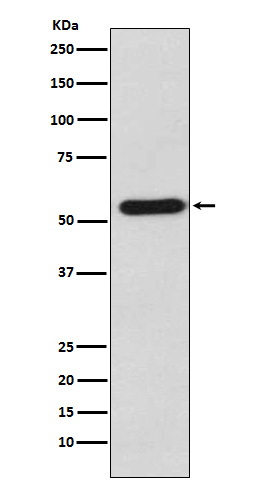
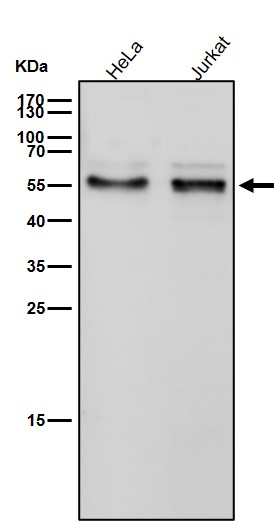
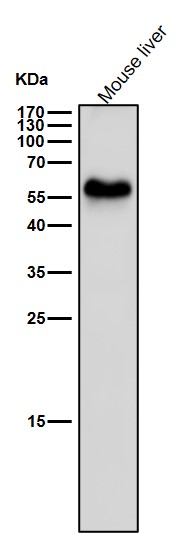
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Double-stranded RNA-binding protein Staufen homolog 1; PPP1R150; STAU; staufen; Staufen RNA binding protein (Drosophila); Staufen, Drosophila, homolog of, 1;;STAU1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 63 kDa ; Observed MW: 55 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human STAU1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Staufen抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"Staufen, a gene required to localize maternal RNAs in the Drosophila egg"**
- 作者:St Johnston, D., Beuchle, D., & Nüsslein-Volhard, C.
- 摘要:该研究首次鉴定了果蝇Staufen蛋白在调控母源性RNA定位中的作用,通过抗体标记揭示了其在胚胎发育早期对RNA分布的调控机制,为后续研究Staufen功能提供了关键工具。
2. **"Staufen1 interacts with multiple components of the RNA interference and microRNA pathways in mammalian cells"**
- 作者:Marion, R.M., Fortes, P., & Beloso, A.
- 摘要:本文利用Staufen1特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和蛋白质组学分析,揭示了哺乳动物Staufen1与RNA干扰通路蛋白的相互作用,表明其在miRNA介导的基因沉默中可能发挥调控作用。
3. **"Staufen2-containing complexes in neuronal RNA granules: roles in dendritic mRNA transport and translation regulation"**
- 作者:Duchaine, T.F., et al.
- 摘要:研究通过Staufen2抗体的免疫荧光和生化实验,证明其在神经元RNA颗粒中的富集,并参与树突mRNA的运输及局部翻译调控,提示其与突触可塑性和学习记忆相关。
4. **"HIV-1 replication complexes are associated with Staufen1-containing ribonucleoprotein particles"**
- 作者:Thomas, M.G., et al.
- 摘要:该文献利用Staufen1抗体发现HIV-1病毒复制复合体与宿主Staufen1蛋白颗粒共定位,揭示了Staufen1在病毒RNA包装和出芽过程中的潜在作用,为抗病毒靶点研究提供了线索。
这些文献均通过Staufen抗体的实验手段(如免疫沉淀、荧光标记等)探讨了Staufen蛋白在RNA代谢、病毒复制及神经功能中的分子机制。
Staufen antibodies are essential tools in studying the Staufen family of RNA-binding proteins, first identified in *Drosophila* for their role in mRNA localization during oogenesis and embryonic patterning. In mammals, two paralogs exist: Staufen1 (STAU1) and Staufen2 (STAU2). These proteins contain double-stranded RNA-binding domains (dsRBDs) and participate in various post-transcriptional regulatory processes, including mRNA transport, stability, translation, and decay. Staufen proteins are particularly crucial in neurons, where they regulate dendritic mRNA trafficking and local protein synthesis, impacting synaptic plasticity and long-term memory formation.
Staufen1 is implicated in Staufen-mediated decay (SMD), a pathway that degrades mRNAs by binding to secondary structures or overlapping with Alu elements in their 3'UTRs. Staufen2. while structurally similar, exhibits distinct functions, such as influencing microtubule dynamics and dendritic spine morphology. Dysregulation of Staufen proteins has been linked to neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease) and viral infections (e.g., HIV-1 replication exploits Staufen1 for viral RNA packaging).
Antibodies against Staufen proteins enable researchers to investigate their expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blot, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Specificity is critical, as cross-reactivity between Staufen1 and Staufen2 can occur due to sequence homology. These antibodies have advanced studies in neurobiology, virology, and disease mechanisms, underscoring Staufen's role in cellular RNA metabolism and its broader biomedical relevance.
×