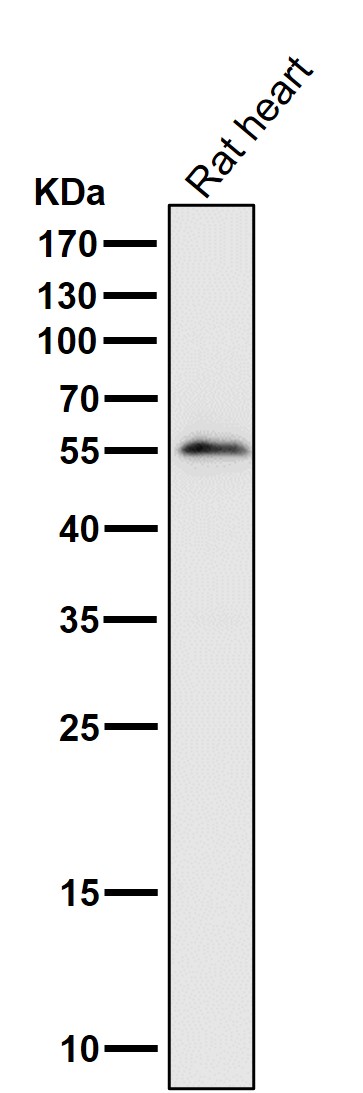
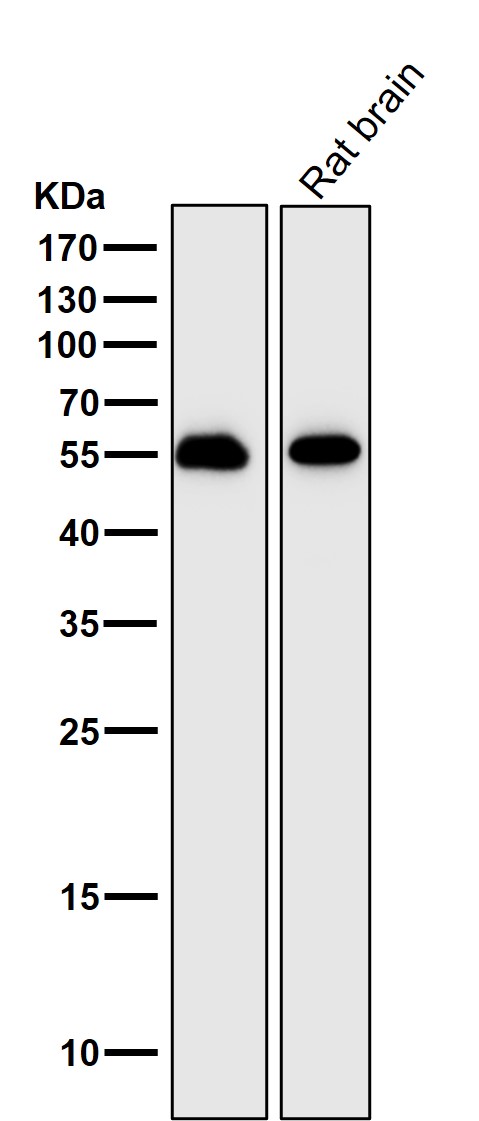
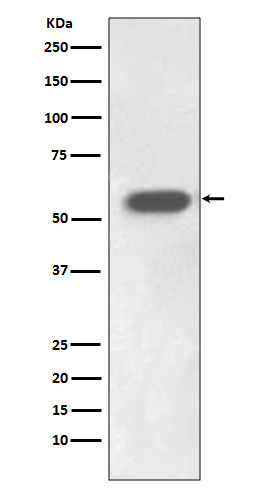
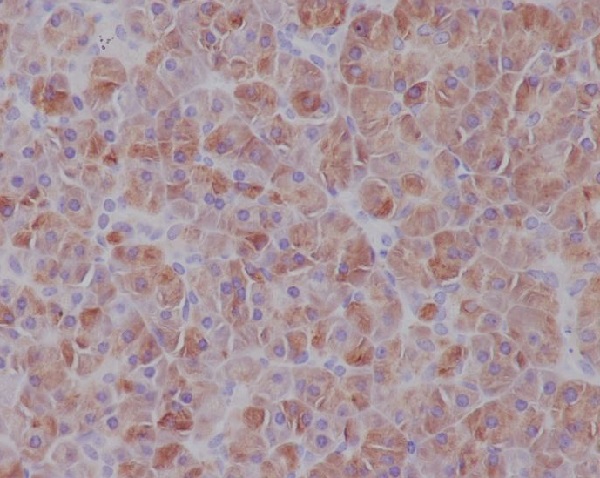
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IRF7; Interferon regulatory factor 7; IRF-7; IRF7A; IRF-7H;;IRF7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human IRF7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于IRF7抗体的代表性文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: "IRF7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses"
**作者**: Honda K, Yanai H, Takaoka A, Taniguchi T
**摘要**: 该研究通过基因敲除小鼠模型,证实IRF7是I型干扰素产生的核心调控因子。研究利用IRF7抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现IRF7在病毒感染后通过TLR和RIG-I通路被激活,并驱动干扰素基因表达。抗体实验表明IRF7的磷酸化是其功能的关键步骤。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Distinct roles of MDA5 and RIG-I in antiviral signaling mediated by IRF7"
**作者**: Sato M, Hata N, Asagiri M, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究探讨IRF7在RNA病毒免疫应答中的作用。通过IRF7特异性抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫组化分析,发现MDA5和RIG-I通路分别通过IRF7的不同结构域激活干扰素β(IFN-β)。抗体实验显示IRF7在细胞核内的积累与病毒清除效率相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Phosphorylation-induced dimerization of IRF7 enhances its DNA-binding specificity"
**作者**: Paun A, Reinert JT, Jiang Z, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用IRF7抗体进行磷酸化位点分析和共免疫沉淀实验,发现IRF7的C端结构域在磷酸化后形成二聚体,从而增强其与干扰素启动子区域的结合能力。实验表明,IRF7抗体可阻断其二聚化,抑制下游抗病毒基因表达。
---
4. **文献名称**: "IRF7 overexpression in human cancer cells promotes chemoresistance via autophagy"
**作者**: Ning S, Pagano JS, Barber GN
**摘要**: 通过IRF7抗体检测肿瘤细胞中的IRF7表达水平,发现IRF7高表达与化疗耐药性相关。研究证明IRF7通过激活自噬相关基因(如LC3和Beclin-1)介导耐药性,抗体阻断实验显示IRF7下调可增强化疗药物敏感性。
---
以上文献均涉及IRF7抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化、ChIP等),并聚焦于IRF7在免疫调控、病毒感染和癌症中的分子机制。
Interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) is a key transcription factor in the innate immune response, primarily regulating type I interferon (IFN-α/β) production during viral infections. As the master regulator of IFN-dependent immune activation, IRF7 is activated via pathogen-sensing pathways (e.g., TLRs, RIG-I) and forms homodimers or heterodimers with other IRFs to initiate antiviral gene expression. IRF7 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, post-translational modifications, and subcellular localization in immune cells and disease models.
These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to investigate IRF7's role in viral infections (e.g., influenza, SARS-CoV-2), autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus), and cancers. Structural studies using IRF7 antibodies have revealed its two critical domains: an N-terminal DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain containing phosphorylation sites essential for activation. Researchers also employ these antibodies to explore IRF7's regulatory mechanisms, including its negative feedback loop involving ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.
As dysregulated IRF7 activity correlates with chronic inflammation and oncogenesis, specific antibodies help identify its therapeutic potential as a drug target or biomarker. Commercial IRF7 antibodies are typically validated for cross-reactivity across human, mouse, and rat samples, supporting translational research in immunology and virology.
×