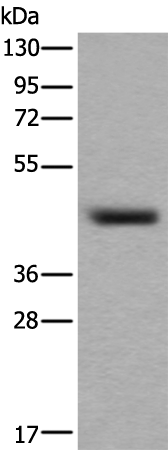
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HSS; CMDR; CX43; EKVP; GJAL; ODDD; AVSD3; HLHS1; PPKCA |
| WB Predicted band size | 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human GJA1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cytokeratin14抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"Catalog of human cytokeratins: Patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells"**
- **作者**: Moll, R., Franke, W.W., Schiller, D.L.
- **摘要**: 该研究系统分类了人类细胞角蛋白(包括CK14),揭示了其在正常上皮、肿瘤及培养细胞中的特异性表达模式,强调CK14作为基底上皮细胞的标志物。
2. **"Differential expression of keratins in human breast cancers"**
- **作者**: Nagle, R.B., et al.
- **摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析,发现CK14在乳腺癌基底样亚型中高表达,提示其可作为区分乳腺癌分子亚型的潜在标志物。
3. **"Involvement of cytokeratin 14 in stem cell maintenance and differentiation in human epidermis"**
- **作者**: Watt, F.M., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用CK14抗体证实其在表皮干细胞中的特异性表达,揭示CK14对维持干细胞特性及调控终末分化细胞的关键作用。
4. **"Cytokeratin 14 expression in epithelial neoplasms: A marker of squamous differentiation"**
- **作者**: Fillies, T., et al.
- **摘要**: 分析CK14在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中的表达,表明其抗体染色可用于病理诊断中确认肿瘤的鳞状分化特征。
这些文献涵盖了CK14抗体在基础研究、癌症诊断及干细胞领域的应用。
Cytokeratin 14 (CK14) is a member of the keratin family, intermediate filament proteins critical for maintaining structural integrity in epithelial cells. As a type I keratin, CK14 pairs with type II keratin K5 to form heterodimers, predominantly expressed in basal epithelial cells of stratified epithelia, such as skin, mammary glands, and prostate. This expression pattern makes CK14 a key marker for identifying basal or progenitor cell populations in tissues.
CK14 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to study epithelial differentiation, tissue development, and disease. In cancer biology, CK14 expression is associated with aggressive basal-like subtypes in breast cancer and squamous cell carcinomas, aiding in tumor classification. It also serves as a tool to investigate epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer stem cells.
In dermatopathology, CK14 antibodies help diagnose blistering disorders (e.g., epidermolysis bullosa simplex) caused by CK14 mutations. Additionally, they are employed in wound healing studies to track keratinocyte migration. Common applications include immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and Western blotting.
Commercial CK14 antibodies are typically monoclonal, raised against specific epitopes (e.g., C-terminal regions), with validated reactivity across human and murine samples. However, interpretation requires context, as CK14 may be downregulated during epithelial differentiation or aberrantly expressed in certain malignancies. Its role in both normal homeostasis and disease underscores its versatility as a biological tool.
×