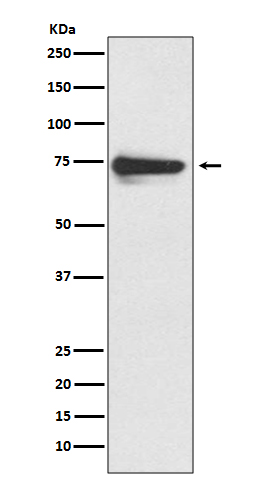
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATN; CMM8; LB24 AB; SHEP3; SK29 AB; Tumor rejection antigen AB; TYR;;Tyrosinase |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 60 kDa ; Observed MW: 70-80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Tyrosinase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于酪氨酸酶(Tyrosinase)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **《Autoantibodies to tyrosinase-related protein-1 detected in the sera of vitiligo patients using a quantitative radiobinding assay》**
- 作者:Kemp EH, Waterman EA, Gawkrodger DJ, et al.
- 摘要:该研究通过放射性结合实验发现,部分白癜风患者血清中存在针对酪氨酸酶相关蛋白-1(TRP-1)的自身抗体,提示此类抗体可能与白癜风中黑色素细胞的自身免疫破坏相关。
2. **《Tyrosinase antibody responses in melanoma patients: correlation with clinical outcome》**
- 作者:Kawakami Y, Suzuki Y, Shofuda T, et al.
- 摘要:文章分析了黑色素瘤患者体内酪氨酸酶抗体的水平与预后的关系,发现抗体阳性患者的生存期较长,表明抗酪氨酸酶抗体可能作为免疫治疗的潜在生物标志物。
3. **《Detection of tyrosinase autoantibodies in patients with vitiligo using recombinant protein》**
- 作者:Song YH, Connor E, Li Y, et al.
- 摘要:该研究利用重组酪氨酸酶蛋白检测白癜风患者血清中的自身抗体,发现抗体阳性率与疾病活动性显著相关,支持酪氨酸酶抗体在白癜风病理机制中的作用。
4. **《Immunoreactivity of anti-tyrosinase monoclonal antibody in melanocytic lesions》**
- 作者:Chen YT, Stockert E, Tsang S, et al.
- 摘要:研究通过免疫组化方法评估抗酪氨酸酶单克隆抗体在黑色素细胞病变中的表达,结果显示该抗体在恶性黑色素瘤中高表达,可作为辅助诊断工具。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过学术数据库核对具体细节。)
Tyrosinase is a key enzyme involved in melanin biosynthesis, catalyzing the oxidation of tyrosine to dopaquinone during pigment production in melanocytes. As a transmembrane glycoprotein located in melanosomes, its expression is primarily restricted to pigment-producing cells, making it a critical marker for studying melanocyte-related processes and disorders. In clinical contexts, tyrosinase has gained attention as a tumor-associated antigen in melanoma, where its overexpression is commonly observed. This has spurred the development of tyrosinase-specific antibodies for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications.
Anti-tyrosinase antibodies are widely utilized in research to detect melanocytic differentiation in tissues (e.g., via immunohistochemistry) and investigate pigmentary disorders like vitiligo, where autoimmune targeting of tyrosinase may contribute to melanocyte destruction. In oncology, these antibodies aid in melanoma diagnosis and monitoring residual disease. Therapeutically, tyrosinase serves as a target for immunotherapy approaches, including antibody-based therapies, cancer vaccines, and adoptive T-cell therapies that leverage its antigenic properties. However, challenges persist due to potential off-target effects on normal pigment cells and variable antigen presentation in tumors. Recent advances in epitope mapping and engineered antibodies aim to enhance specificity while minimizing autoimmune responses, reflecting ongoing efforts to optimize tyrosinase-targeted biomedical interventions.
×