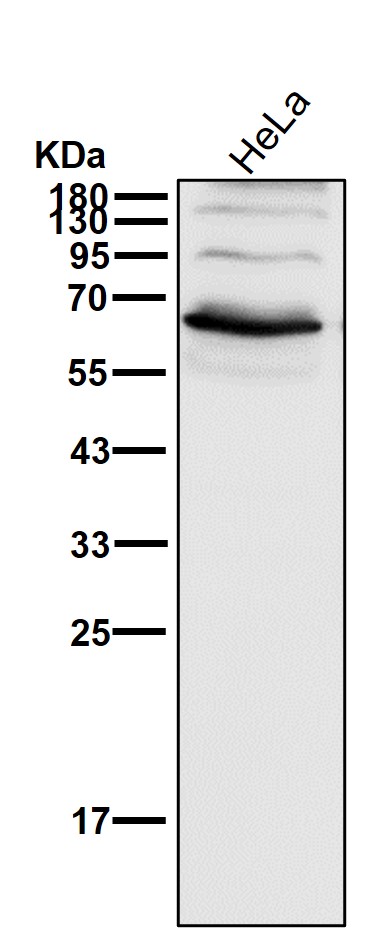
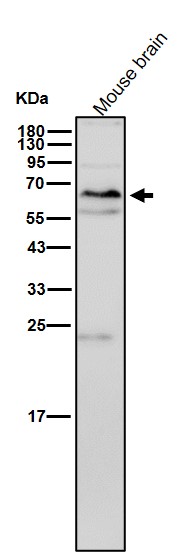
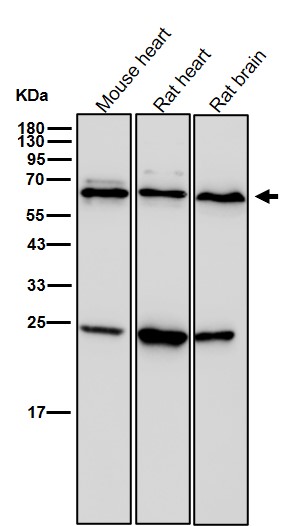
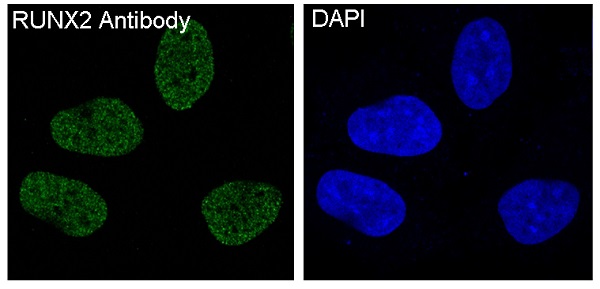
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
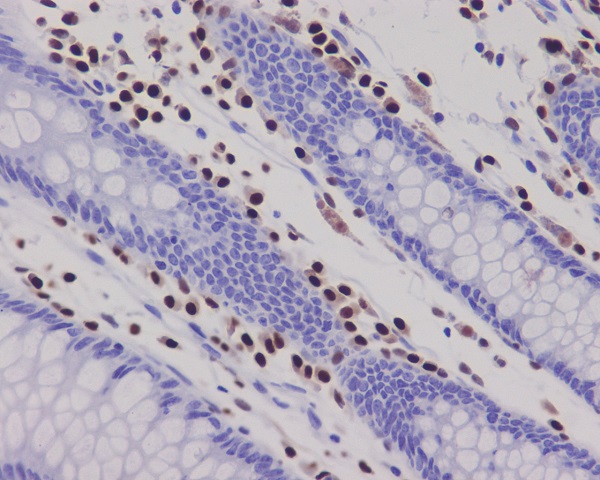
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Runt-related transcription factor 2; Acute myeloid leukemia 3 protein; Core-binding factor subunit alpha-1; CBF-alpha-1; Oncogene AML-3; Osteoblast-specific transcription factor 2; OSF-2; Polyomavirus enhancer-binding protein 2 alpha A subunit; CBFA1; CCD1; PEBP2aA;;RUNX2 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 57 kDa ; Observed MW: 56 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human RUNX2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与RUNX2抗体相关的代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Runx2 control of organization, assembly and activity of the regulatory machinery for skeletal gene expression*
**作者**:Franceschi RT et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了RUNX2通过招募染色质修饰复合物(如组蛋白乙酰转移酶)调控成骨细胞特异性基因表达的分子机制,文中使用RUNX2抗体进行染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)实验,证实其直接结合骨钙素(osteocalcin)等基因启动子区。
---
2. **文献名称**:*TGF-β-induced interaction of SMAD3 with RUNX2 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells*
**作者**:Zhang Y et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot(使用RUNX2抗体)证明,TGF-β信号通路通过SMAD3与RUNX2的相互作用促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化,揭示了两种转录因子的协同调控机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*RUNX2 promotes breast cancer bone metastasis by enhancing integrin α5-mediated colonization*
**作者**:Browne G et al.
**摘要**:文章利用RUNX2抗体进行免疫组化(IHC)和免疫荧光分析,发现乳腺癌细胞中RUNX2的高表达通过上调整合素α5促进骨转移,为RUNX2在肿瘤微环境中的促转移功能提供了证据。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Epigenetic regulation of Runx2 in skeletal development and diseases*
**作者**:Wu M et al.
**摘要**:综述总结了RUNX2在骨骼发育及相关疾病(如骨肉瘤、骨质疏松)中的表观遗传调控机制,强调通过ChIP-seq(使用RUNX2抗体)等技术揭示其与DNA甲基化、组蛋白修饰的关联。
---
以上文献均涉及RUNX2抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、ChIP、IHC),并聚焦于其在骨骼发育、肿瘤转移及表观遗传调控中的功能。如需具体DOI或发表年份,可进一步补充数据库检索。
The RUNX2 antibody is a key tool in studying the Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), a master regulator of osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development. RUNX2. also known as CBFα1 or AML3. belongs to the RUNX family of transcription factors characterized by a conserved Runt homology domain for DNA binding and protein interactions. It plays critical roles in bone formation, chondrocyte maturation, and tooth development by regulating genes like *COL1A1*, *OSTERIX*, and *ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE*. Dysregulation of RUNX2 is implicated in skeletal disorders (e.g., cleidocranial dysplasia), osteoporosis, and cancer metastasis, particularly in bone-invasive cancers (e.g., breast, prostate).
RUNX2 antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to detect RUNX2 expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. These antibodies often target specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal transactivation domain or the C-terminal regulatory regions. Researchers rely on them to study RUNX2's role in stem cell differentiation, bone remodeling, and oncogenesis. Validation includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity. Commercial RUNX2 antibodies vary in host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse), clonality (monoclonal/polyclonal), and applications, with some distinguishing between isoforms (e.g., RUNX2-II, a longer osteoblast-specific variant). Proper controls are essential due to potential cross-reactivity with other RUNX family members or post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) affecting detection.
×