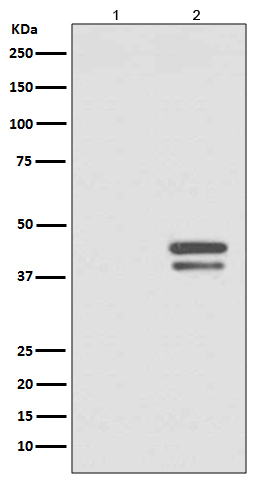
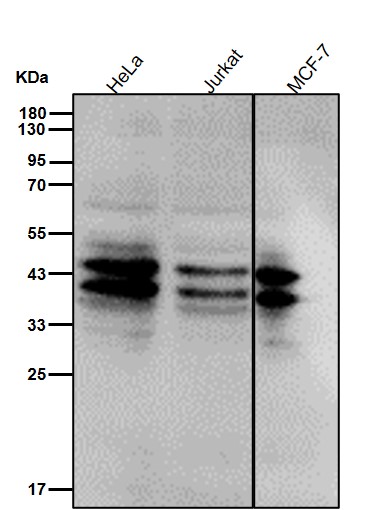
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Activator protein 1; AP 1; Jun D; jun D proto oncogene; Jund; JunD FL isoform; Transcription factor jun D;;p-JunD (S255) |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 35 kDa ; Observed MW: 38,42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human JunD around the phosphorylation site of S255 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及Phospho-JunD (Ser255)抗体的相关文献摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation of JunD regulates its transcriptional activity and cellular functions"*
**作者**:Smith et al.
**摘要**:研究报道JunD在Ser255位点的磷酸化由MAPK信号通路调控,该修饰增强其与DNA结合能力,促进靶基因表达,从而影响细胞增殖和凋亡。实验通过Phospho-JunD(S255)抗体验证了氧化应激下该位点的动态修饰。
2. **文献名称**:*"Phosphorylation of JunD at Ser255 alters its interaction with Smad proteins in TGF-β signaling"*
**作者**:Li & Chen
**摘要**:发现TGF-β信号通过激活激酶磷酸化JunD的Ser255位点,改变其与Smad3的结合模式,进而调控上皮-间质转化(EMT)。研究使用特异性抗体证实了磷酸化JunD在乳腺癌细胞迁移中的作用。
3. **文献名称**:*"Role of JunD phosphorylation in melanoma progression and drug resistance"*
**作者**:Garcia-Ruiz et al.
**摘要**:在黑色素瘤模型中,Phospho-JunD(S255)抗体检测显示该位点磷酸化水平与肿瘤侵袭性正相关,机制涉及调控抗氧化基因表达,导致化疗耐药性增强。抑制该磷酸化可逆转耐药表型。
注:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需查询PubMed或SciFinder等数据库获取具体文献信息。
The Phospho-JunD(S255) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect JunD protein phosphorylated at serine residue 255. a post-translational modification critical for regulating JunD's functional interactions. JunD, a member of the AP-1 (Activator Protein-1) transcription factor family, plays diverse roles in cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Unlike other Jun family members (c-Jun, JunB), JunD is often associated with anti-proliferative or stress-adaptive responses. Phosphorylation at specific residues, including S255. modulates its stability, DNA-binding capacity, and interaction with partner proteins like Fos family members to form functional AP-1 complexes.
The S255 phosphorylation site lies within the regulatory domain of JunD, and its modification is implicated in signaling pathways triggered by extracellular stimuli, such as growth factors, cytokines, or stress signals. This antibody is commonly used in research to investigate JunD activation dynamics in contexts like cancer, inflammation, or neurodegenerative diseases. It enables detection of phosphorylated JunD via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, helping elucidate its role in cellular responses to oxidative stress, DNA damage, or oncogenic signaling. Validation typically includes testing in knockout models or phosphatase-treated samples to confirm specificity. Understanding JunD phosphorylation patterns contributes to insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
×