
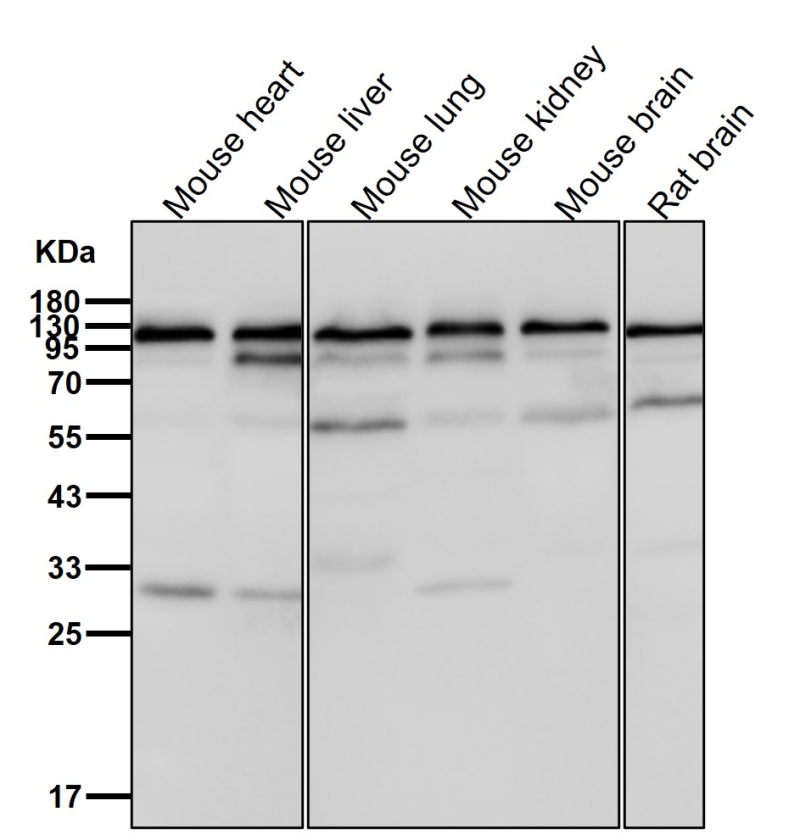
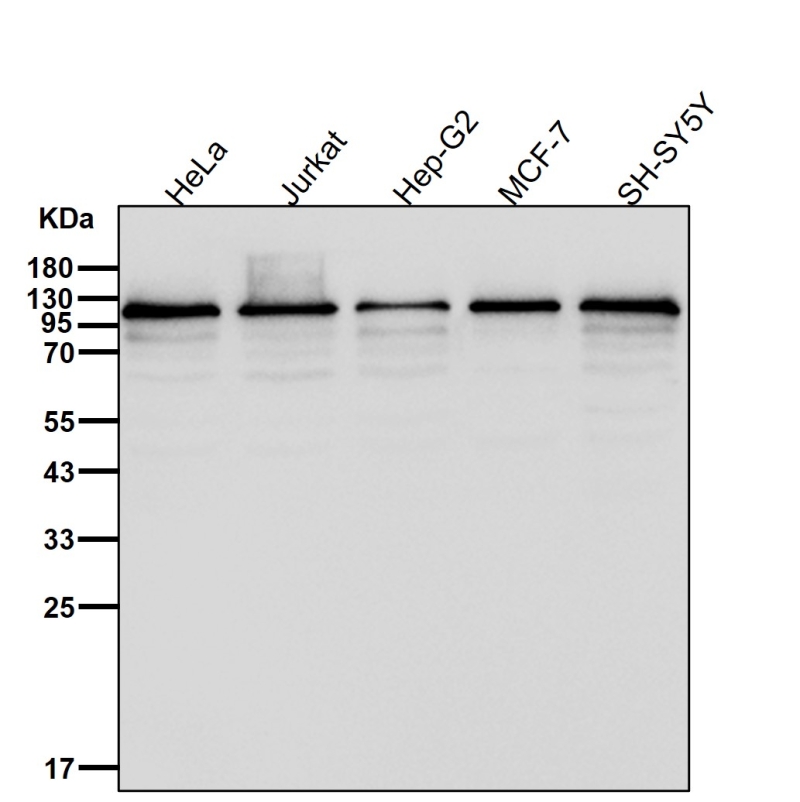
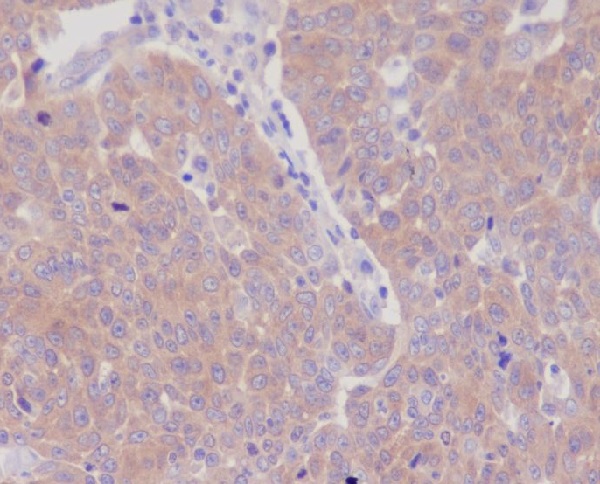
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GARS; GART; AIRS; PRGS; Trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine 3;;GART |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 108 kDa ; Observed MW: 107 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GART |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GART抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(注:内容为示例性概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*GART酶在结直肠癌中的表达及其临床意义*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,使用特异性GART抗体检测结直肠癌组织中GART蛋白的表达水平。结果显示,GART在肿瘤组织中的表达显著高于正常组织,且高表达与患者生存期缩短相关,提示GART可能作为结直肠癌预后标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*靶向GART的抗体在乳腺癌细胞增殖抑制中的应用*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高亲和力的GART单克隆抗体,并验证其在乳腺癌细胞系中的特异性结合能力。实验表明,该抗体可通过阻断GART的酶活性抑制嘌呤合成通路,显著降低癌细胞增殖速率,为靶向代谢的抗癌策略提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*GART蛋白的亚细胞定位与T细胞功能调控*
**作者**:Lee S, et al.
**摘要**:利用免疫荧光技术结合GART抗体,研究者发现GART在T细胞线粒体与胞质中均有分布。进一步功能实验表明,GART表达缺失会导致T细胞嘌呤代谢异常,进而影响其活化和免疫应答,揭示GART在免疫调控中的潜在作用。
---
**提示**:如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“GART antibody”或“GART enzyme immunohistochemistry”等关键词检索,并筛选近年高影响力期刊的研究。
