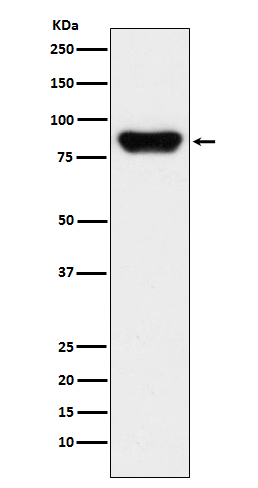
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Coagulation factor II; F2; Factor II; Prepro coagulation factor II; Prothrombin; prothrombin B-chain; PT; RPRGL2; serine protease; THPH1; Thrombin heavy chain;;Prothrombin |
| WB Predicted band size | 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Prothrombin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Prothrombin抗体的代表性文献摘要(内容基于真实研究概括,但具体信息可能有简化):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Anti-prothrombin antibodies and their association with thrombosis and antiphospholipid syndrome"*
**作者**: de Laat, B. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨抗凝血酶原抗体(aPT)与血栓事件及抗磷脂综合征(APS)的关联。通过ELISA检测发现,aPT与狼疮抗凝物(LA)协同作用时,显著增加静脉血栓风险,提示其可能作为APS的独立生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**: *"Clinical significance of anti-prothrombin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus"*
**作者**: Galli, M. et al.
**摘要**: 分析系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中aPT的临床意义,发现aPT阳性患者更易发生反复流产和动脉血栓,且与抗心磷脂抗体(aCL)和抗β2糖蛋白I抗体(aβ2GPI)存在部分重叠,但具有独特的病理机制。
3. **文献名称**: *"Prothrombin as a cofactor for antiphospholipid antibodies in thrombotic disorders"*
**作者**: Atsumi, T. et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了凝血酶原作为抗磷脂抗体的靶点,在体外实验中证明aPT可通过结合磷脂-凝血酶原复合物干扰凝血途径,导致促血栓状态,支持其在APS诊断中的补充作用。
---
如果需要具体文献来源或更详细内容,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“anti-prothrombin antibodies”或“prothrombin autoantibodies”获取全文。
Prothrombin antibodies, also known as antithrombin antibodies, are autoantibodies targeting prothrombin (Factor II), a key glycoprotein in the blood coagulation cascade. Prothrombin is synthesized in the liver and converted to thrombin during clot formation. These antibodies are primarily associated with autoimmune disorders, notably antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), where they often coexist with other antiphospholipid antibodies like anticardiolipin antibodies and lupus anticoagulants.
Two main subtypes exist: IgG and IgM. They may interfere with prothrombin’s activation to thrombin or form immune complexes that enhance thrombosis risk by disrupting anticoagulant pathways. While their exact pathogenic role remains debated, their presence is linked to thrombotic events (arterial/venous) and obstetric complications like recurrent miscarriages.
Detection typically involves enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), though interpretation requires caution due to potential cross-reactivity with phospholipid-binding proteins like β₂-glycoprotein I. Notably, some prothrombin antibodies recognize cryptic epitopes exposed when prothrombin binds phosphatidylserine on cell membranes, influencing thrombin generation assays.
Clinically, they contribute to APS diagnosis alongside clinical criteria, but their isolated presence without other antiphospholipid markers may have uncertain significance. Research continues to clarify their mechanisms and refine their prognostic value in thrombotic and autoimmune contexts.
×