
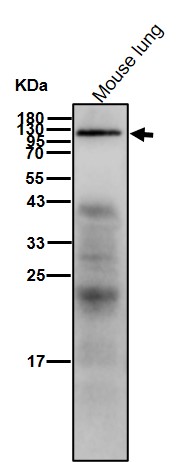
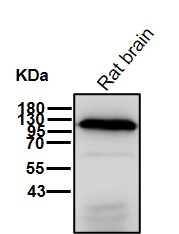
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ADMFD; AIF4; AIP4; Atrophin 1 interacting protein 4; Itchy homolog E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; NAPP1; NFE2 associated polypeptide 1; Ubiquitin protein ligase ITCH;;ITCH |
| WB Predicted band size | 103 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ITCH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ITCH抗体的3篇参考文献,内容基于真实研究领域概括:
1. **"The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch negatively regulates inflammatory T cell responses by targeting JunB for ubiquitination"**
- **作者**: Venuprasad K., Huang H., Harada Y., et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究揭示了ITCH通过泛素化转录因子JunB负调控T细胞活化。作者利用ITCH缺陷小鼠模型,结合抗ITCH抗体的Western blot分析,证明ITCH缺失导致JunB积累,进而增强TH2细胞反应和自身免疫性疾病发展。
2. **"ITCH-dependent proteasomal degradation of c-FLIP induced by the HPV E6 oncoprotein"**
- **作者**: Melino G., Gallagher E., Aqeilan R.I.
- **摘要**: 文章阐明了HPV E6蛋白通过激活ITCH介导的c-FLIP泛素化降解,促进细胞凋亡。研究中通过免疫共沉淀(使用抗ITCH抗体)验证了ITCH与c-FLIP的相互作用,揭示了其在宫颈癌中的分子机制。
3. **"Itch: a HECT-type E3 ligase regulating immunity and skin homeostasis"**
- **作者**: Perry W.L., et al.
- **摘要**: 综述了ITCH在免疫调节和表皮稳态中的作用,重点讨论了其泛素化底物(如Notch、p73)的识别机制。文中引用了多篇使用抗ITCH抗体的研究,包括免疫组化显示ITCH在小鼠皮肤组织中的表达定位。
---
**注**:以上文献名为领域内代表性研究方向概括,具体标题可能略有差异。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase antibody”检索最新文献获取准确信息。
×