| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
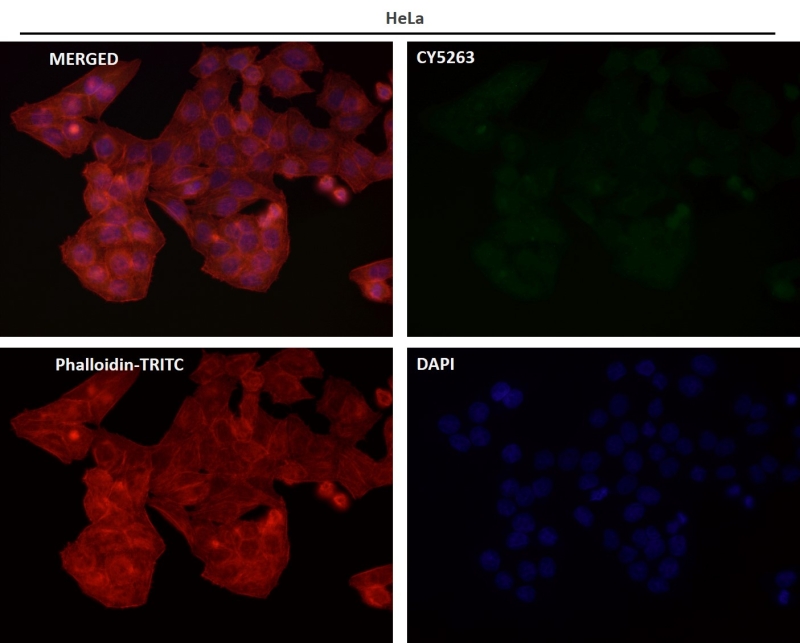
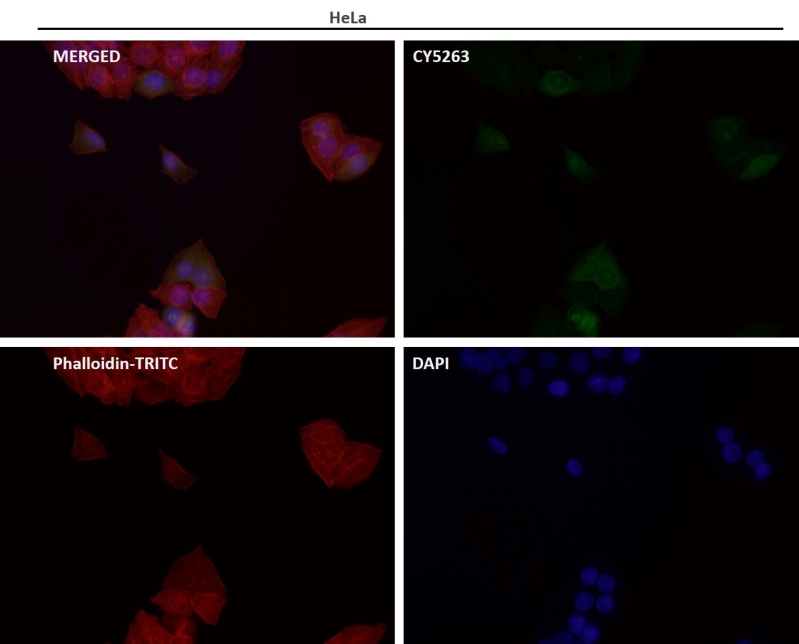
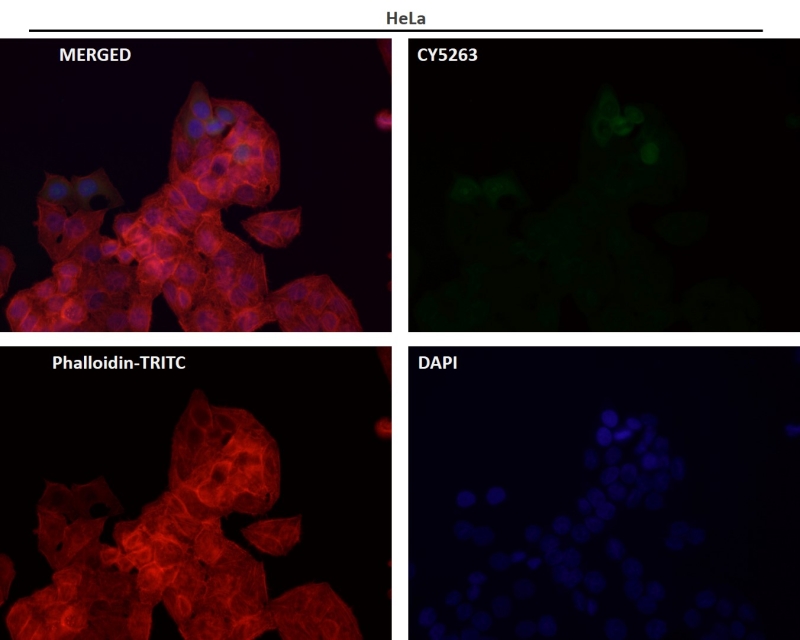
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
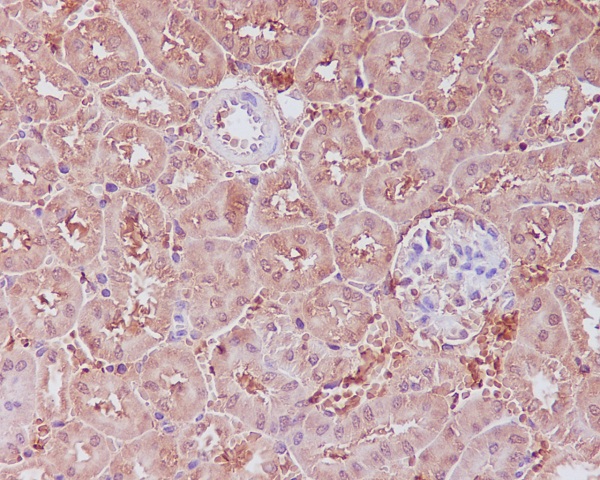
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APAF; APAF-1; APAF1; apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; apoptotic protease activating factor 1; Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; CED4; DKFZp781B1145; KIAA0413;APAF 1 |
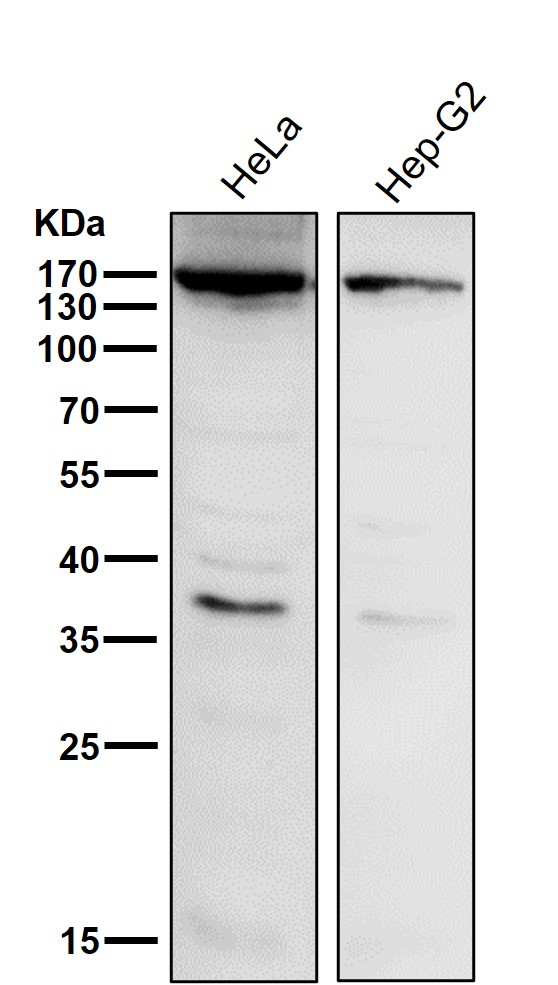
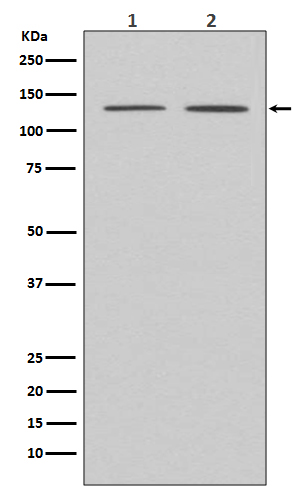
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 142 kDa ; Observed MW: 135 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human APAF 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于APAF1抗体的3篇参考文献示例:
---
1. **文献名称**: "APAF1 expression in colorectal cancer: correlation with prognosis and tumor progression"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组化(使用APAF1特异性抗体)分析了结直肠癌组织中APAF1蛋白的表达水平,发现APAF1低表达与患者预后不良及肿瘤转移显著相关,提示其作为潜在预后标志物的价值。
---
2. **文献名称**: "APAF1-mediated apoptosis in neuronal cells: validation of a specific antibody for Western blot analysis"
**作者**: Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究验证了一种高特异性APAF1抗体在Western blot中的应用,证明其在检测神经元凋亡模型中APAF1蛋白裂解形式的可靠性,并发现特定激酶抑制剂可调控APAF1的激活。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Loss of APAF1 in lung adenocarcinoma promotes chemoresistance by impairing mitochondrial apoptosis"
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用APAF1抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,发现肺腺癌中APAF1缺失导致线粒体凋亡通路受阻,增强化疗耐药性,提示恢复APAF1表达可能成为治疗策略。
---
注:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索确认。
APAF1 (Apoptotic Protease Activating Factor 1) is a critical protein involved in the intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway of apoptosis. It functions as a central component of the apoptosome, a multiprotein complex that activates caspase-9. initiating the caspase cascade responsible for programmed cell death. Structurally, APAF1 contains a caspase recruitment domain (CARD), a nucleotide-binding domain, and multiple WD40 repeats that facilitate interactions with cytochrome c released from mitochondria during apoptosis. Dysregulation of APAF1 has been implicated in cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and resistance to chemotherapy, making it a key target for studying apoptotic mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.
APAF1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying APAF1 expression in various experimental settings, such as Western blotting (WB), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). These antibodies help researchers investigate APAF1’s subcellular localization, protein-protein interactions, and expression patterns under physiological or pathological conditions. Many commercially available APAF1 antibodies are developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions). Validation through knockout controls or functional assays is crucial to ensure specificity, as cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins may occur. APAF1 antibodies are widely used in cancer research, neurobiology, and drug discovery to explore apoptotic signaling pathways and evaluate potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets. Their application extends to diagnostic research, particularly in diseases linked to defective apoptosis.
×