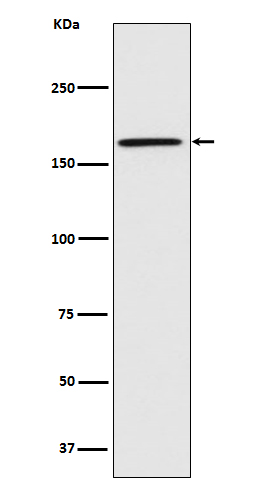
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Caspr; Caspr1; CNTNAP; Cntnap1; Contactin associated protein 1; MHDNIV; NCP1; Neurexin-4; Nrxn4; p190; Paranodin;;Caspr |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 156 kDa ; Observed MW: 165 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Caspr |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Caspr抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*Neurexin IV/Caspr/Paranodin at the Axon Hillock of Myelinated Fibers*
**作者**:Peles E. 等
**摘要**:该研究揭示了Caspr(Neurexin IV)与Contactin形成的复合物在神经元轴突膜结构中的关键作用,特别是在有髓神经纤维的旁结区(paranodal region)。研究证明Caspr对维持轴突细胞膜与髓鞘之间的连接至关重要。
2. **文献名称**:*Axon-Glia Interactions and the Domain Organization of Myelinated Axons Requires Caspr and Caspr2*
**作者**:Bhat M.A. 等
**摘要**:通过基因敲除小鼠模型,研究发现Caspr缺失会导致旁结区结构异常,造成神经传导功能紊乱,强调了Caspr在髓鞘形成和轴突-胶质细胞相互作用中的必要性。
3. **文献名称**:*Caspr Regulates the Processing of Contactin and Controls Its Cell Surface Expression*
**作者**:Gollan L. 等
**摘要**:该文献探讨Caspr在神经元细胞表面蛋白Contactin的转运和加工中的作用,证明Caspr抗体可用于检测两者结合对轴突分域化(如节点与旁结区)的影响,为研究脱髓鞘疾病提供了分子机制依据。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对期刊名称、年份及具体作者信息。
Caspr (Contactin-associated protein), also known as CNTNAP1. is a transmembrane protein critical for the organization and function of myelinated axons in the nervous system. It is a key component of the paranodal junctions, specialized structures located at the edges of myelinated segments where glial cells (Schwann cells in the periphery and oligodendrocytes in the CNS) interact with axons. Caspr forms a complex with Contactin-1 and neurofascin-155. stabilizing the adhesion between axons and myelin sheaths. This complex ensures proper ion channel clustering (e.g., Kv1 channels) and maintains the integrity of saltatory conduction.
Antibodies targeting Caspr are primarily used in research to study paranodal architecture, demyelinating disorders, and autoimmune neuropathies. In clinical contexts, anti-Caspr antibodies have been identified in some patients with autoimmune neurological conditions, such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) or multifocal motor neuropathy. These autoantibodies may disrupt paranodal junctions, leading to impaired nerve conduction and neurological symptoms. Caspr antibodies also serve as biomarkers in diagnostic assays, aiding in the characterization of paranodal autoimmunity. Their role in disease pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targeting remains an active area of investigation, particularly in understanding how disrupted axoglial interactions contribute to neuropathy.
×