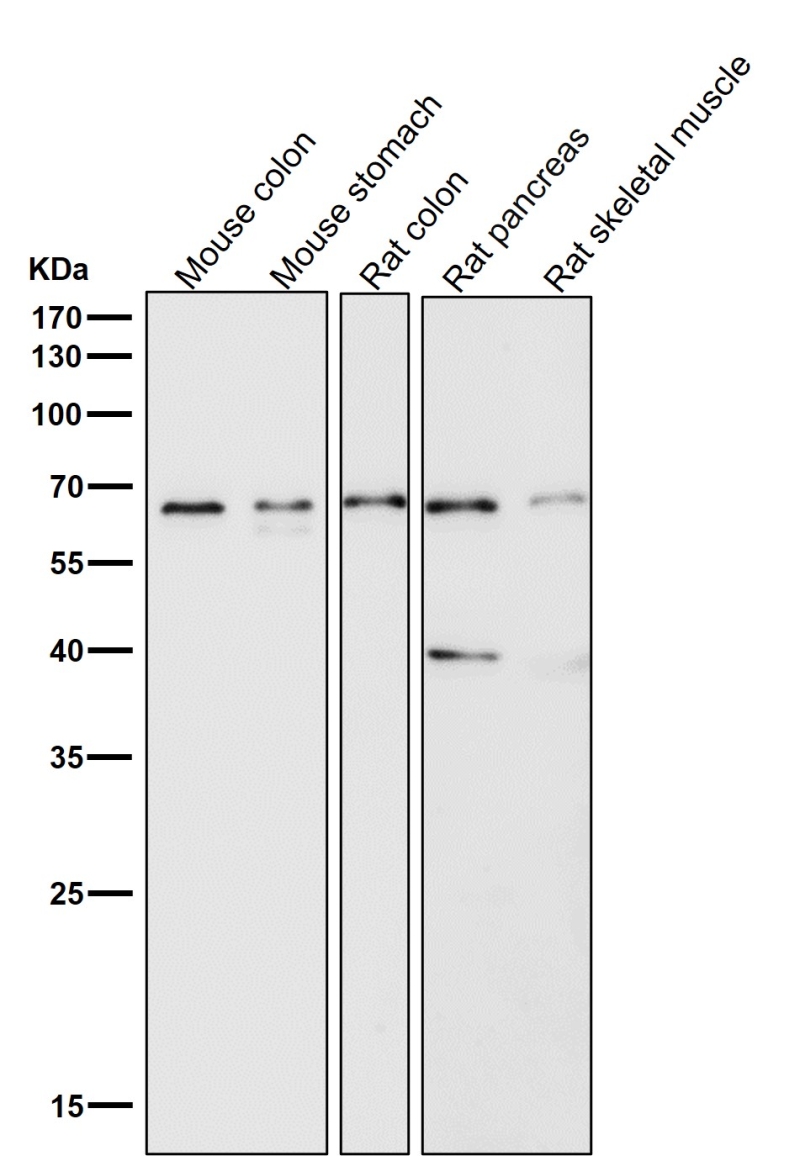
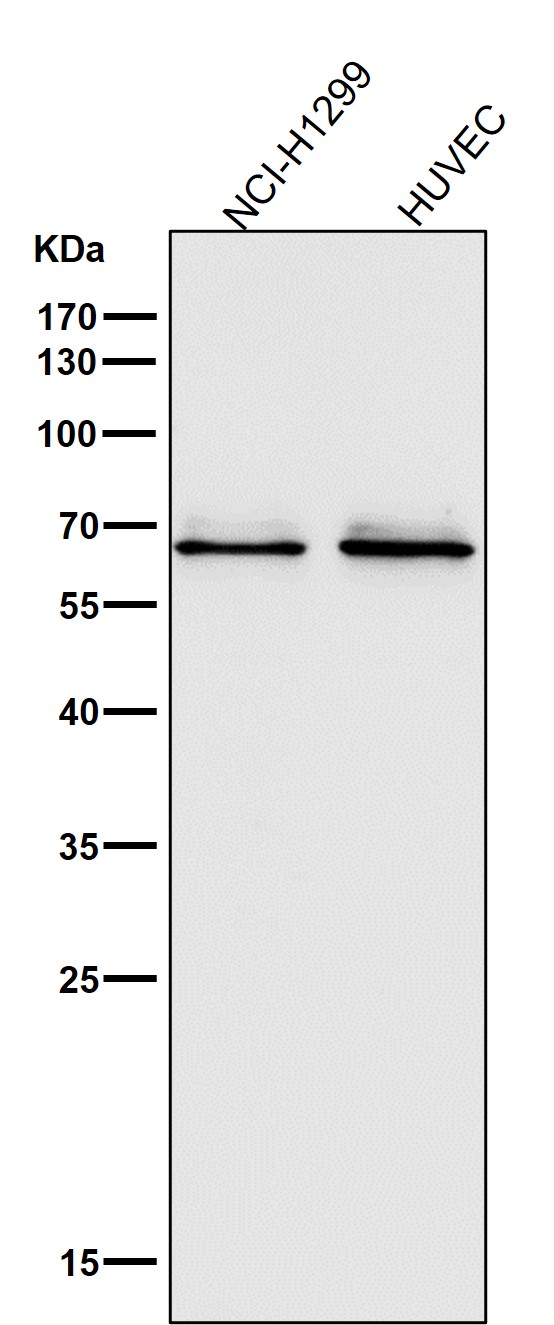
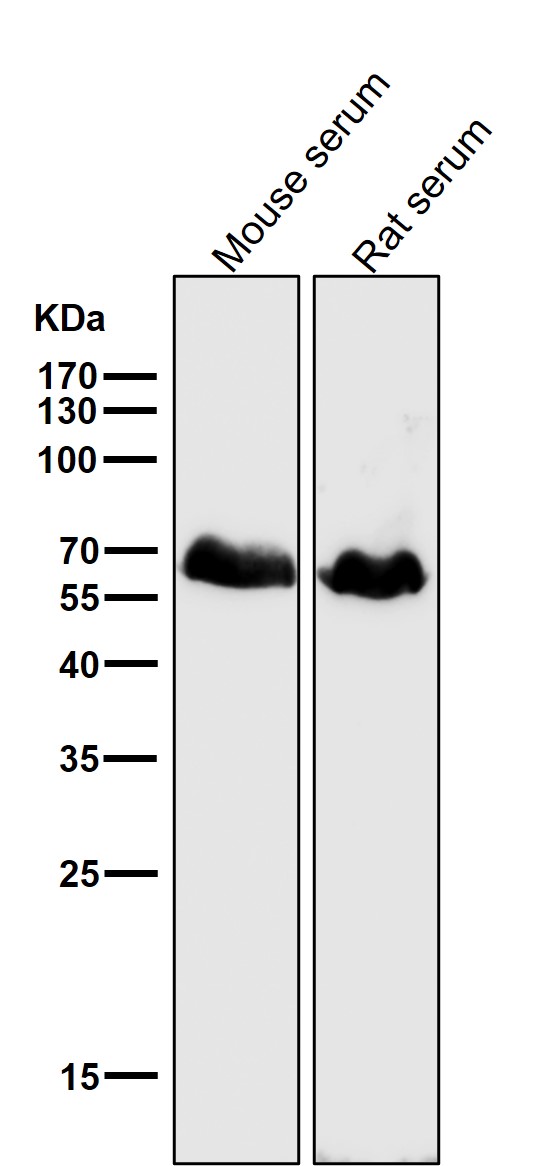
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OCLN; Occludin; BLCPMG;;Occludin |
| WB Predicted band size | 59 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Occludin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Occludin抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息,涵盖其功能研究和应用方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions*
**作者**:Furuse, M., et al. (1993)
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆并鉴定了Occludin蛋白,证实其作为紧密连接(tight junction)的核心跨膜蛋白,参与上皮和内皮细胞屏障的形成。通过抗体标记实验,揭示了Occludin在细胞极性建立和屏障功能调控中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Loss of occludin expression leads to impaired differentiation of intercellular junctions in cultured renal epithelial cells*
**作者**:Saitou, M., et al. (1998)
**摘要**:研究利用Occludin抗体观察其在肾上皮细胞中的表达,发现Occludin缺失会导致细胞间连接结构异常,证明其不仅是紧密连接的标志物,还对连接复合体的组装和功能维持至关重要。
3. **文献名称**:*Vascular endothelial growth factor induces rapid phosphorylation of tight junction proteins occludin and zonula occludens 1*
**作者**:Antonetti, D.A., et al. (1999)
**摘要**:通过Occludin抗体检测,该研究揭示了VEGF(血管内皮生长因子)通过磷酸化修饰Occludin,调控血视网膜屏障通透性,为糖尿病视网膜病变等血管渗漏疾病的机制提供了依据。
---
以上文献涉及Occludin的分子特性、结构功能及病理生理调控,抗体应用方向包括免疫染色、蛋白表达分析和磷酸化研究。如需扩展特定领域(如肠道屏障或神经系统),可进一步补充相关研究。
Occludin is a key transmembrane protein component of tight junctions, specialized cell-cell adhesion structures that regulate paracellular permeability and maintain polarity in epithelial and endothelial cells. Discovered in the early 1990s, occludin interacts with other junctional proteins like claudins and ZO-1 to form dynamic barriers controlling solute transport, cell signaling, and tissue integrity. Occludin antibodies are essential tools for studying tight junction organization and function in physiological and pathological contexts, including cancer, inflammation, and neurological disorders. These antibodies enable the detection of occludin expression, localization, and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry.
Structurally, occludin contains four transmembrane domains, two extracellular loops, and cytoplasmic N- and C-termini. Its C-terminal region interacts with cytoskeletal adaptors, making epitope specificity critical for antibody performance. Researchers often validate occludin antibodies using knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm selectivity. Species cross-reactivity (human, mouse, rat) is a key consideration in experimental design. Both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are available, with monoclonal antibodies offering higher specificity and polyclonal antibodies capturing broader epitopes. Dysregulation of occludin expression correlates with barrier dysfunction in diseases like inflammatory bowel disease and Alzheimer's, underscoring the antibody's utility in mechanistic and therapeutic research.
×