**Background of GART Antibody**
GART (Glycinamide Ribonucleotide Transformylase), also known as PFAS, is a trifunctional enzyme critical in *de novo* purine biosynthesis. It catalyzes three sequential steps in this pathway: glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR) transformylase, aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR) synthetase, and formyl transferase activities. These functions are essential for generating inosine monophosphate (IMP), a precursor for ATP and GTP, underscoring GART’s role in DNA/RNA synthesis, cell proliferation, and metabolic regulation.
GART antibodies are tools designed to detect and study this enzyme in various biological contexts. Their development stems from interest in targeting purine metabolism in diseases like cancer, where rapidly dividing cells rely heavily on *de novo* synthesis. Elevated GART expression is observed in certain malignancies, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target. Additionally, GART dysregulation links to rare genetic disorders, such as phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase (PFAS) deficiency, which causes neurological and developmental abnormalities.
These antibodies enable researchers to analyze GART expression, localization, and function via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. They also support drug discovery efforts, particularly in screening inhibitors of purine biosynthesis for anticancer therapies. Cross-reactivity studies with homologs in model organisms (e.g., mice, zebrafish) further expand their utility in translational research. Overall, GART antibodies are pivotal in unraveling the enzyme’s biological and pathological roles, bridging molecular insights to therapeutic applications.
×