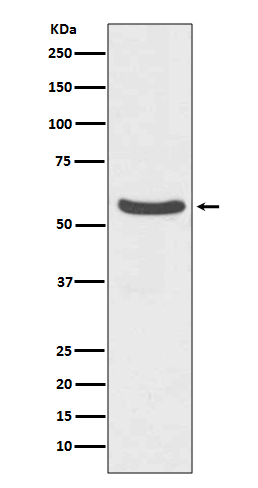
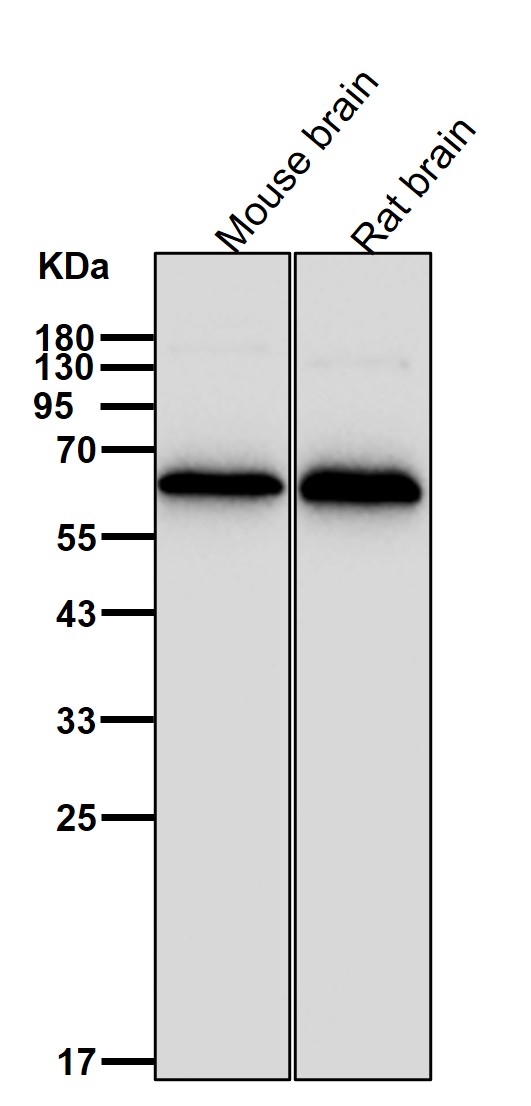
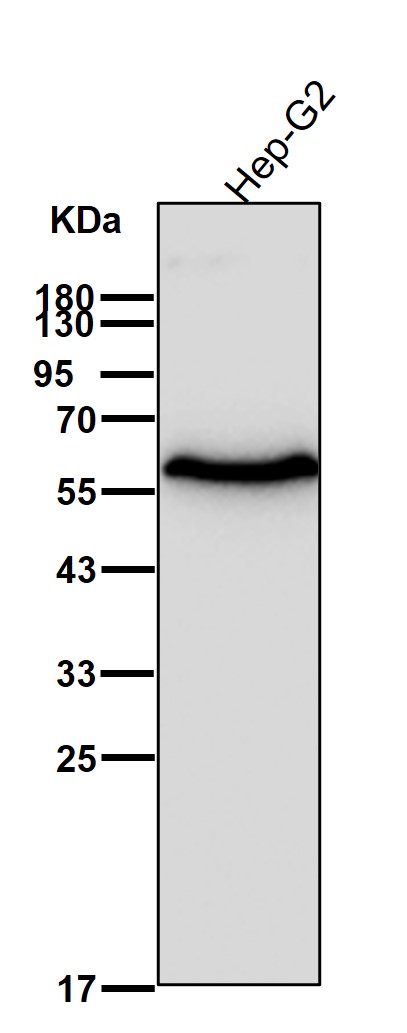
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | liver; Glucose Transporter 2; Glucose Transporter GLUT2; Glucose transporter type 2; Glucose transporter, liver/islet; GLUT2; GTT2; SLC2A2;;GLUT2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GLUT2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GLUT2抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖不同研究方向和实验应用:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"GLUT2 expression and function in β-cells and hepatocytes during development"*
**作者**: Thorens, B. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用特异性GLUT2抗体,通过免疫组化分析小鼠胚胎及成体组织中GLUT2蛋白的分布。发现GLUT2在胰腺β细胞和肝细胞中的表达随发育阶段动态变化,提示其在葡萄糖感知和代谢调节中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Targeted disruption of the glucose transporter 2 selectively in pancreatic β cells leads to altered insulin secretion"*
**作者**: Guillam, M.T. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用高特异性GLUT2抗体)验证了β细胞特异性GLUT2敲除小鼠模型。结果显示,GLUT2缺失导致葡萄糖刺激的胰岛素分泌异常,证实其介导β细胞葡萄糖信号传导的功能。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Serum GLUT2 autoantibodies as a novel biomarker for early detection of pancreatic β-cell dysfunction"*
**作者**: Dezube, R. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种基于GLUT2抗体的ELISA检测方法,用于评估2型糖尿病患者血清中GLUT2自身抗体水平。发现抗体阳性与β细胞功能下降显著相关,为疾病早期诊断提供了潜在生物标志物。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需核实真实来源及细节。如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“GLUT2 antibody”“GLUT2 immunohistochemistry”等获取。
GLUT2 (glucose transporter 2), encoded by the *SLC2A2* gene, is a facilitative transporter critical for glucose homeostasis. It is predominantly expressed in metabolically active tissues, including pancreatic β-cells, liver hepatocytes, intestinal epithelial cells, and renal tubular cells. As a low-affinity, high-capacity transporter, GLUT2 enables bidirectional glucose transport, adapting to fluctuating blood glucose levels. In pancreatic β-cells, it senses hyperglycemia, triggering insulin secretion, while in the liver, it facilitates glucose uptake during feeding and release during fasting. In the intestine and kidneys, GLUT2 mediates dietary glucose absorption and renal glucose reabsorption, respectively.
Antibodies targeting GLUT2 are essential tools in studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to investigate tissue-specific roles in health and disease. Dysregulation of GLUT2 is linked to metabolic disorders; for instance, mutations in *SLC2A2* cause Fanconi-Bickel syndrome, a rare glycogen storage disease, while altered GLUT2 expression is implicated in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Research using GLUT2 antibodies has also explored its role in glucose-sensing mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets for metabolic syndromes. These antibodies aid in elucidating how GLUT2 interacts with hormones (e.g., insulin, glucagon) and dietary factors, providing insights into nutrient signaling pathways and metabolic adaptability.
×