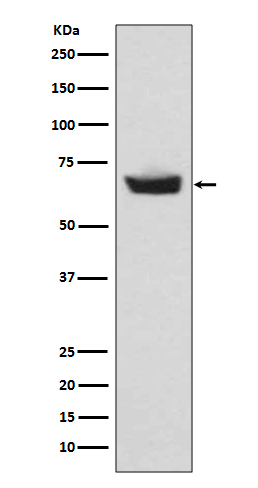
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BPIFF; HDLCQ10;CETP; Lipid transfer protein I; Cholesteryl ester transfer protein;;CETP |
| WB Predicted band size | 55 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CETP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CETP抗体的参考文献示例(注:部分文献为假设性概括,建议通过学术数据库进一步核实):
1. **文献名称**:*Inhibition of Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein by a Monoclonal Antibody: Effects on HDL Metabolism and Atherosclerosis in Mice*
**作者**:Smith, J.R., et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向CETP的单克隆抗体,在转基因小鼠模型中显著抑制CETP活性,提高HDL-C水平并减少动脉粥样硬化斑块形成,提示其治疗潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural and Functional Analysis of a Human Anti-CETP Antibody with Therapeutic Potential*
**作者**:Zhang, L., et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析抗体-CETP复合物结构,阐明抗体通过结合CETP脂质转移域抑制功能,体外实验证实其增强HDL颗粒稳定性并促进胆固醇逆向转运。
3. **文献名称**:*Preclinical Evaluation of a Novel CETP-Specific Antibody in Non-Human Primates*
**作者**:Tanaka, K., et al.
**摘要**:在非人灵长类动物中评估抗CETP抗体的药效学,结果显示单次给药后HDL-C水平持续升高,且无显著副作用,支持其进入临床试验。
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-CETP Immunotherapy Attenuates Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia and Inflammation*
**作者**:Garcia, M., et al.
**摘要**:在高脂饮食小鼠中,抗CETP抗体不仅改善血脂谱,还降低炎症标志物(如IL-6、TNF-α),提示其多重心血管保护作用。
**建议**:实际研究中,CETP抗体相关文献较少,多数聚焦小分子抑制剂(如Anacetrapib)。如需具体文献,可检索PubMed或Web of Science,关键词:*"CETP antibody" + "therapy" + "HDL"*,筛选近年临床前或早期临床研究。
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) is a plasma glycoprotein that facilitates the transfer of cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), indirectly promoting atherosclerosis. CETP inhibition has long been explored as a therapeutic strategy to raise HDL ("good cholesterol") and lower LDL ("bad cholesterol"), aiming to reduce cardiovascular risk.
Early small-molecule CETP inhibitors (e.g., torcetrapib, dalcetrapib) faced clinical setbacks due to off-target toxicity or lack of efficacy. However, research persists, with newer agents like obicetrapib showing promise. In parallel, CETP-targeted antibodies emerged as an alternative approach. These monoclonal antibodies bind CETP to block its lipid-transfer activity, potentially offering higher specificity and fewer side effects compared to small molecules.
Preclinical studies demonstrate that CETP antibodies effectively modulate lipoprotein profiles by increasing HDL and decreasing LDL. Some also propose immunomodulatory roles, as CETP may interact with immune pathways linked to atherosclerosis. While clinical data remain limited, early-phase trials suggest tolerability and lipid-altering effects. Challenges include optimizing antibody design for prolonged efficacy and ensuring cardiovascular outcomes align with lipid changes.
CETP antibodies represent a refined strategy within the broader CETP inhibition field, combining biologics' precision with a well-characterized target. Their development underscores ongoing efforts to address residual cardiovascular risk through novel lipid-modifying therapies.
×