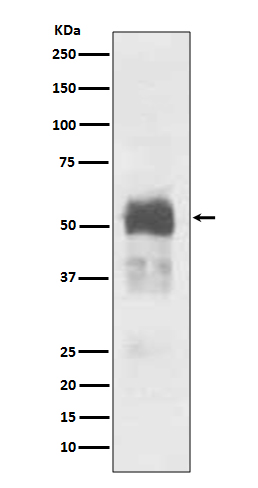
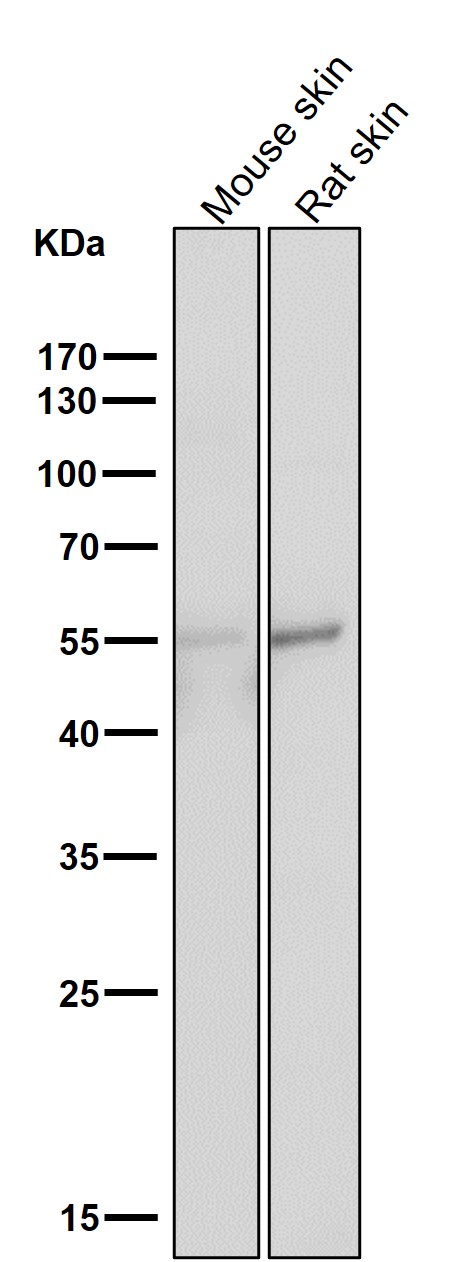
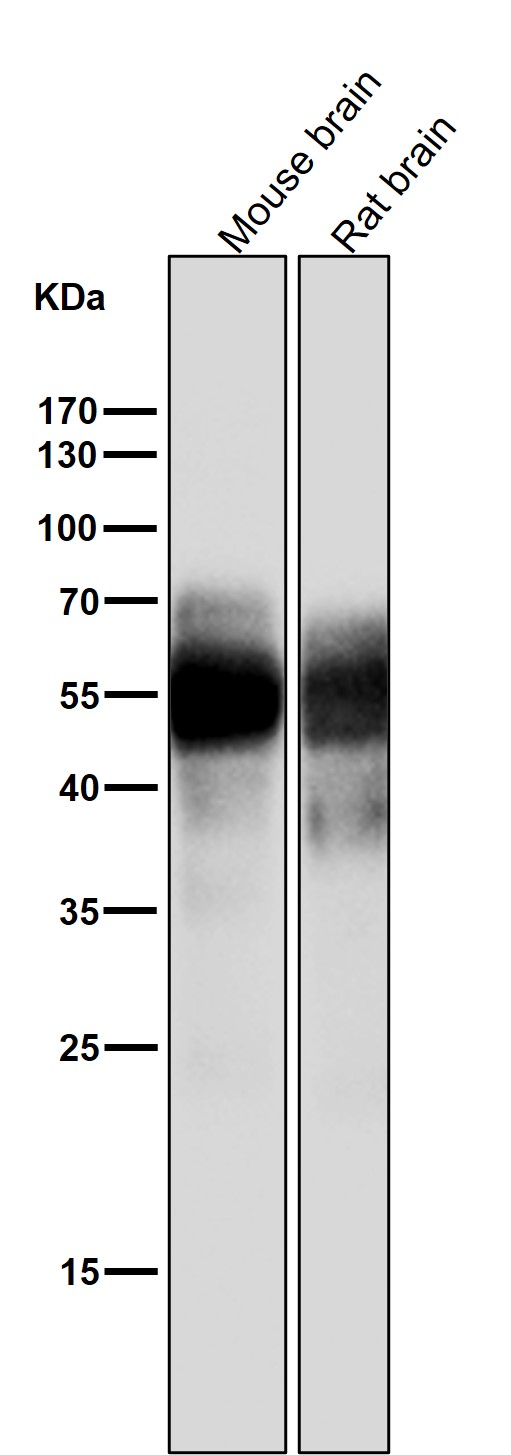
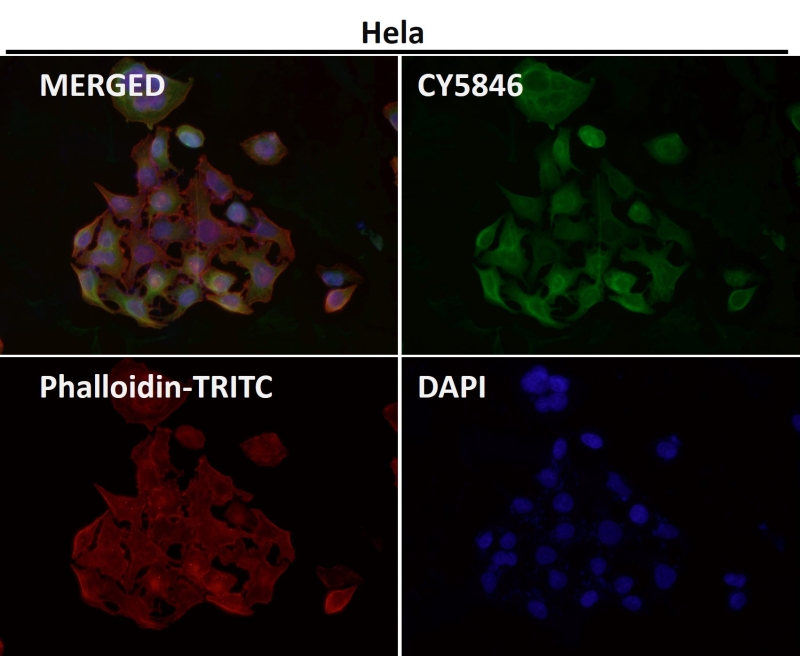
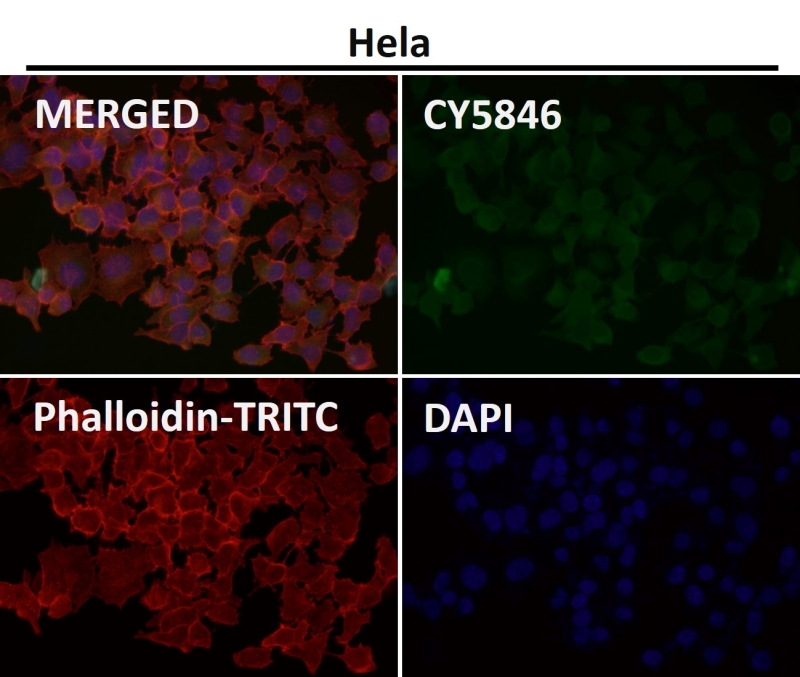
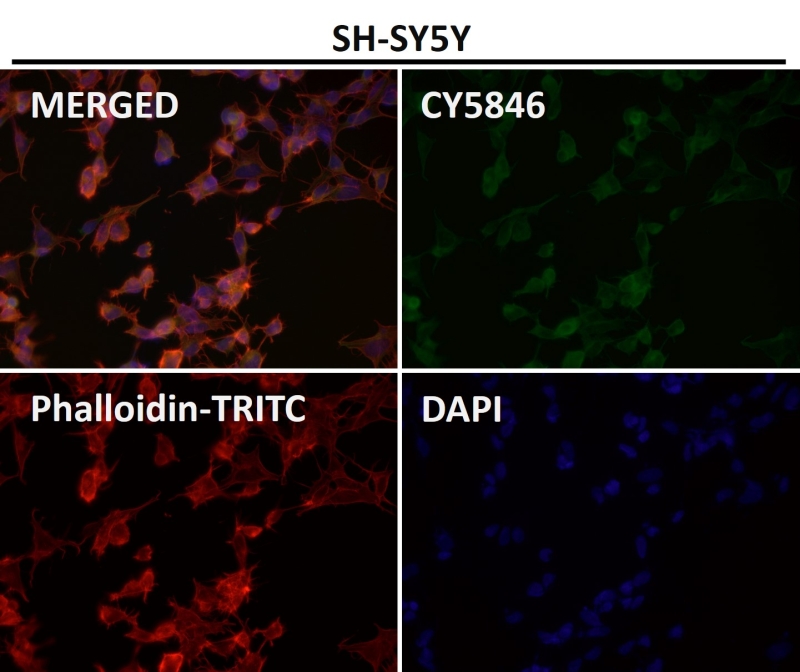
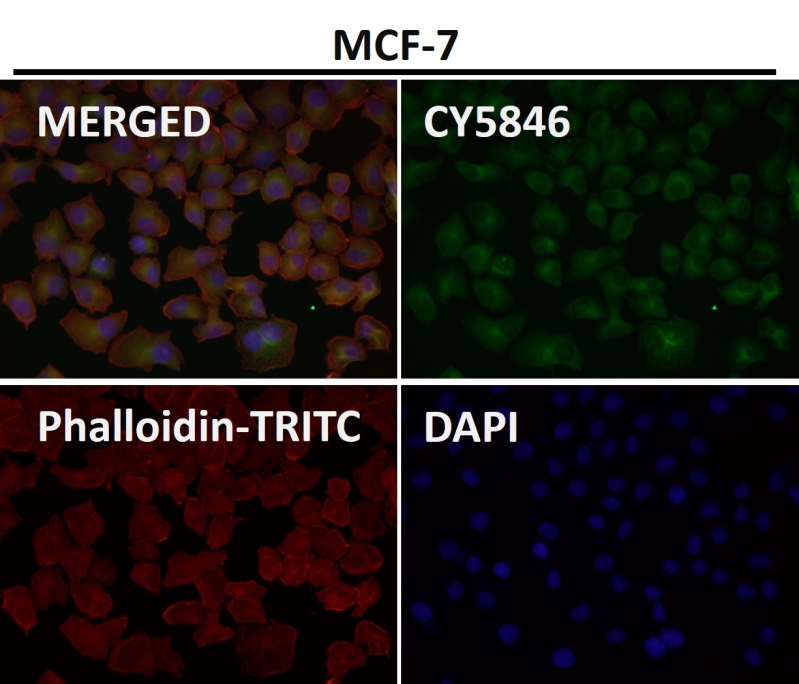
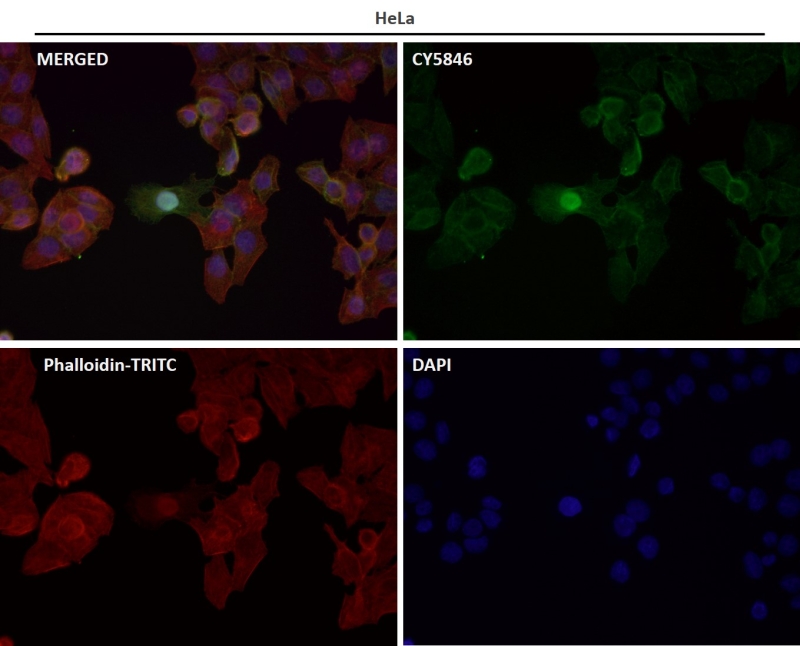
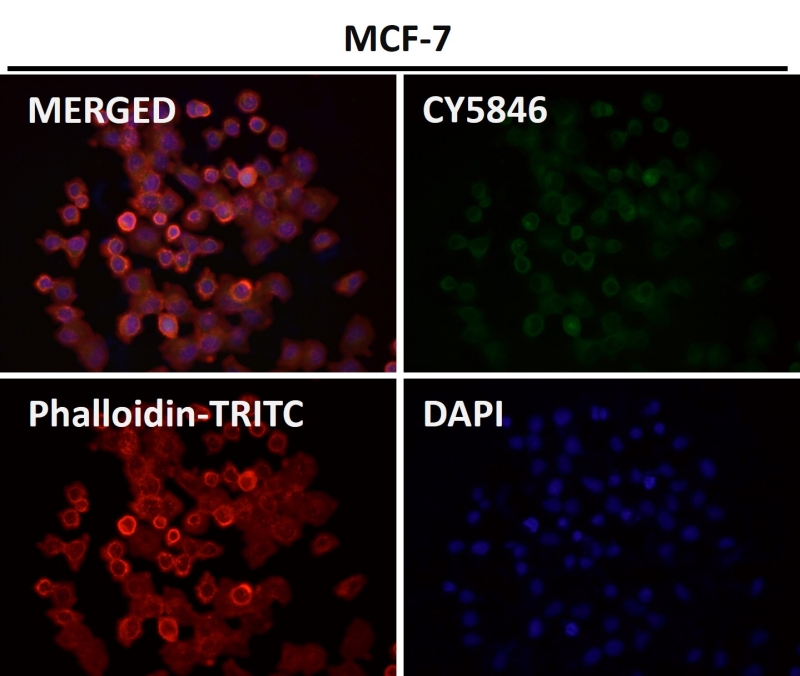
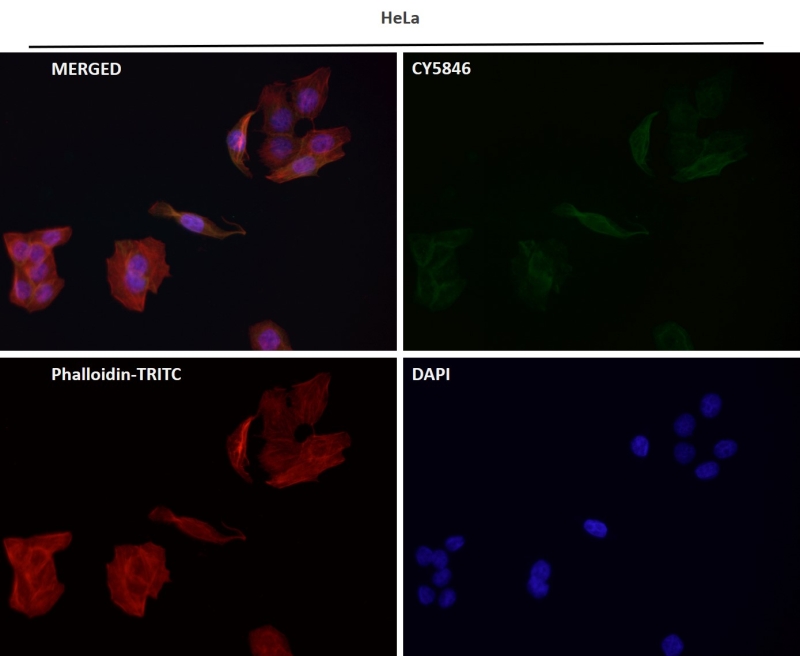
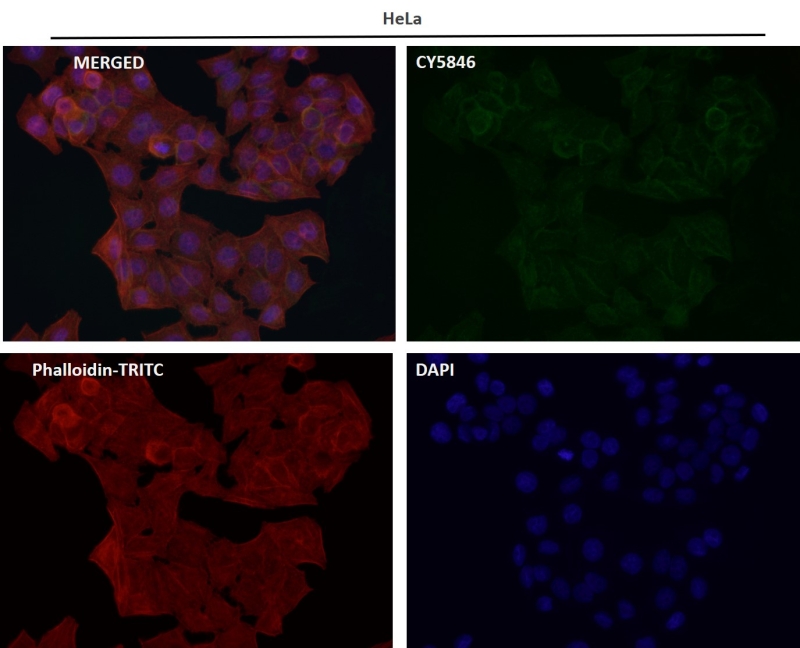
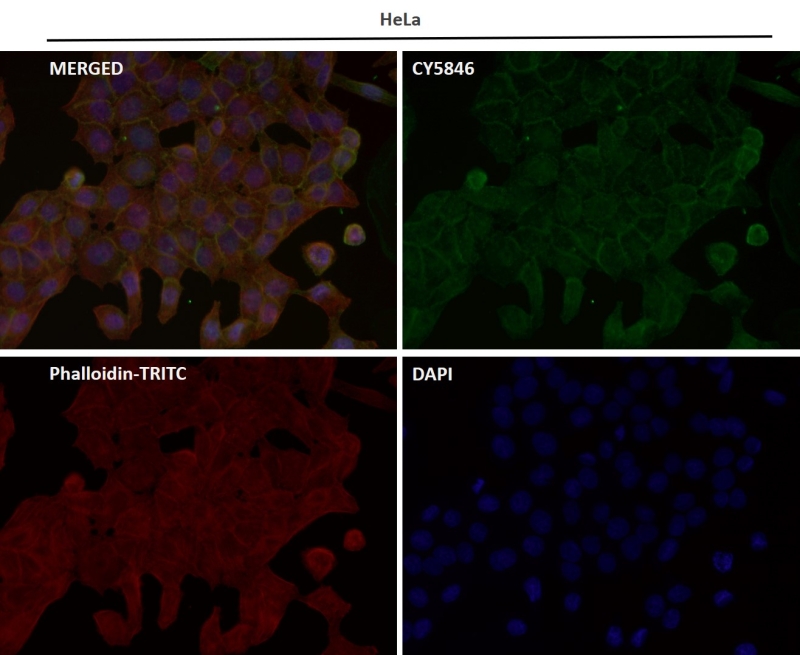
