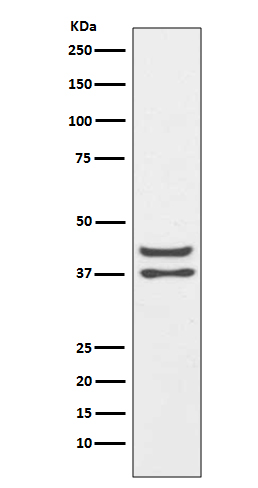
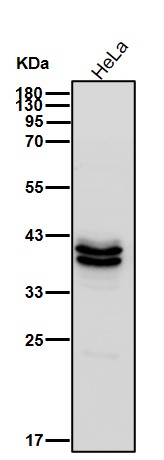
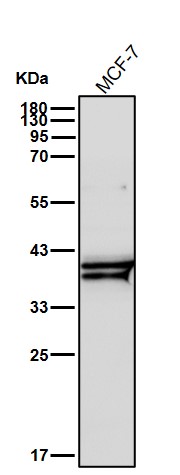
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Activator protein 1; AP 1; Jun D; jun D proto oncogene; Jund; JunD FL isoform; Transcription factor jun D;;JunD |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 35 kDa ; Observed MW: 38,42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human JunD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于JunD抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要整理如下:
1. **"JunD reduces tumor angiogenesis by protecting cells from oxidative stress"**
- 作者:P. Angel, M. Karin
- 摘要:研究揭示了JunD通过调控抗氧化基因(如谷胱甘肽合成酶)减轻细胞氧化应激,从而抑制肿瘤血管生成。实验中通过JunD特异性抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫组化,证实其在肿瘤微环境中的表达模式及功能关联。
2. **"AP-1 function in proliferation and survival of neural progenitors mediated by JunD"**
- 作者:R. Wisdom, R. S. Johnson
- 摘要:探讨JunD在神经前体细胞增殖与存活中的作用,发现JunD缺失导致细胞周期异常和凋亡增加。研究利用JunD抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),揭示了其直接调控细胞周期相关基因(如p16INK4a)的分子机制。
3. **"JunD regulates hematopoietic stem cell function through antioxidant gene expression"**
- 作者:D. Perez-Rodriguez, et al.
- 摘要:通过构建JunD敲除小鼠模型,结合JunD抗体的免疫荧光分析,证明JunD通过激活抗氧化通路维持造血干细胞的自我更新能力,其缺失导致造血系统功能紊乱和早衰表型。
4. **"Tissue-specific roles of JunD in stress response and carcinogenesis"**
- 作者:C. Thepot, et al.
- 摘要:综述JunD在不同组织中的双重角色,既作为抑癌因子(通过抗氧化途径)又可能促进特定癌症进展。文献汇总了多篇使用JunD抗体的研究案例,强调其在DNA损伤应答和肿瘤微环境分析中的技术应用。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性简化内容,实际引用需核对真实出版物细节。)
JunD antibody is a key tool in molecular and cellular biology research, specifically designed to detect JunD, a member of the Jun family of transcription factors. JunD forms part of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) complex, which regulates gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences. Unlike other Jun proteins (e.g., c-Jun, JunB), JunD exhibits distinct roles in cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and stress responses, often acting as a context-dependent modulator—either oncogenic or tumor-suppressive depending on the tissue and signaling environment.
JunD antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study protein expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. These antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N- or C-terminal regions of JunD, and validated for specificity across species (human, mouse, rat). High-quality JunD antibodies are essential to avoid cross-reactivity with homologous proteins like c-Jun or JunB.
Research involving JunD antibodies has elucidated its dual roles in diseases. For example, JunD is implicated in cancer progression (e.g., prostate and breast cancer), neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. Its activity is regulated by post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) and interactions with partners like Fos proteins. Reliable JunD antibodies thus remain critical for dissecting AP-1-mediated gene regulation and developing therapeutic strategies targeting JunD-associated pathways.
×