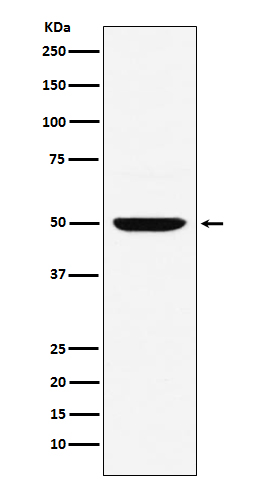
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LSIRF; Multiple myeloma oncogene 1; NF-EM5; IRF4; MUM1; Transcriptional activator PIP;;IRF4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human IRF4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MUM1抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*MUM1/IRF4 expression in multiple myeloma: association with t(6;14) and CD20 positivity*
**作者**:Iida S, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了MUM1/IRF4在骨髓瘤细胞中的表达与染色体易位t(6;14)及CD20标记的关联,发现MUM1高表达可能与浆细胞分化异常及特定遗传学异常相关,为多发性骨髓瘤的分子分型提供依据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*MUM1 expression is a specific marker of plasmablastic differentiation in B-cell lymphomas*
**作者**:Natkunam Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过免疫组化分析发现,MUM1抗体在弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)的浆母细胞亚型中显著表达,提示其可作为区分DLBCL亚型及浆细胞分化的重要标记物。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Prognostic significance of MUM1/IRF4 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma*
**作者**:Tsuboi K, et al.
**摘要**:该文献评估了MUM1/IRF4在DLBCL中的预后价值,发现MUM1阳性患者总生存率较低,提示其可能作为DLBCL的不良预后指标,并与BCL6等标志物联合用于临床分层。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为示例性概括,具体内容建议通过PubMed或学术数据库检索原文以验证细节。
The MUM1 (Multiple Myeloma Oncogene 1) antibody detects the IRF4 (Interferon Regulatory Factor 4) protein, a transcription factor critical in immune regulation and lymphocyte differentiation. Initially identified in multiple myeloma, MUM1/IRF4 is encoded by the *IRF4* gene on chromosome 6p25.3 and belongs to the interferon regulatory factor family. Structurally, it contains a DNA-binding domain and a transactivation domain, enabling interaction with specific DNA motifs to regulate gene expression.
MUM1/IRF4 plays a dual role: it promotes plasma cell differentiation by cooperating with transcription factors like PU.1 and represses B-cell-specific genes during lymphocyte development. In diagnostic pathology, MUM1 antibody is widely used as an immunohistochemical marker. It is expressed in late-stage B-cell malignancies, including subsets of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), classical Hodgkin lymphoma, and plasma cell neoplasms. Its expression often inversely correlates with BCL6. aiding in lymphoma subclassification.
Notably, MUM1 is also expressed in non-lymphoid tissues, such as melanocytes, and aberrant expression may occur in melanoma. However, its utility in distinguishing lymphoid vs. non-lymphoid tumors requires careful interpretation. While MUM1's prognostic significance varies across malignancies, it remains a valuable tool for diagnosing and stratifying hematologic cancers, reflecting its complex role in oncogenesis and immune regulation.
×