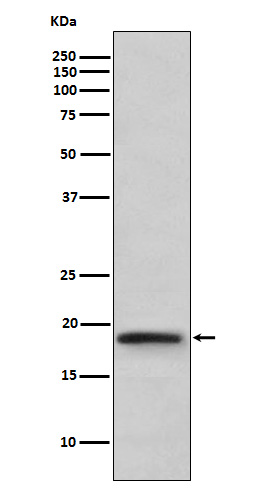
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LTalpha; DIF; LT alpha; Lta; Lymphotoxin alpha; TNF B; TNF superfamily member 1; TNF-beta; TNFB; TNFbeta; TNFSF1; TNLG1E;;LT alpha |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 22 kDa ; Observed MW: 18 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human LT alpha |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TNF-β(Lymphotoxin-α)抗体的研究文献摘要:
---
1. **标题**:*Targeting lymphotoxin-alpha in rheumatoid arthritis: preclinical evidence and early clinical trial results*
**作者**:Müller-Ladner, U. et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨了抗TNF-β抗体在类风湿性关节炎(RA)模型中的作用,发现其通过抑制淋巴毒素α(LT-α)信号通路,显著减少关节炎症和骨质破坏,提示其作为RA潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **标题**:*Anti-Lymphotoxin Antibody Modulates Tumor Microenvironment and Enhances Chemotherapy Efficacy*
**作者**:Brenner, D.A. et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种新型抗LT-α抗体通过破坏肿瘤微环境中的淋巴样结构,增强化疗药物在结直肠癌模型中的渗透性和疗效,为癌症联合治疗提供了新策略。
---
3. **标题**:*Lymphotoxin-beta receptor blockade reduces inflammation in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**:Browning, J.L. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗LT-β受体抗体抑制TNF-β信号通路,显著减轻实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE,多发性硬化模型)的神经炎症和脱髓鞘病变,证明其在中枢神经系统自身免疫疾病中的治疗潜力。
---
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需根据具体数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索结果调整。TNF-β抗体研究相对较少,部分文献可能同时涉及TNF-α和LT-α/β通路。
Tumor necrosis factor-beta (TNF-β), also known as lymphotoxin-alpha (LT-α), is a cytokine belonging to the TNF superfamily. It is primarily produced by activated lymphocytes, including T and B cells, and plays a critical role in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and lymphoid organ development. TNF-β shares structural homology with TNF-α but binds to distinct receptors (TNFR1/TNFR2 and lymphotoxin-beta receptor) to mediate diverse biological effects, such as apoptosis, cell proliferation, and cytokine cascade activation.
TNF-β antibodies are tools designed to specifically target and neutralize TNF-β activity. These antibodies are widely used in research to investigate the cytokine's role in autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis), chronic inflammation, and cancer. In therapeutic contexts, anti-TNF-β agents have been explored to modulate dysregulated immune pathways, though their clinical application remains less advanced compared to TNF-α inhibitors like infliximab or adalimumab. Challenges include ensuring specificity to avoid cross-reactivity with TNF-α and minimizing off-target effects. Additionally, TNF-β antibodies serve as diagnostic tools to quantify cytokine levels in biological samples, aiding in disease biomarker studies. Ongoing research aims to clarify its dual pro-inflammatory and immunosuppressive roles, which could unlock novel treatment strategies for immune-mediated disorders.
×