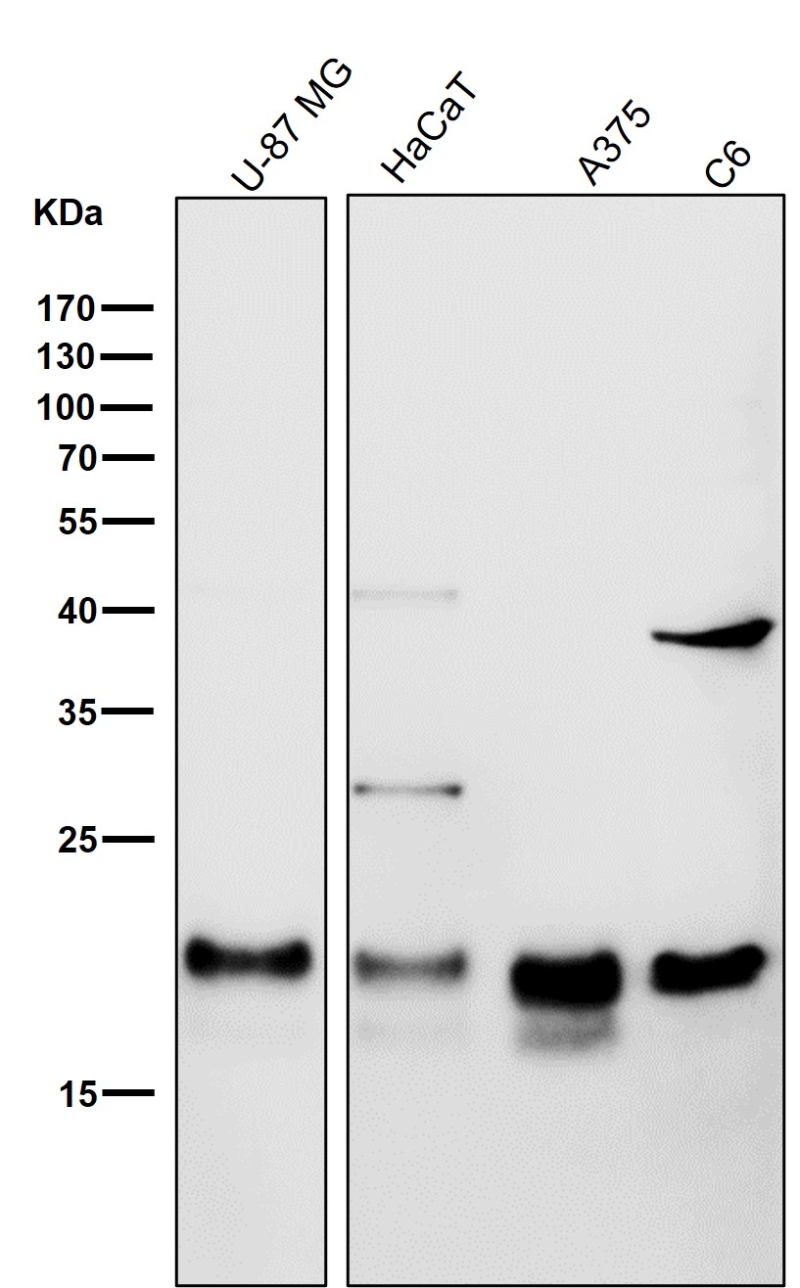
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Apoferritin; F HC; Ferritin H subunit; FHC; FRIH; FTH; FTH1; FTHL6; N-terminally processed; PIG15; PLIF;;Ferritin heavy chain |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Ferritin heavy chain |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Ferritin Heavy Chain(FTH1)抗体的代表性文献概览:
1. **"Ferritin heavy chain upregulation by NF-κB inhibits TNFα-induced apoptosis by suppressing reactive oxygen species"**
*作者:Pham et al. (2004)*
*摘要:* 研究使用FTH1抗体通过Western blot证实,NF-κB通过上调铁蛋白重链抑制TNFα诱导的细胞凋亡,机制与减少活性氧(ROS)有关。
2. **"Differential regulation of ferritin heavy chain gene during hypoxia and hypoxia/reoxygenation in neuronal cells"**
*作者:Schneider et al. (2014)*
*摘要:* 通过免疫荧光和qPCR结合FTH1抗体,发现缺氧/复氧条件下神经元细胞中FTH1表达动态变化,提示其在氧化应激中的神经保护作用。
3. **"Ferritin heavy chain-mediated iron homeostasis modulates β-catenin signaling to drive colorectal cancer progression"**
*作者:Wang et al. (2021)*
*摘要:* 利用FTH1抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示结直肠癌中FTH1通过调控铁代谢激活Wnt/β-catenin通路,促进肿瘤侵袭和转移的机制。
*注:以上文献均涉及FTH1抗体的实验应用(如蛋白检测、定位分析),并探讨其在疾病中的功能。建议通过PubMed或期刊官网输入标题获取完整文献。*
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1) is a key subunit of the ferritin protein complex, essential for intracellular iron storage and homeostasis. Ferritin, composed of 24 subunits of heavy (FTH1) and light (FTL) chains, forms a nanocage structure that sequesters excess iron in a non-toxic, bioavailable form, protecting cells from oxidative damage. FTH1 possesses ferroxidase activity, enabling iron oxidation (Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺) for safe storage. Dysregulation of FTH1 expression is linked to iron-related disorders, including anemia, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), and cancer, where iron metabolism often supports tumor growth.
Antibodies targeting FTH1 are critical tools for studying iron metabolism, protein localization, and disease mechanisms. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to quantify FTH1 levels, assess tissue-specific iron distribution, or investigate pathological iron accumulation. Commercial FTH1 antibodies are typically raised against epitopes in conserved regions, ensuring cross-reactivity across human, mouse, and rat samples. Validation often involves knockout controls or iron-modulation experiments to confirm specificity.
Research applications include exploring FTH1's dual role in cancer (pro-tumorigenic vs. tumor-suppressive) and its involvement in ferroptosis, an iron-dependent cell death pathway. Additionally, FTH1 antibodies aid in diagnosing iron overload conditions (e.g., hemochromatosis) and monitoring therapeutic responses in preclinical models. Their utility underscores FTH1's importance as both a biomarker and a functional mediator in cellular iron biology.
×