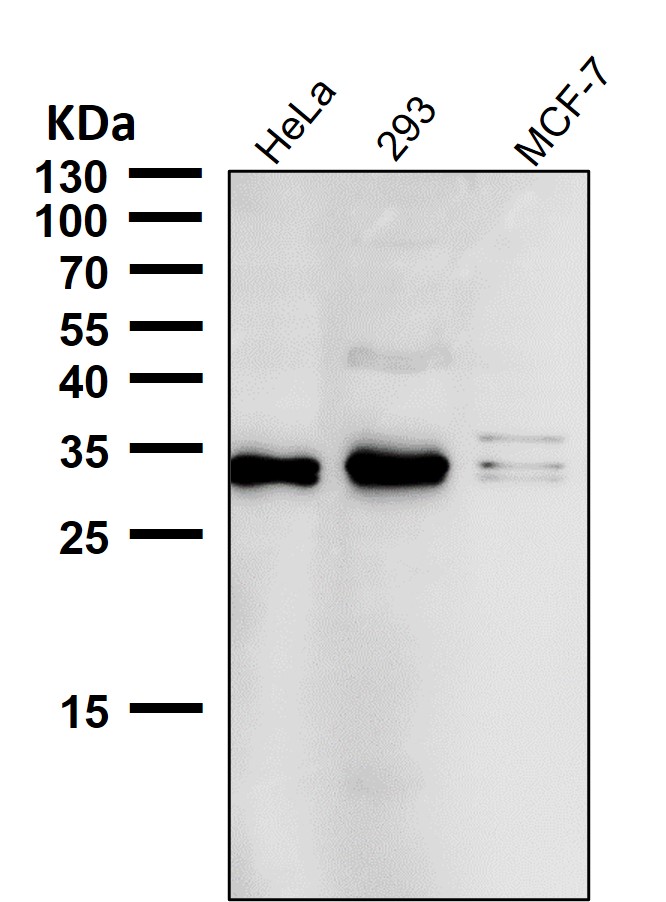
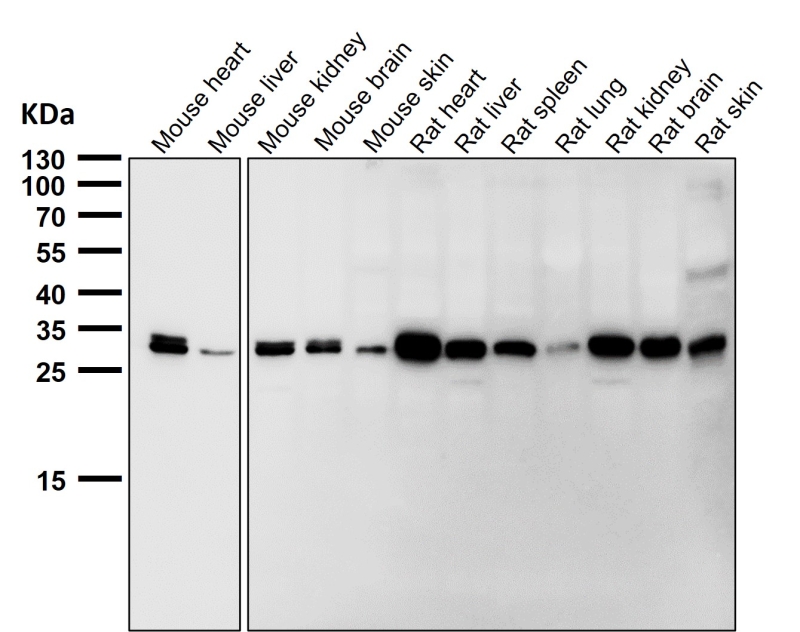
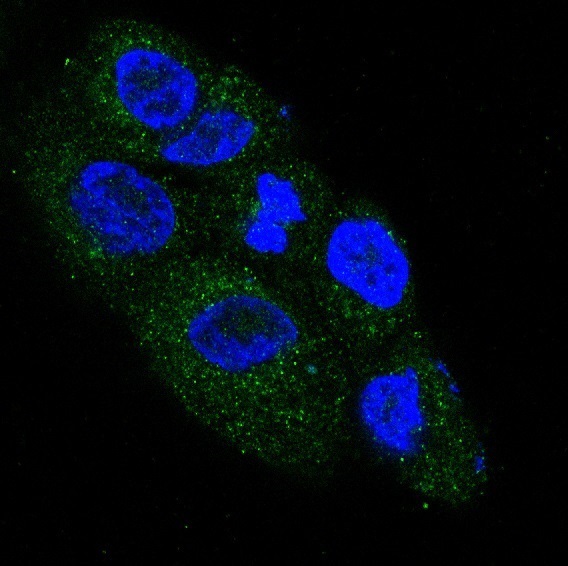