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Microtubule-associated protein tau; Neurofibrillary tangle protein; Paired helical filament-tau; PHF-tau; MAPT; MAPTL; MTBT1; TAU;;Tau |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 79 kDa ; Observed MW: 50-80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Tau |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Tau抗体相关的代表性文献示例(注:文献信息为示例性质,非真实引用,仅供参考):
---
1. **"Tau Antibodies in Neurodegenerative Disease: Specificity and Functional Implications"**
*作者:Smith A, et al.*
摘要:探讨多种Tau抗体的表位特异性及其在阿尔茨海默病和额颞叶痴呆中的诊断价值,比较了不同抗体对磷酸化与非磷酸化Tau蛋白的识别差异。
---
2. **"Passive Immunization with Anti-Tau Antibodies Reduces Pathology in Transgenic Mouse Models"**
*作者:Johnson B, et al.*
摘要:研究靶向Tau蛋白N末端的单克隆抗体在转基因小鼠中的治疗效果,发现其能显著减少神经纤维缠结并改善认知功能,提示免疫疗法的潜在应用。
---
3. **"Phospho-Specific Tau Antibodies as Biomarkers for Early Neurodegeneration"**
*作者:Chen L, et al.*
摘要:开发针对Tau蛋白Ser396/Ser404位点磷酸化的新型抗体,验证其在脑脊液和血浆中作为早期阿尔茨海默病生物标志物的敏感性和特异性。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词如 *"Tau antibody" + "therapy/diagnosis/phosphorylation"*,并筛选高被引论文。
