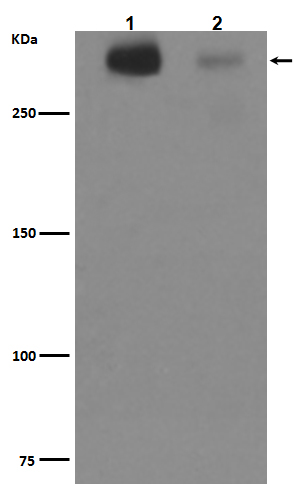
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tenascin; TN; Cytotactin; GMEM; GP 150-225; Glioma-associated-extracellular matrix antigen; Hexabrachion; JI; Myotendinous antigen; Neuronectin; Tenascin C; TN-C; TNC; HXB;Tenascin |
| WB Predicted band size | 241 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Tenascin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Tenascin-C抗体的3篇代表性文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
1. **"Tenascin-C in development and disease: gene regulation and cell function"**
- **作者**:Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Orend G
- **摘要**:综述了Tenascin-C在胚胎发育、组织修复及癌症中的生物学功能,重点讨论了其抗体在检测病理组织重塑(如肿瘤基质和炎症)中的应用价值。
2. **"A monoclonal antibody against human tenascin: a tool for tissue pathology"**
- **作者**:Saito Y, Imai T
- **摘要**:报道了一种特异性识别Tenascin-C的单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在免疫组化中对肿瘤和纤维化组织中Tenascin-C高表达的检测能力。
3. **"Targeting tenascin-C with antibody-drug conjugates in preclinical models of cancer"**
- **作者**:Rybak JN, et al.
- **摘要**:研究利用Tenascin-C抗体偶联药物(ADC)靶向肿瘤微环境,证明其在动物模型中可抑制肿瘤生长并减少转移,提示其治疗潜力。
4. **"Tenascin-C promotes fibrosis in inflammatory diseases via antibody-mediated activation of fibroblasts"**
- **作者**:Midwood K, Husain-Krautter S
- **摘要**:揭示了Tenascin-C抗体通过识别病变区域的蛋白构象变化,激活成纤维细胞促进纤维化,为抗体干预纤维化疾病提供机制依据。
以上文献覆盖了抗体开发、病理检测及治疗应用等方向。如需具体文章细节,可进一步通过PubMed或期刊数据库查询。
Tenascin-C (TNC) is a large extracellular matrix glycoprotein involved in tissue development, remodeling, and disease. It features a hexameric structure with multiple functional domains, including epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats, fibronectin type III repeats, and a fibrinogen-like domain. TNC regulates cell adhesion, migration, and signaling, playing dual roles in physiological processes (embryogenesis, wound healing) and pathologies such as cancer, fibrosis, and inflammation. In tumors, TNC promotes angiogenesis, metastasis, and stemness while suppressing immune responses.
Antibodies targeting Tenascin-C are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. Developed against specific domains (e.g., FNIII repeats), these antibodies enable detection via Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), or immunofluorescence (IF). Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clones BC24. MTn-12) offer high specificity, while polyclonal antibodies capture broader epitopes. Clinically, TNC antibodies have been explored as diagnostic markers in gliomas, breast cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis, and as therapeutic carriers for radioimmunotherapy or drug delivery.
Commercial TNC antibodies vary in species reactivity (human, mouse, rat) and applications. Researchers must validate them in context-dependent conditions, as TNC undergoes splice variants and post-translational modifications. Recent studies also highlight its potential as a biomarker for tissue regeneration and fibrotic progression.
×