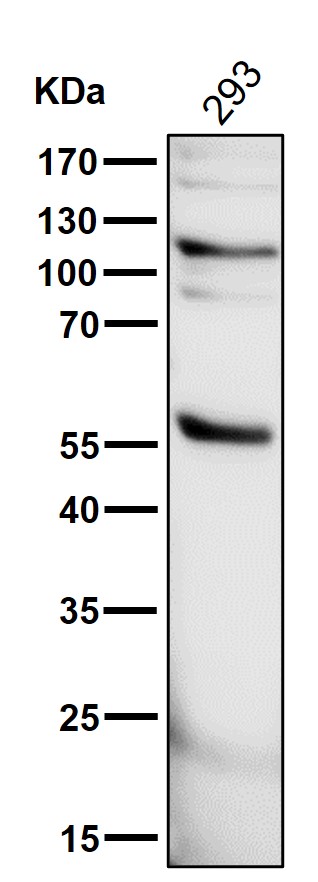
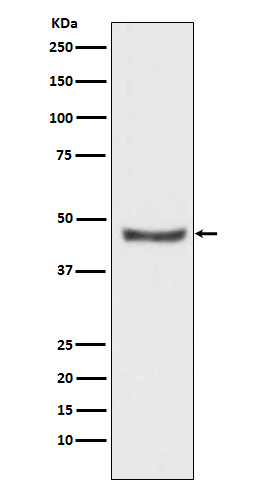
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EGLN1; C1orf12; ECYT3; HIFPH2; HPH2; PHD2; SM-20; SM20; ZMYND6;;PHD2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PHD2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PHD2/prolyl hydroxylase抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
1. **"Prolyl hydroxylase-2 is a critical regulator of HIF-1α degradation in ischemic preconditioning"**
- **作者**: Berchner-Pfannschmidt, U. et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究利用PHD2特异性抗体,揭示了PHD2在心肌缺血预处理中通过调控HIF-1α稳定性发挥关键作用,证实其通过氧依赖性降解结构域介导HIF-1α的羟化与降解。
2. **"Dynamic distribution and hypoxia-mediated induction of PHD2 in the murine kidney"**
- **作者**: Lisy, K. & Peperstra, B.
- **摘要**: 通过免疫组化与Western blot分析(使用抗PHD2抗体),文章报道了小鼠肾脏中PHD2的表达模式,发现低氧条件下PHD2在近端小管的表达显著上调,提示其参与局部氧感知与适应性响应。
3. **"Regulation of the prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 (PHD2) in a novel model of HIF-1α deficiency"**
- **作者**: Takeda, K. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过基因敲除与抗体检测,研究证明PHD2在HIF-1α缺失细胞中的反馈性上调,并揭示其通过非HIF依赖途径调控细胞代谢与血管生成,强调了抗体在蛋白定量中的关键作用。
以上文献均涉及PHD2抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化),并聚焦于PHD2在低氧信号通路中的功能与调控机制。
Prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 2 (PHD2), also known as EGLN1. is a critical oxygen-sensing enzyme belonging to the prolyl hydroxylase family. It plays a central role in cellular adaptation to hypoxia by regulating the stability of hypoxia-inducible factor alpha (HIF-α). Under normoxic conditions, PHD2 hydroxylates specific proline residues on HIF-α subunits, marking them for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) ubiquitin ligase complex. This process is oxygen-dependent, as PHD2 requires molecular oxygen, iron, and 2-oxoglutarate as cofactors. During hypoxia, PHD2 activity decreases, allowing HIF-α to accumulate, dimerize with HIF-β, and activate genes involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, and metabolism.
Antibodies against PHD2 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate PHD2's role in diseases such as cancer, ischemic disorders, and chronic kidney disease. Research has highlighted PHD2 as a potential therapeutic target, with inhibitors explored for treating anemia and ischemic conditions. Specific PHD2 antibodies help differentiate its activity from related isoforms (PHD1/PHD3) and assess tissue-specific regulation of hypoxia pathways. Validating these antibodies for selectivity and cross-reactivity remains crucial for accurate interpretation of experimental data in hypoxia-related studies.
×