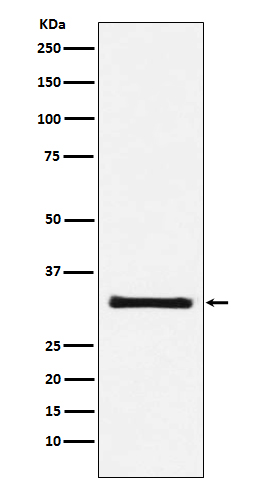
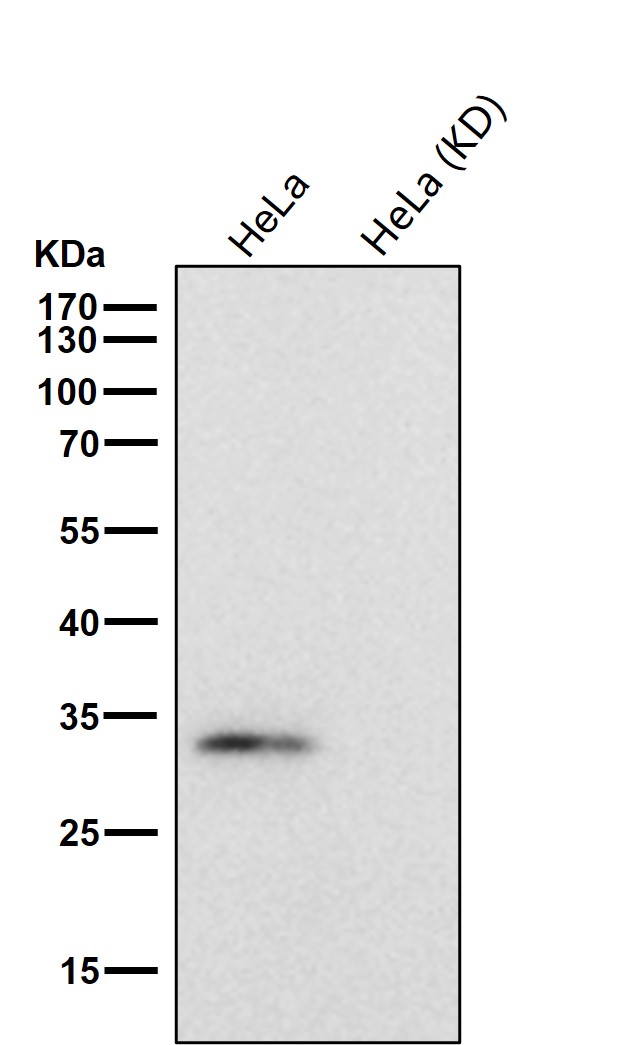
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ASF/SF2 associated protein p32; C1q globular domain binding protein; C1qBP; GC1Q R; GC1QBP; GC1QR; p32 splicing factor; SF2p32;;Complement C1q binding protein |
| WB Predicted band size | 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Complement C1q binding protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于gC1qR(C1QBP)抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要概括内容:
---
1. **文献名称**:*The receptor for complement component C1q (gC1qR) binds to the viral envelope glycoprotein of HIV-1 and mediates viral infection*
**作者**:Ghebrehiwet B, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现gC1qR与HIV-1包膜糖蛋白gp41结合,通过抗体阻断实验证实gC1qR在HIV-1感染过程中促进病毒进入宿主细胞的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*gC1qR as a potential biomarker for cancer: Overexpression in tumors and association with angiogenesis*
**作者**:van Leeuwen HC, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析,发现gC1qR在多种肿瘤组织中高表达,其抗体阻断可抑制肿瘤血管生成,提示其作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Mitochondrial gC1qR interacts with the Ebola virus VP35 protein and contributes to viral pathogenesis*
**作者**:Ning YJ, et al.
**摘要**:揭示埃博拉病毒VP35蛋白与宿主细胞线粒体gC1qR的相互作用,利用特异性抗体证实该互作可抑制宿主抗病毒反应,促进病毒免疫逃逸。
---
以上文献涉及病毒感染机制、肿瘤治疗及病毒免疫逃逸研究,均通过gC1qR抗体实验验证其功能。如需更多细节建议通过PubMed或SciHub获取全文。
**Background of GC1qR Antibody**
The gC1qR (globular head domain of C1q receptor), also known as p32/HABP1. is a multifunctional protein localized predominantly in mitochondria but also expressed on the cell surface. It interacts with diverse ligands, including the globular regions of complement component C1q, viral proteins, and extracellular matrix components, playing roles in immune regulation, infection, and cellular processes like apoptosis and inflammation.
GC1qR antibodies are tools used to detect and study this protein’s expression, localization, and function. Research highlights its involvement in pathological conditions: it serves as a receptor for pathogens (e.g., HIV, hepatitis viruses), contributes to autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus) by enhancing complement activation, and is overexpressed in cancers, promoting tumor progression and metastasis. Antibodies against GC1qR help elucidate its role in viral entry, immune evasion, and cancer biology, making them valuable in diagnostic and therapeutic research.
Recent studies also explore GC1qR as a potential therapeutic target. Inhibiting its interactions with pathogens or modulating complement activity could mitigate disease progression. However, its dual intracellular/extracellular roles and tissue-specific expression necessitate careful interpretation in experimental models. GC1qR antibodies thus remain critical for unraveling its complex biology and translational applications.
×