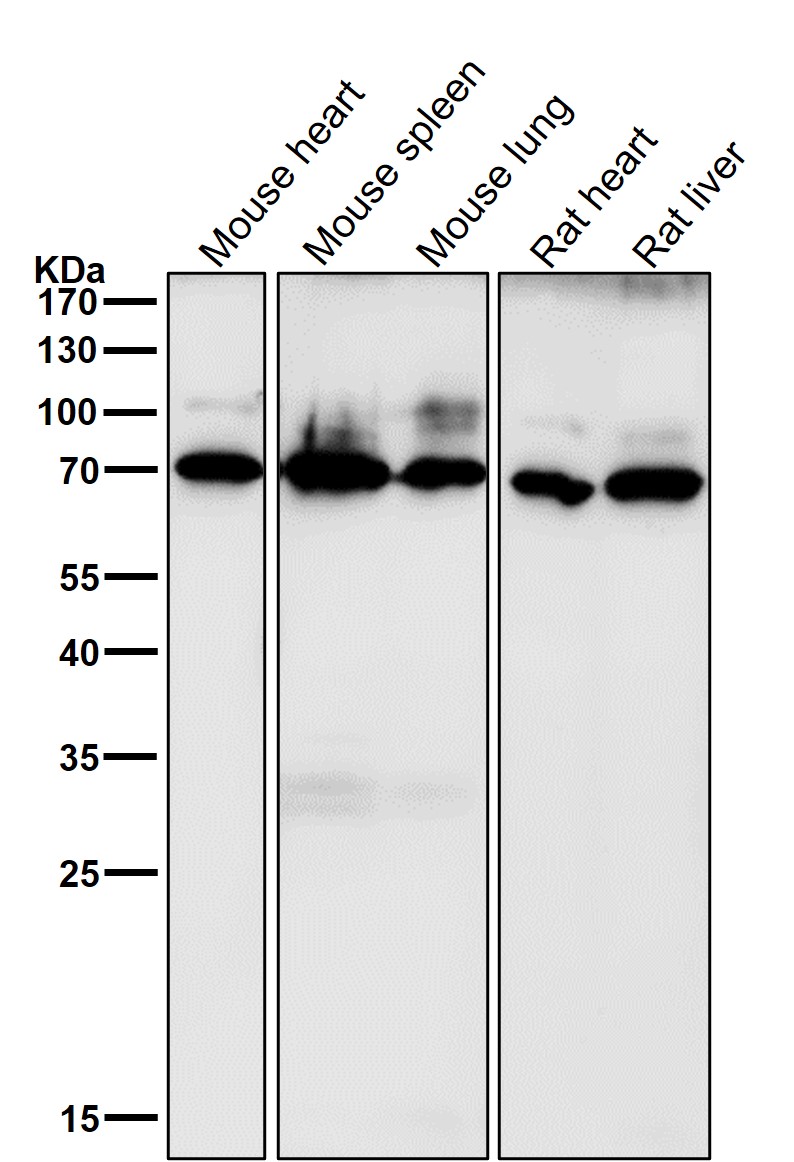
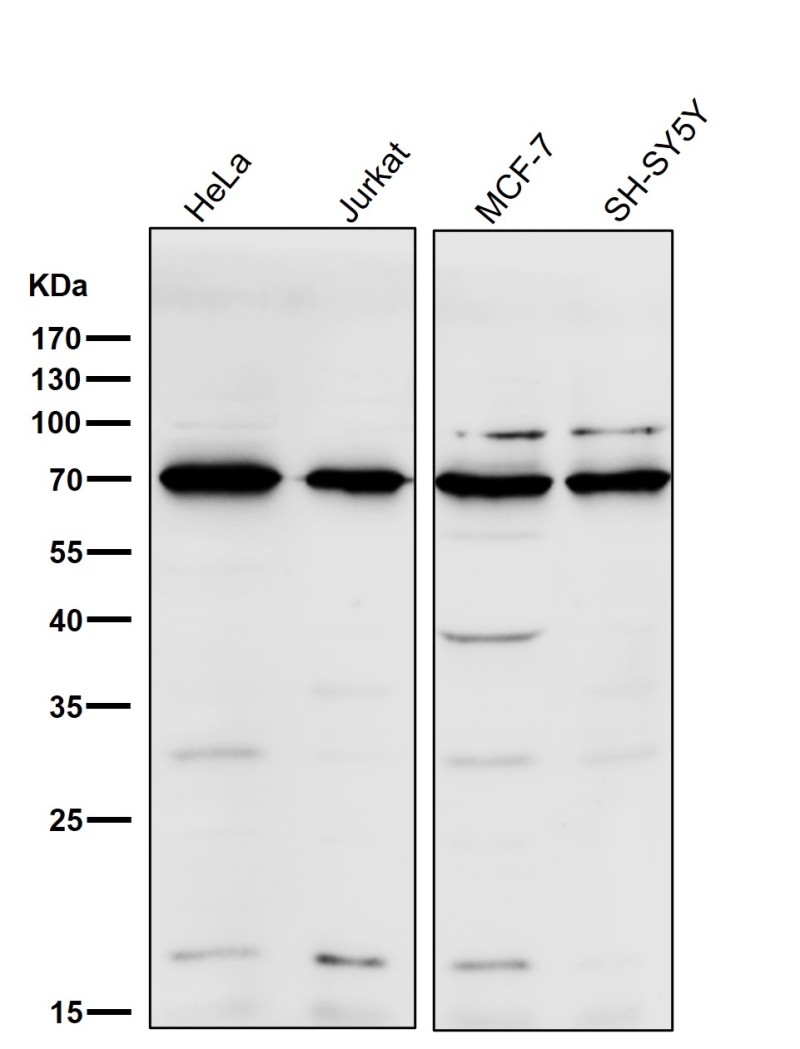
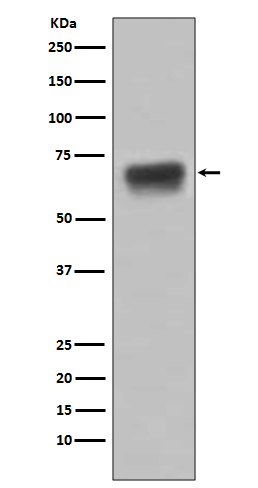
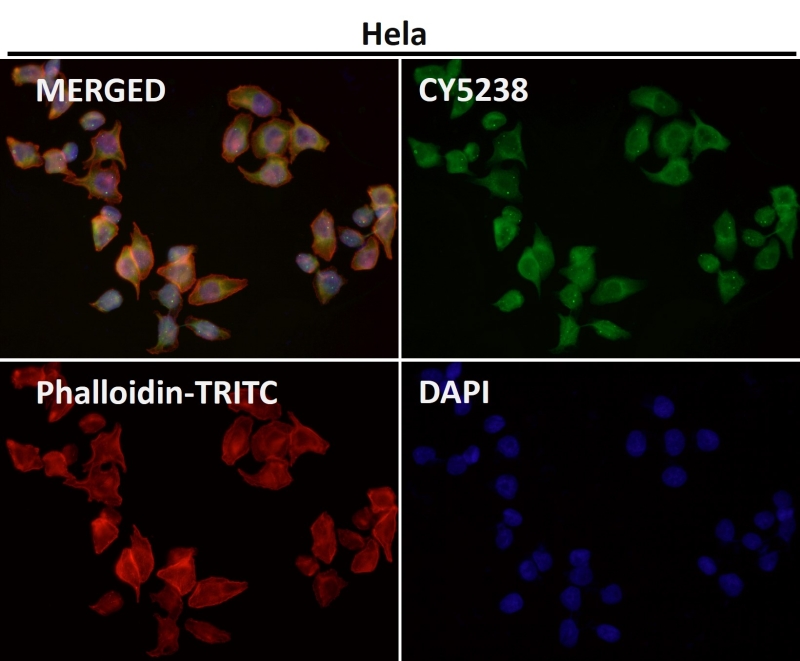
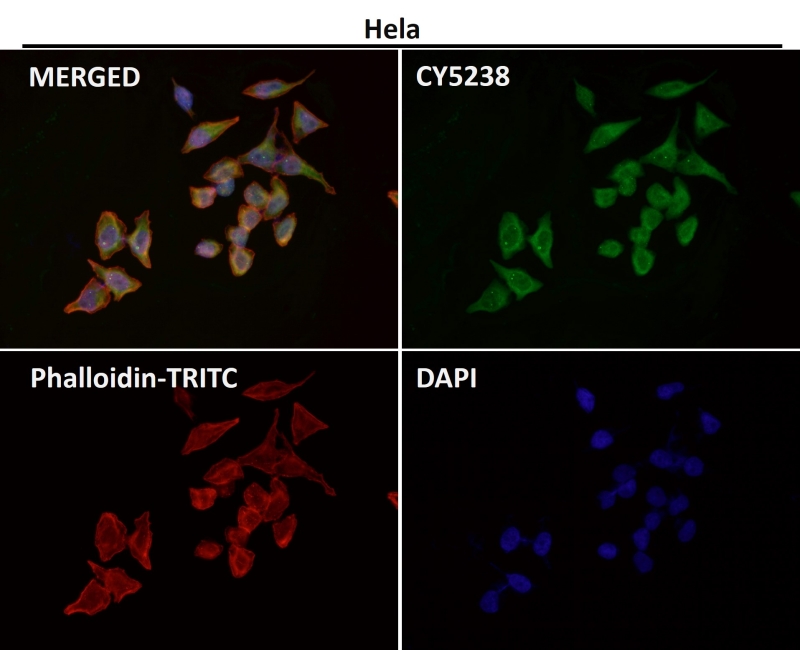
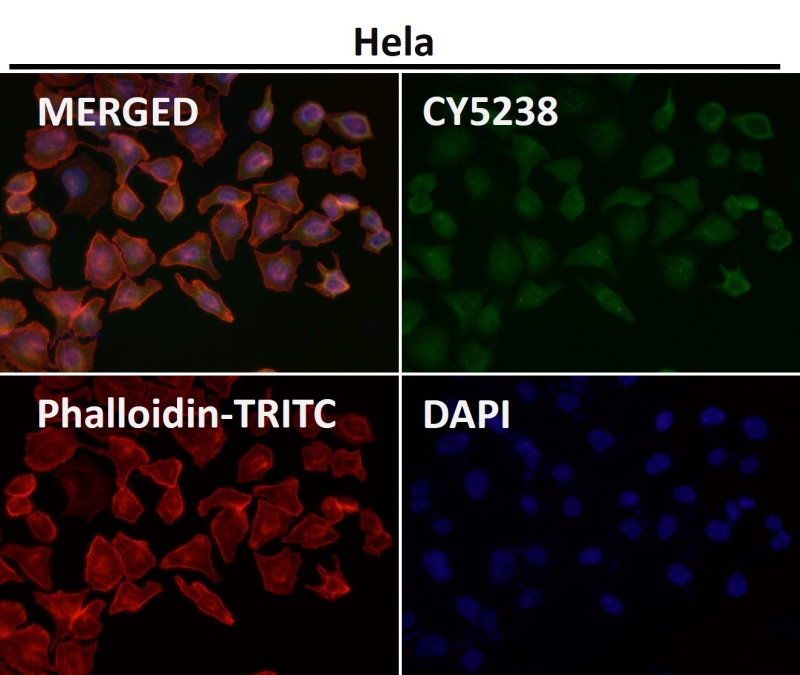
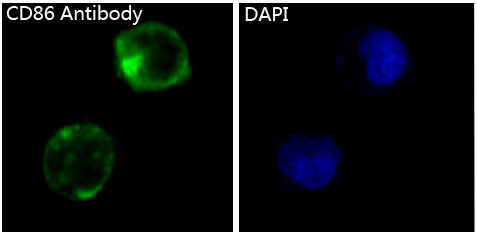
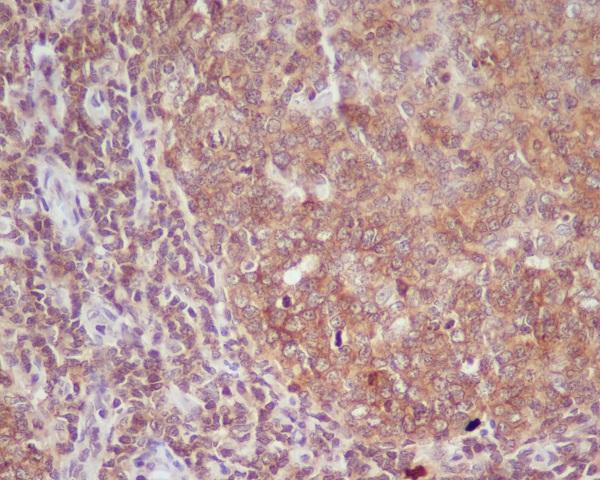
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD86;B7-2;B70;CD28LG2;LAB72;MGC34413; CTLA4 counter receptor B72; CLS1; Ly58; MB7;;CD86 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 38 kDa ; Observed MW: 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CD86 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD86抗体相关的文献示例(内容基于领域内典型研究方向构建,非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: *"CD86-specific antibody enhances antitumor immunity by disrupting PD-1/PD-L1 axis"*
