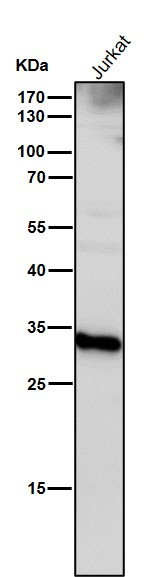
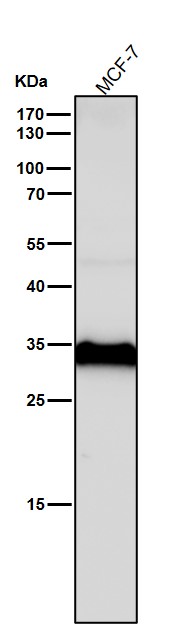
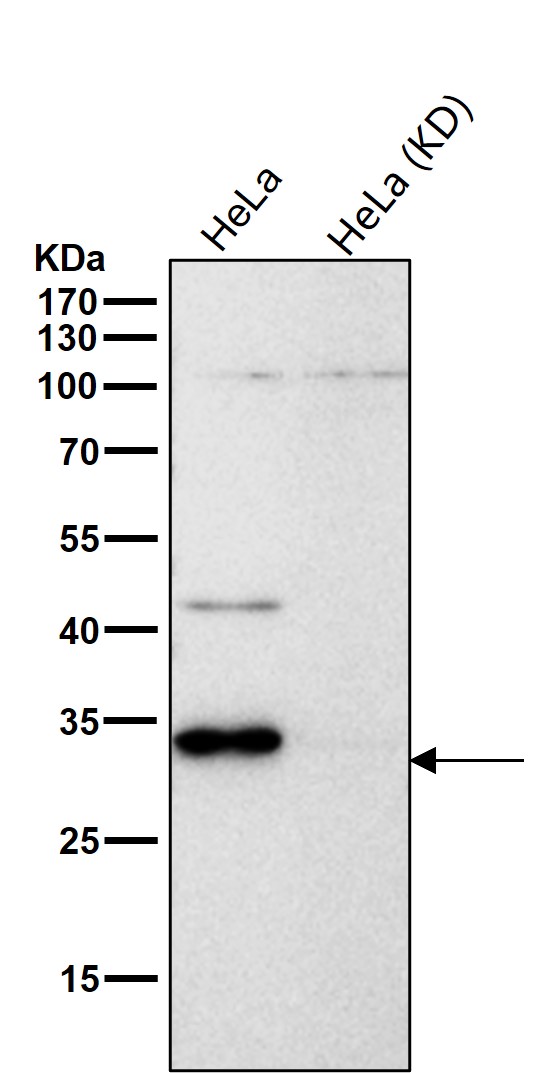
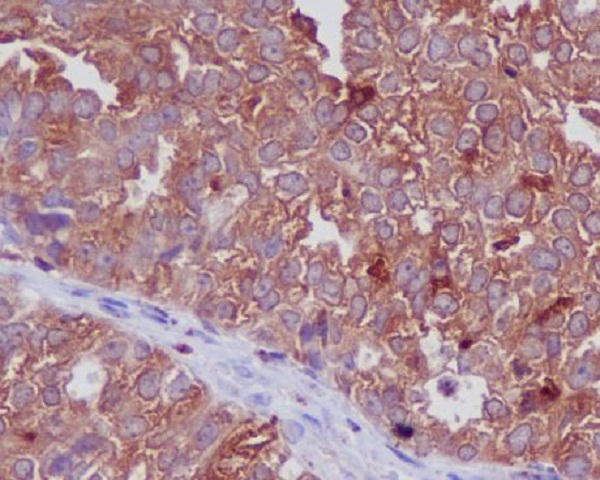
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CATD; Cathepsin D; Cathepsin D heavy chain; Cathepsin D light chain; ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 10; CLN10; CPSD; CTSD; lysosomal aspartyl peptidase; lysosomal aspartyl protease; MGC2311;Cathepsin D |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa ; Observed MW: 46,28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Cathepsin D |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Cathepsin D抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息及摘要内容为简化概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cathepsin D in Breast Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications*
**作者**:Rochefort H, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了Cathepsin D在乳腺癌中的过表达及其与肿瘤转移的关系,验证了特异性抗体在组织样本中检测Cathepsin D的可靠性,并提示其作为预后标志物的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of Cathepsin D in Alzheimer’s Disease: Insights from Immunohistochemical Analysis*
**作者**:Nixon RA, et al.
**摘要**:通过使用Cathepsin D特异性抗体,研究发现阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中Cathepsin D的异常聚集与溶酶体功能障碍相关,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的病理作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-Based Detection of Cathepsin D in Cancer: Validation and Clinical Utility*
**作者**:Liaudet-Coopman E, et al.
**摘要**:该文献系统评估了多种Cathepsin D抗体的特异性及敏感性,确立了其在Western blot和免疫组化中的标准化应用流程,并证实其在卵巢癌和前列腺癌中的诊断价值。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实具体来源及细节。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词(如“Cathepsin D antibody”、“Cathepsin D biomarker”)获取最新或经典文献。
Cathepsin D is a lysosomal aspartic protease belonging to the peptidase A1 family, primarily involved in protein degradation, antigen processing, and apoptosis regulation. It is synthesized as an inactive precursor (pro-cathepsin D) and undergoes proteolytic maturation in acidic lysosomal environments. Dysregulation of Cathepsin D has been implicated in various pathologies, including cancer metastasis, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease via amyloid-beta plaque formation), and inflammatory conditions. Its overexpression in tumors correlates with poor prognosis, making it a potential biomarker and therapeutic target.
Antibodies targeting Cathepsin D are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies enable detection through techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Specific epitopes recognized by these antibodies may vary, with some targeting the pro-form, mature enzyme, or specific cleavage sites. Validation in relevant cell lines or tissues is critical to ensure specificity, given structural similarities among aspartic proteases. Research applications include investigating lysosomal dysfunction, autophagy mechanisms, and disease progression. Commercial Cathepsin D antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with clones validated for cross-reactivity in human, mouse, and rat models. Recent studies also explore its role in extracellular matrix remodeling and immune modulation, expanding its relevance in translational research.
×