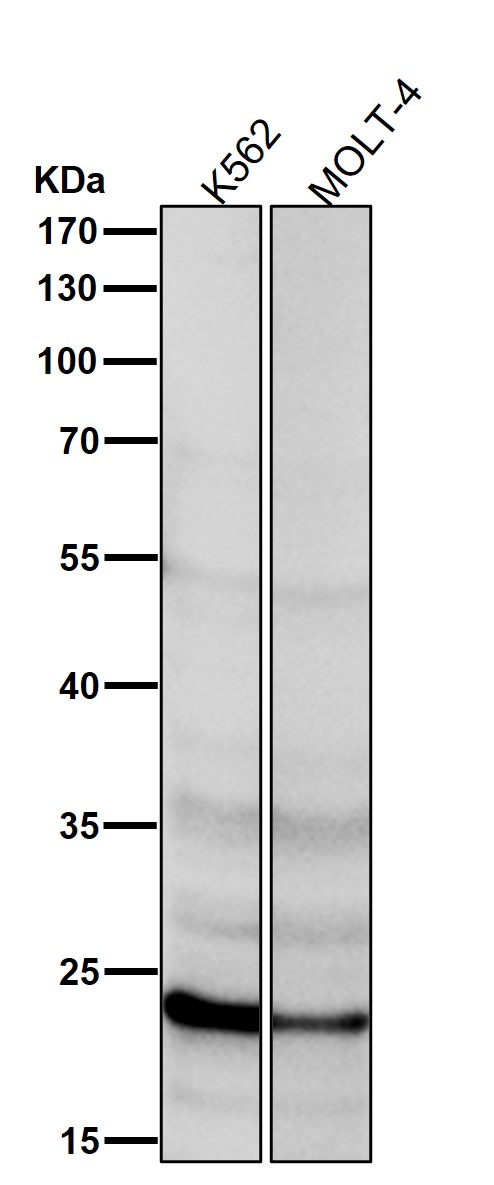

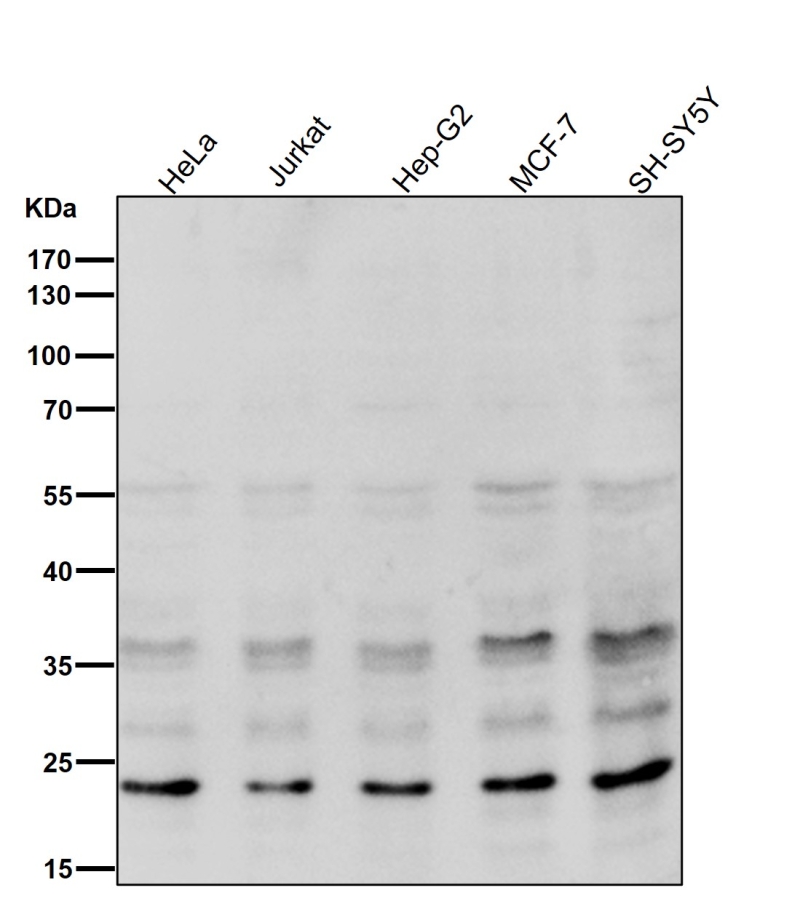
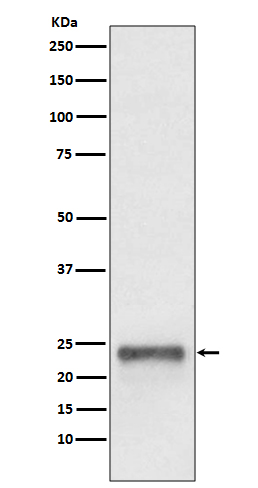
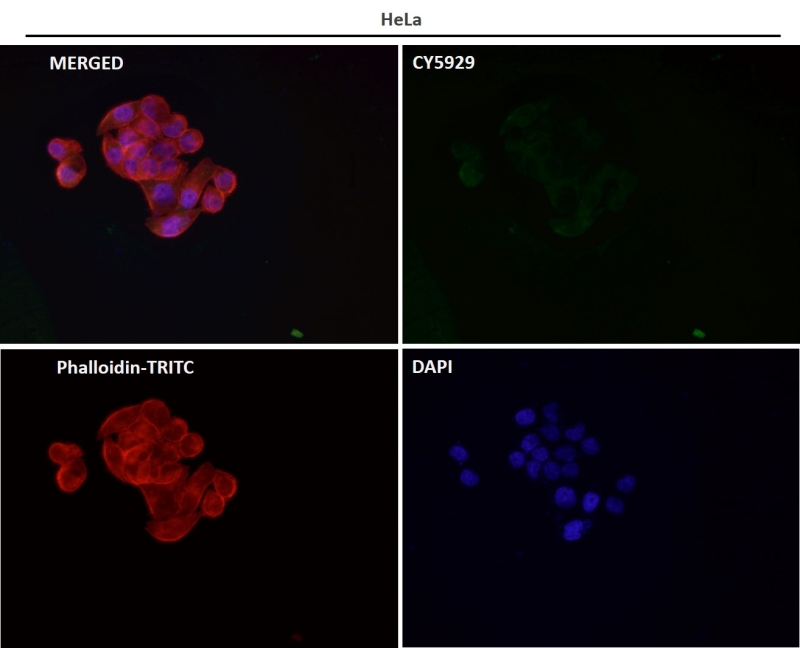
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAT10; UBD-3; GABBR1; UBD; Ubiquitin D;;FAT10 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 18 kDa ; Observed MW: 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FAT10 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与UbiquitinD(Ubiquilin/Dsk2家族)抗体相关的文献概览:
1. **文献名称**: "Ubiquilin promotes the degradation of presenilin 1 to regulate its intracellular localization"
**作者**: Massey et al. (2006)
**摘要**: 研究Ubiquilin抗体在Western blot和免疫荧光中的应用,发现Ubiquilin通过泛素-蛋白酶体系统调控PS1蛋白的降解,揭示其在阿尔茨海默病中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**: "Antibody-based profiling of cerebrospinal fluid suggests loss of Ubiquilin-2 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with TDP-43 pathology"
**作者**: Le et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 利用Ubiquilin-2特异性抗体检测ALS患者脑脊液,发现Ubiquilin-2水平降低与TDP-43蛋白异常聚集相关,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的生物标志物价值。
3. **文献名称**: "Ubiquilin-1 modulates autophagy and ERAD in prion diseases"
**作者**: Hara et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(使用Ubiquilin-1抗体)证明Ubiquilin-1通过协调自噬和内质网相关降解(ERAD)通路,影响朊病毒蛋白的清除,为治疗朊病毒病提供新靶点。
*注:UbiquitinD常指Ubiquilin蛋白家族(UBQLN),若需更特定亚型抗体研究,可补充说明。*
UbiquitinD (UbD), also known as FAT10 or HLA-F adjacent transcript 10. is a ubiquitin-like protein involved in post-translational modification and proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Unlike canonical ubiquitin, UbD contains two ubiquitin-like domains and is encoded by a gene within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I region. It functions through covalent conjugation to substrates in a process requiring the E1 enzyme UBA6 and E2 enzyme USE1. marking proteins for degradation via the 26S proteasome.
UbD plays roles in immune regulation, cell cycle control, and stress responses. Its expression is tightly regulated, with low levels in most tissues but significant upregulation under inflammatory conditions (e.g., by cytokines like TNF-α and IFN-γ). This links UbD to pathological processes such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegeneration. For instance, abnormal UbD accumulation has been observed in hepatocellular carcinoma and Alzheimer's disease models.
UbiquitinD antibodies are essential tools for detecting UbD-protein conjugates, studying degradation pathways, and exploring disease mechanisms. They enable techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to analyze UbD expression patterns, substrate interactions, and cellular localization. Research using these antibodies continues to clarify UbD's dual roles in protein quality control and inflammation-mediated pathologies.
×