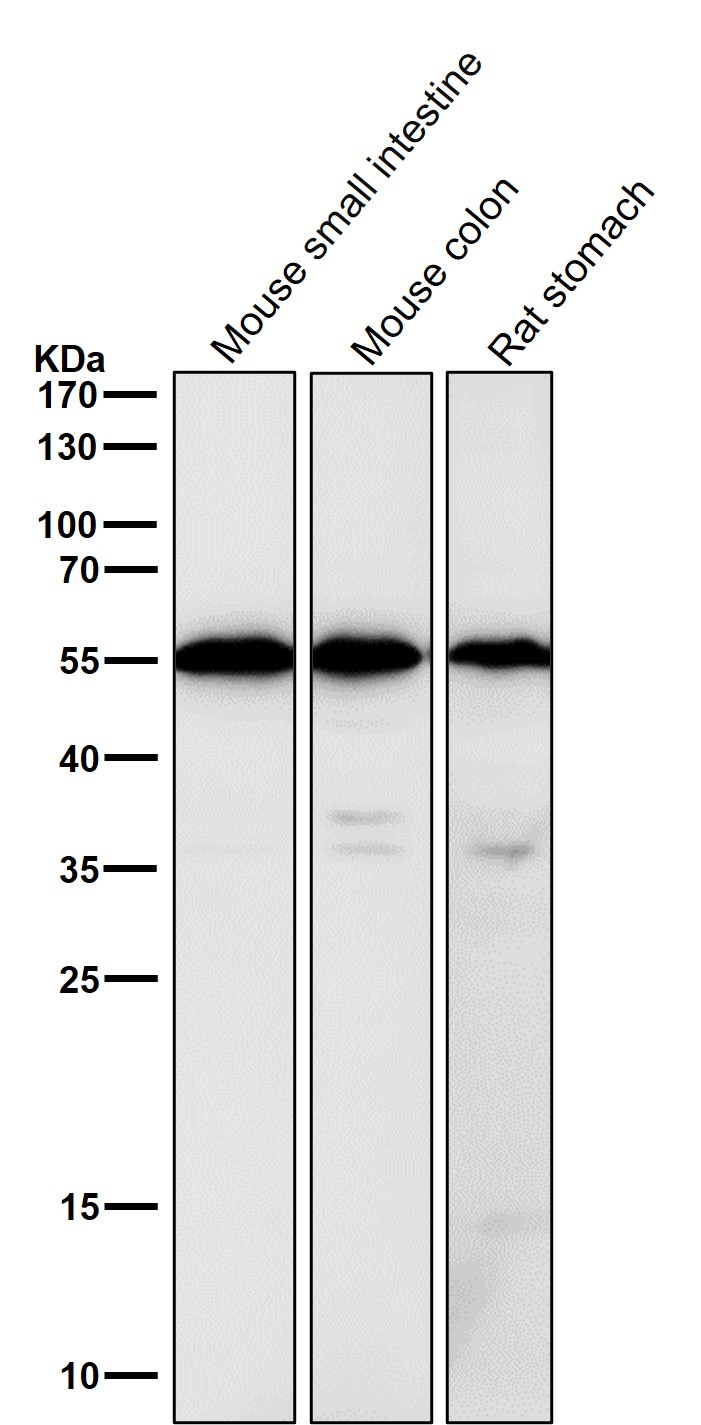
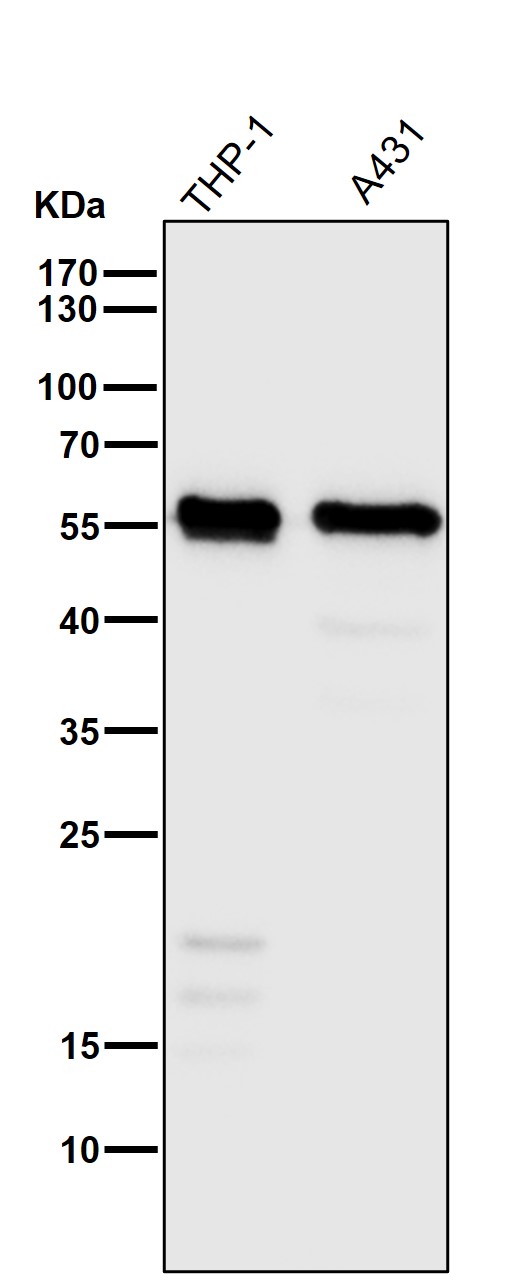
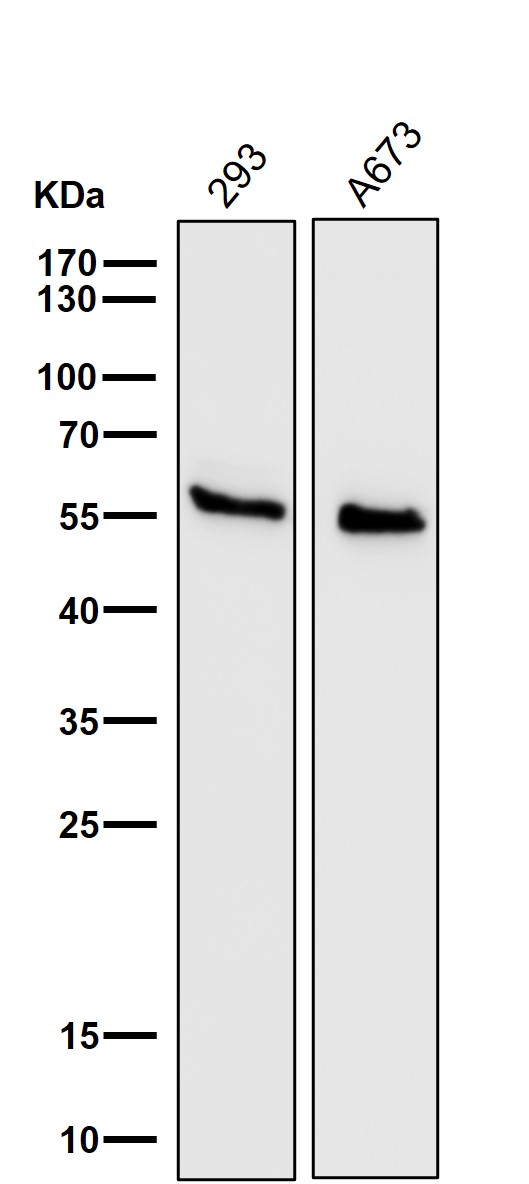
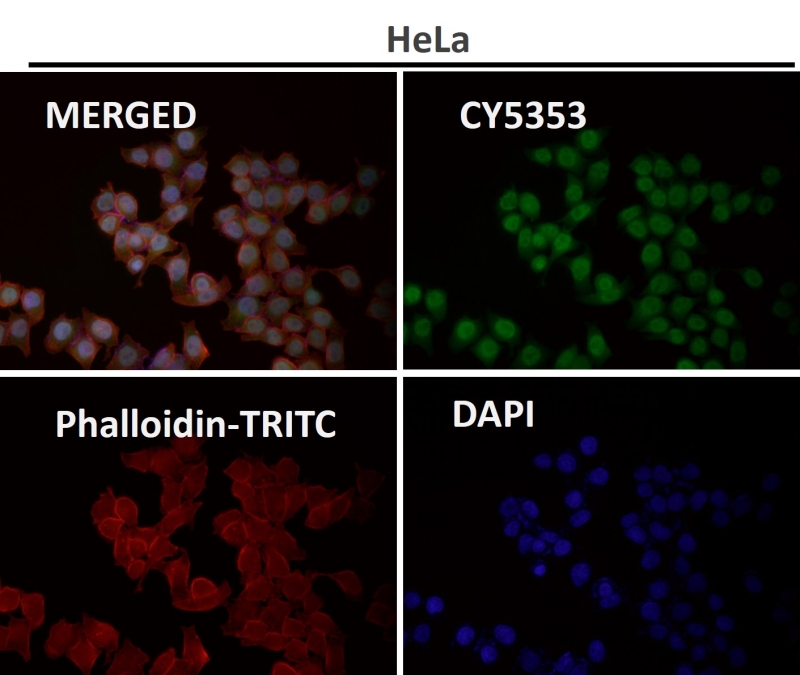
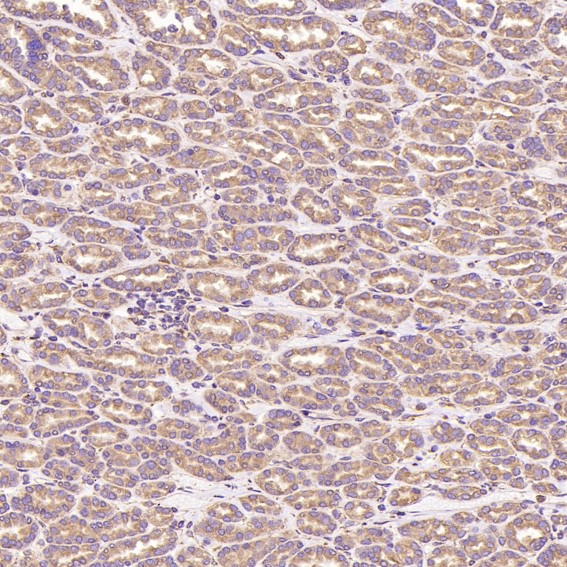
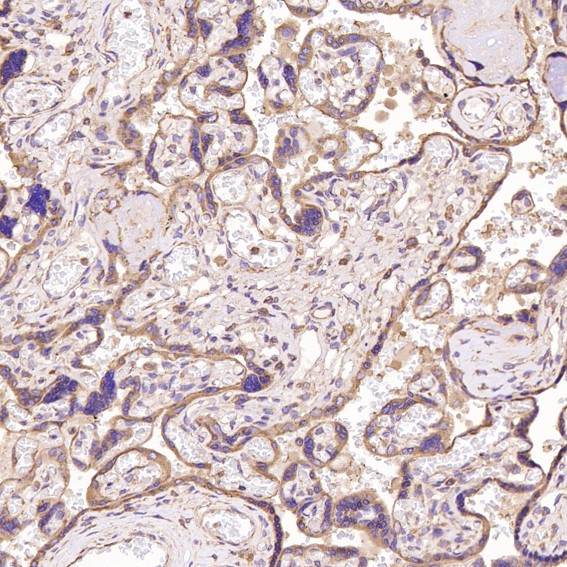
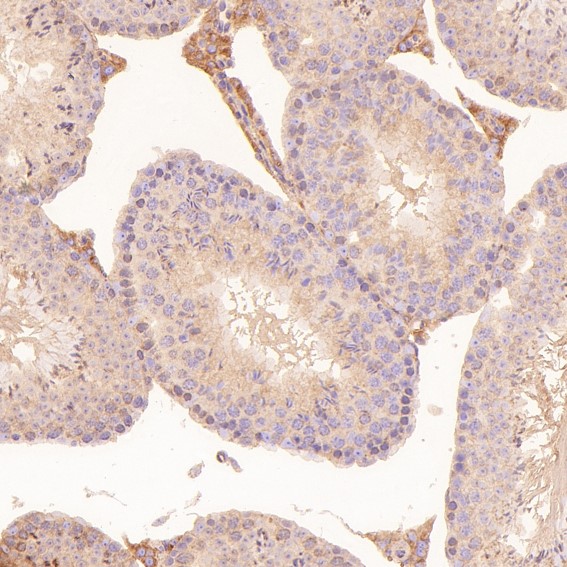
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CALR; CRT; FLJ26680; RO; SSA; cC1Qr; CRP55; CRTC; HACBP;;Calreticulin |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 48 kDa ; Observed MW: 55 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Calreticulin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Calreticulin抗体的3-4篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death*
**作者**:Gold LI, et al.
**摘要**:探讨Calreticulin在细胞表面暴露作为免疫原性细胞死亡(ICD)的关键标志,揭示其通过促进抗原呈递和免疫细胞激活增强化疗和放疗的抗肿瘤效果。