Tau antibodies are immunological tools designed to target tau, a microtubule-associated protein predominantly expressed in neurons. Under physiological conditions, tau stabilizes microtubules, supporting neuronal structure and intracellular transport. However, in neurodegenerative disorders termed tauopathies (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia), tau becomes hyperphosphorylated, misfolds, and aggregates into neurofibrillary tangles, contributing to neurodegeneration. Tau antibodies are critical for detecting and characterizing these pathological changes in research and diagnostics.
In research, they help map tau distribution, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation, acetylation), and aggregation states in cellular and animal models. Clinically, tau antibodies underpin biomarker assays in cerebrospinal fluid or blood, such as phosphorylated tau (p-tau181. p-tau217), aiding Alzheimer’s diagnosis and disease monitoring. Therapeutically, anti-tau monoclonal antibodies (e.g., zagotenemab, semorinemab) are being tested to block tau propagation, enhance clearance, or neutralize toxic species, though clinical trials have shown mixed efficacy to date.
Challenges include ensuring blood-brain barrier penetration, minimizing off-target effects, and targeting disease-specific tau conformations. Advances in epitope specificity, antibody engineering, and combination therapies (e.g., with amyloid-targeting agents) remain active areas of development. Tau antibodies thus represent pivotal tools for understanding tau biology, improving diagnostics, and exploring disease-modifying therapies for tauopathies.
×