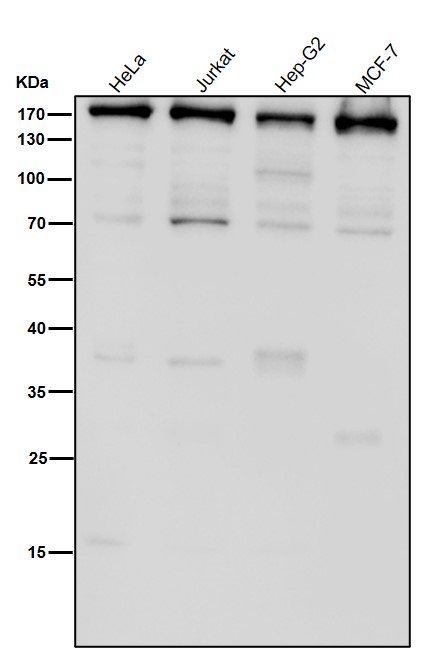

| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FA D2; FA4; FAC D2; FACD 2; FACD; FACD2; FAD; FAD2; FANCD 2; FANCD; FANCD2; Fanconi anemia group D2 protein; FLJ23826; Protein FACD2; Type 4 Fanconi pancytopenia;;FANCD2 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 164 kDa ; Observed MW: 166 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FANCD2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FANCD2抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*"Interaction of the Fanconi anemia proteins and BRCA1 in a common pathway"*
**作者**:Garcia-Higuera, I. et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了FANCD2蛋白通过单泛素化修饰(可通过特异性抗体检测)在DNA损伤修复中的核心作用,其修饰水平与范可尼贫血通路激活直接相关,并促进与BRCA1等修复蛋白的共定位。
2. **文献名称**:*"FANCD2 monoubiquitination links the Fanconi anemia pathway to BRCA1-mediated DNA crosslink repair"*
**作者**:Wang, X. et al.
**摘要**:利用FANCD2抗体验证了其单泛素化修饰在维持基因组稳定性中的必要性,证明FANCD2缺陷导致DNA交联修复失败,并与乳腺癌易感性基因BRCA1功能存在协同关系。
3. **文献名称**:*"Identification of the FANCI protein, a monoubiquitinated component of the Fanconi anemia pathway"*
**作者**:Smogorzewska, A. et al.
**摘要**:通过FANCD2抗体与FANCI抗体的共定位实验,阐明了二者形成复合物的机制,并证实其在DNA损伤后核焦点的形成及修复功能中的依赖性。
4. **文献名称**:*"Fanconi anemia and its diagnosis"*
**作者**:Kottemann, M.C. & Smogorzewska, A.
**摘要**:综述指出FANCD2抗体在临床诊断中的应用,通过免疫印迹或免疫荧光检测患者细胞中FANCD2单泛素化缺失,可作为范可尼贫血亚型分型的生物标志物。
---
这些文献涵盖了FANCD2抗体在机制研究、蛋白互作及临床诊断中的关键应用。如需具体实验方法或更近期研究,可进一步补充说明。
The FANCD2 antibody is a crucial tool in studying the Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway, a key DNA repair mechanism involved in maintaining genomic stability. FANCD2. a 155-165 kDa nuclear protein, plays a central role in the FA/BRCA pathway by coordinating responses to DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) and replication stress. Upon DNA damage, FANCD2 undergoes monoubiquitination (forming FANCD2-L isoform), enabling its recruitment to chromatin where it interacts with repair proteins like BRCA1/2 and RAD51.
Antibodies targeting FANCD2 are widely used to detect both unmodified (FANCD2-S) and monoubiquitinated (FANCD2-L) forms via Western blot, immunofluorescence, or flow cytometry. They help assess FA pathway activation status in clinical diagnostics and research. Deficient FANCD2 monoubiquitination is a hallmark of FA complementation group D2 and other FA subtypes, making these antibodies essential for FA subtype classification.
In cancer research, FANCD2 antibodies help investigate chemotherapy resistance mechanisms, as FA pathway defects correlate with hypersensitivity to DNA-crosslinking agents. They also serve as biomarkers for studying Fanconi anemia-associated malignancies and broader contexts of genomic instability. Commercial FANCD2 antibodies are typically raised against epitopes in the N-terminal region or ubiquitination sites, with validation in knockout cell lines critical for specificity verification.
×