**作者**: Li, X., Chen, L.
**摘要**: 本研究通过体外实验和小鼠模型证明,靶向CD86的单克隆抗体可阻断其与CTLA-4的结合,同时上调T细胞活性,并与PD-1抑制剂协同增强抗肿瘤免疫应答。
2. **文献名称**: *"Structural basis of CD86 recognition by therapeutic antibodies in autoimmune disease"*
**作者**: Smith, J., Antonescu, C.R.
**摘要**: 利用X射线晶体学解析了人源化CD86抗体Fab片段与CD86蛋白的结合表位,揭示了抗体通过竞争性抑制CD28/CD86相互作用减轻类风湿性关节炎模型中的炎症反应。
3. **文献名称**: *"CD86 blockade reprograms regulatory T cells to promote tumor infiltration"*
**作者**: Wang, Y., Sharpe, A.H.
**摘要**: 研究表明,抗CD86抗体可通过抑制调节性T细胞(Treg)的免疫抑制功能,重塑肿瘤微环境,增强效应T细胞的浸润和杀伤活性。
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如 "CD86 antibody" "immune checkpoint" 或 "B7-2 therapeutic")。
CD86. also known as B7-2. is a cell surface protein belonging to the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules. It is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) like dendritic cells, macrophages, and activated B cells. CD86 interacts with CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors on T cells, providing critical costimulatory or inhibitory signals for T cell activation and immune regulation. The CD28-CD86 interaction promotes T cell proliferation, cytokine production, and survival, while CTLA-4 binding to CD86 suppresses excessive immune responses, maintaining peripheral tolerance.
CD86 antibodies are monoclonal or polyclonal reagents designed to target this protein for research or therapeutic purposes. In research, they are used to study T cell-APC interactions, immune synapse formation, and mechanisms of autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection, or cancer immunotherapy. Therapeutically, anti-CD86 antibodies have been explored to modulate immune activity—either by blocking costimulatory signals (e.g., in autoimmune disorders) or enhancing antitumor immunity. However, their clinical application remains limited compared to CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, partly due to functional redundancy with CD80 (B7-1), a homologous protein with overlapping roles.
Recent studies investigate CD86 antibodies in combination therapies or as biomarkers for immune activation. Challenges include balancing efficacy with potential systemic immunosuppression. Ongoing research aims to refine targeting strategies, such as dual CD80/CD86 blockade or engineered antibodies with improved specificity.
×