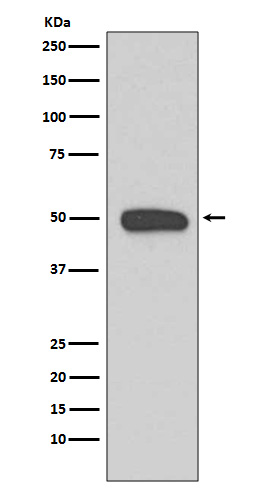
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
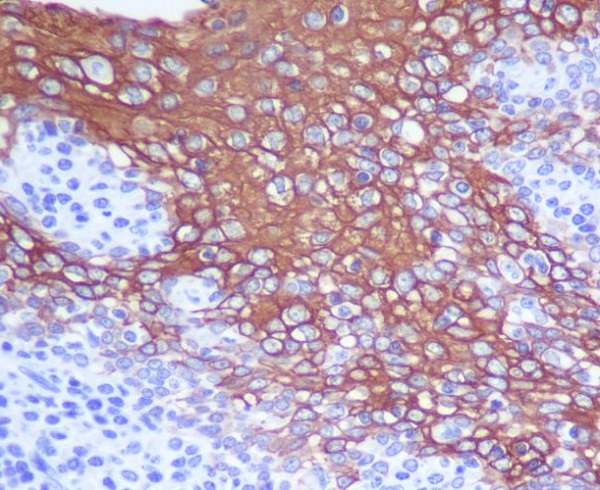
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13; Krt1-13; Cytokeratin 13; CK13; Keratin 13; KRT13; WSN2;;Cytokeratin 13 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Cytokeratin 13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cytokeratin13(CK13)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟概括,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**: *Differential Expression of Cytokeratin13 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Normal Mucosa*
**作者**: Chu PG, Weiss LM
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组化分析发现,CK13在正常口腔黏膜中高表达,但在口腔鳞癌中表达显著降低,提示其可能作为口腔癌诊断或预后评估的潜在标志物。
2. **文献名称**: *Cytokeratin Expression Patterns in Esophageal Epithelial Lesions*
**作者**: Nishimura T, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨CK13在食管上皮病变(包括发育不良和鳞癌)中的表达模式,发现CK13表达缺失与食管鳞癌分化程度及侵袭性相关,支持其在肿瘤病理鉴别中的应用。
3. **文献名称**: *Technical Optimization of Cytokeratin13 Antibody in Immunohistochemistry*
**作者**: Brown KA, et al.
**摘要**: 研究优化了CK13抗体的免疫组化实验条件(如抗原修复和抗体稀释度),显著提高了在福尔马林固定石蜡包埋组织中的检测灵敏度和特异性。
---
**备注**:实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索确认,推荐关键词“Cytokeratin13 antibody”、“CK13 immunohistochemistry”或结合具体研究领域(如“CK13 cancer”)。
Cytokeratin 13 (CK13) is a member of the cytokeratin family, a group of structural proteins that form intermediate filaments in epithelial cells. As a type I acidic cytokeratin (K13), it pairs with type II basic cytokeratin 4 (K4) to establish the cytoskeletal framework in non-keratinized stratified epithelia, such as those lining the oral mucosa, esophagus, cervix, and vaginal tract. CK13 is predominantly expressed in differentiated, post-mitotic epithelial cells, playing a critical role in maintaining tissue integrity and mechanical resilience. Its expression is often inversely correlated with cell proliferation, making it a marker for epithelial maturation.
Antibodies targeting CK13 are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) to study epithelial differentiation, tissue-specific pathologies, and neoplasms. In cancer research, reduced CK13 expression is associated with malignant progression in squamous cell carcinomas (e.g., head and neck cancers), where loss of differentiation markers signifies tumor dedifferentiation and aggressive behavior. CK13 antibodies also aid in diagnosing benign conditions, such as oral lichen planus or leukoplakia, by highlighting abnormal epithelial differentiation patterns.
Commercially available CK13 antibodies (monoclonal or polyclonal) are typically validated for cross-reactivity and specificity across human and rodent tissues. Researchers must optimize protocols (e.g., antigen retrieval methods) for accurate detection, given potential variations in fixation and embedding techniques. As a ~54 kDa protein, CK13 is detectable via Western blot, though its primary utility remains in tissue-based applications.
×