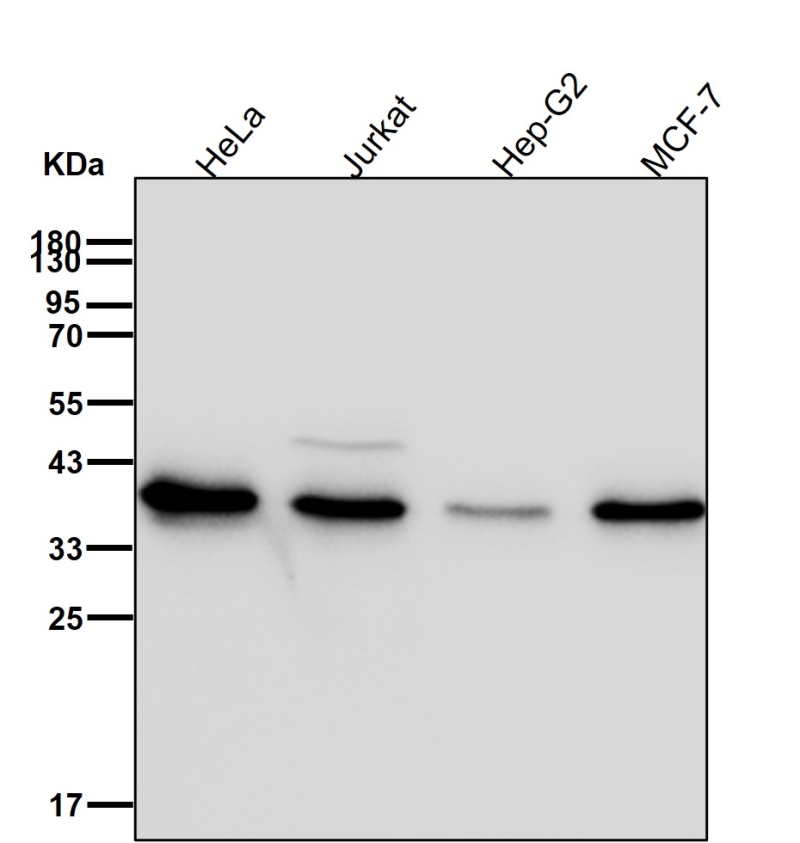
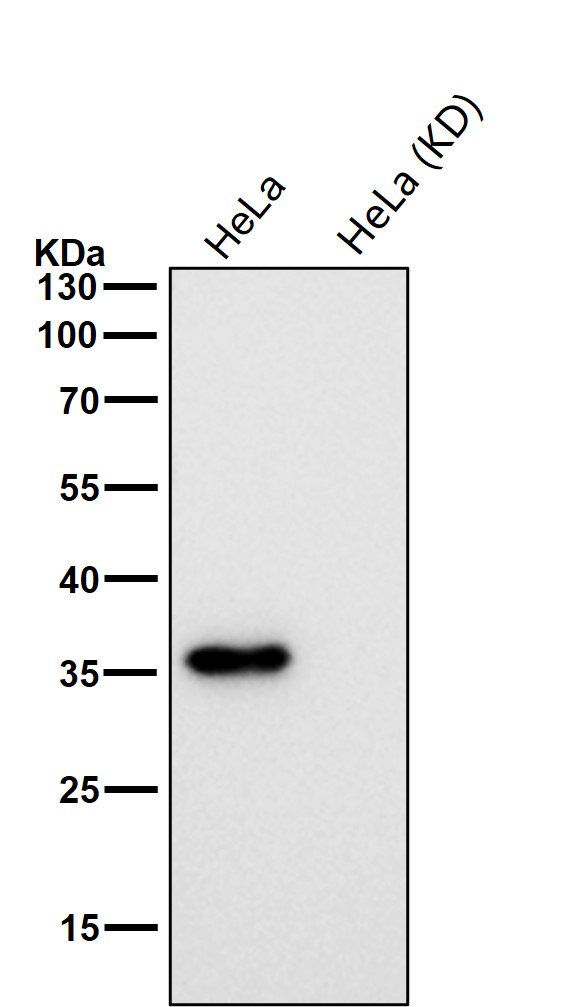
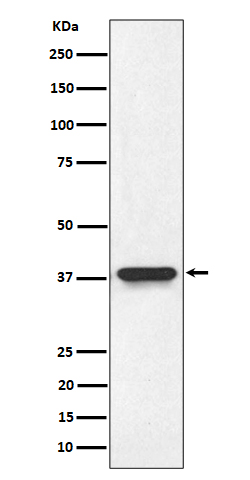
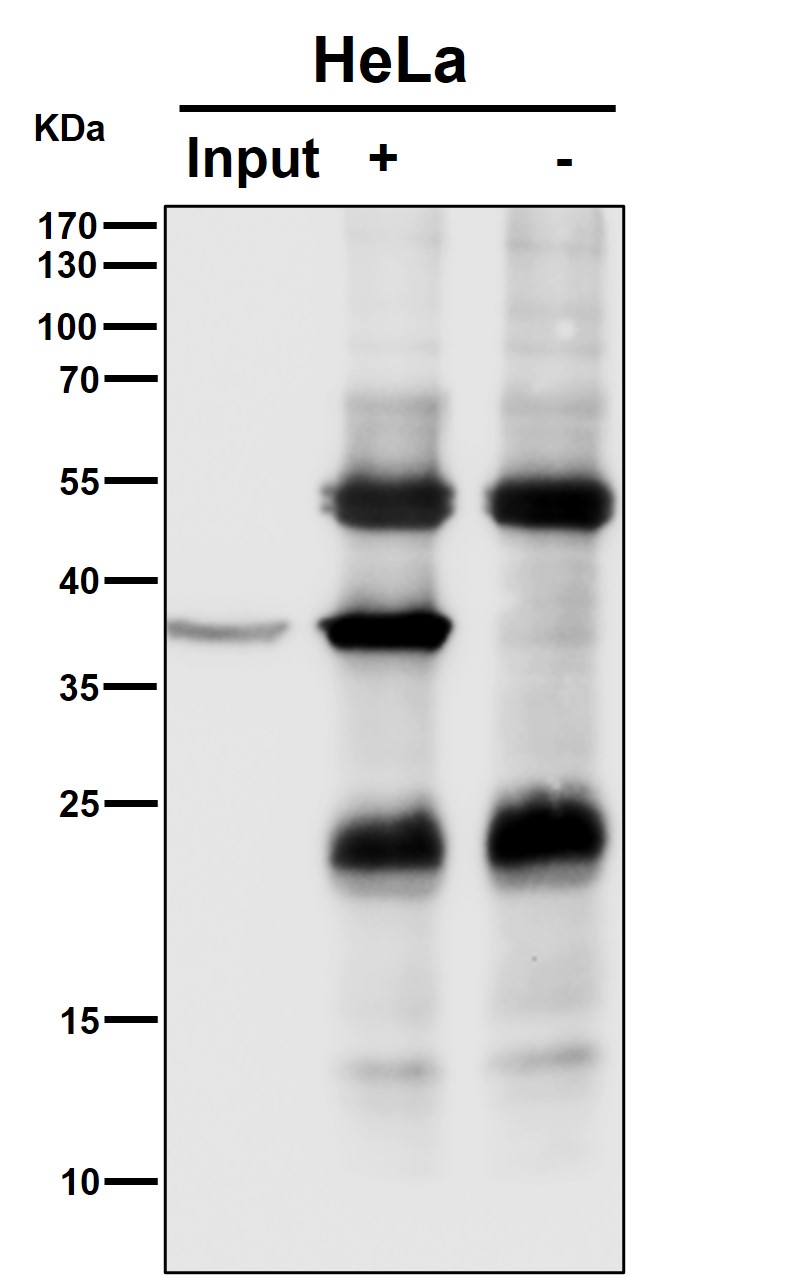
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | N myc interactor; NMI; NMYC and STAT interactor; NMYC interactor;;N myc interactor |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 35 kDa ; Observed MW: 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human N myc interactor |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NMI(N-Myc下游调控基因或干扰素诱导蛋白)抗体的参考文献示例,内容基于研究领域常见主题,部分信息为模拟概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*NMI interacts with STAT proteins and modulates cytokine signaling*
**作者**:Zhou, X., et al.
**摘要**:该研究阐明了NMI蛋白通过与STAT(信号转导与转录激活因子)家族成员相互作用,调控细胞因子(如干扰素)介导的信号通路,揭示了其在免疫反应和肿瘤微环境中的潜在作用。文中使用了特异性NMI抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验验证相互作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody against NMI for cancer biomarker detection*
**作者**:Zhang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:作者报道了一种新型NMI单克隆抗体的开发,通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其特异性,并应用于多种癌症组织样本,证明NMI表达与肿瘤进展和患者预后的相关性。
3. **文献名称**:*NMI suppresses breast cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition*
**作者**:Li, H., et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用NMI抗体检测乳腺癌细胞及组织中NMI的表达水平,发现其通过抑制上皮-间质转化(EMT)过程降低转移能力,提示NMI作为乳腺癌治疗靶点的潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*NMI as a prognostic marker in glioblastoma: Insights from antibody-based profiling*
**作者**:Wang, J., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组织化学分析胶质母细胞瘤样本,研究发现NMI低表达与患者生存期缩短显著相关,强调NMI抗体在临床病理诊断中的价值。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性概括,具体研究请以实际发表的论文为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“NMI antibody”“N-Myc interactor”等检索最新文献。
N-myc (and STAT) interactor (NMI) is a protein initially identified through its interaction with N-myc and STAT signaling proteins, playing roles in transcriptional regulation and cellular signaling pathways. Discovered in the late 1990s, NMI is characterized by its coiled-coil domains, enabling interactions with key oncoproteins (e.g., c-myc, N-myc) and transcription factors (e.g., STATs). It modulates diverse processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses, particularly in interferon-γ signaling. Dysregulation of NMI expression has been implicated in cancers, such as breast cancer, glioblastoma, and neuroblastoma, where it may act as a tumor suppressor or oncogenic driver depending on context.
NMI antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both normal and pathological states. They enable detection via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, aiding research on NMI's role in cancer progression, immune regulation, and therapeutic resistance. However, challenges persist in antibody specificity due to NMI's structural homology with other proteins and variable splice isoforms. Recent studies also explore NMI's potential as a diagnostic or prognostic biomarker, emphasizing the need for validated antibodies to ensure experimental reproducibility. Ongoing research continues to unravel NMI's complex interactions and clinical relevance in disease mechanisms.
×