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to calreticulin in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with disease activity and lupus nephritis*
**作者**:Mehta AM, et al.
**摘要**:研究系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中Calreticulin抗体的存在与疾病活动性、肾脏损害的相关性,提示其可能作为SLE临床分层的生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of calreticulin recognition by antibodies in autoimmune disorders*
**作者**:Fucikova J, et al.
**摘要**:通过重组蛋白片段分析,揭示Calreticulin的特定结构域(如C端)是自身抗体结合的主要表位,为理解自身免疫性疾病机制提供分子基础。
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-calreticulin antibodies in cancer: prognostic significance and therapeutic implications*
**作者**:Smith CJ, et al.
**摘要**:分析实体瘤患者血清中Calreticulin抗体的水平与预后的关系,发现高抗体水平与更长的生存期相关,可能反映抗肿瘤免疫应答的增强。
这些文献覆盖了Calreticulin抗体在肿瘤免疫、自身免疫疾病机制及临床应用中的多重角色,可为进一步研究提供方向。
Calreticulin (CALR) is a multifunctional endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident protein involved in calcium homeostasis, glycoprotein folding, and immune regulation. It acts as a molecular chaperone, ensuring proper protein folding, and modulates calcium signaling by binding ER luminal calcium. Beyond its intracellular roles, calreticulin can translocate to the cell surface under stress, where it interacts with immune cells, promoting phagocytosis and immunogenic cell death—a process critical in cancer immunotherapy.
Anti-calreticulin antibodies are autoantibodies targeting this protein, often linked to autoimmune diseases and certain cancers. In myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), somatic mutations in *CALR* exon 9 (e.g., 52-bp deletions or insertions) drive disease pathogenesis, particularly in *JAK2/MPL*-negative primary myelofibrosis and essential thrombocythemia. These mutations alter CALR’s C-terminal domain, creating a novel epitope that may trigger immune responses. While anti-CALR antibodies are not routinely used diagnostically, their presence is explored as a biomarker for disease monitoring or therapeutic targeting.
In autoimmune contexts, anti-calreticulin antibodies are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren’s syndrome, though their clinical significance remains unclear. Research suggests they may contribute to inflammation by disrupting ER function or forming immune complexes. Detection methods include ELISA and indirect immunofluorescence. Further studies are needed to elucidate their pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
×