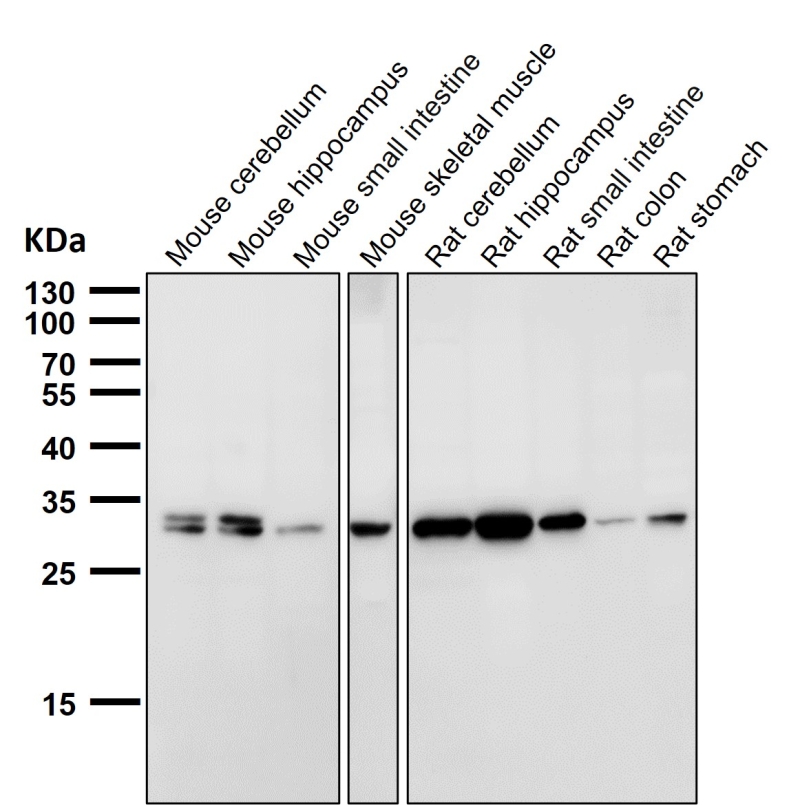
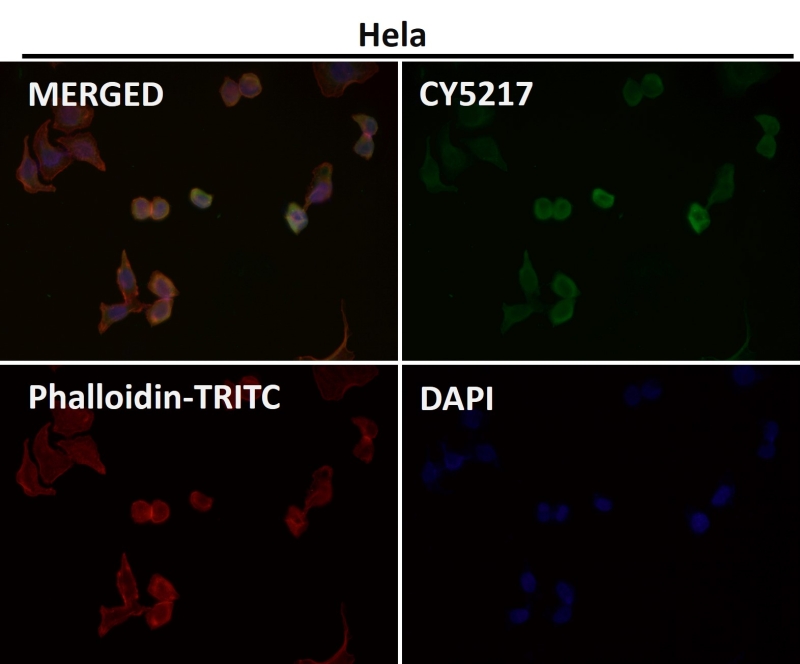
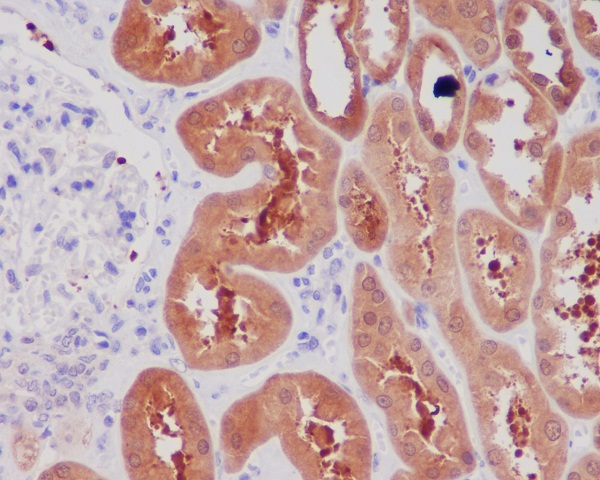
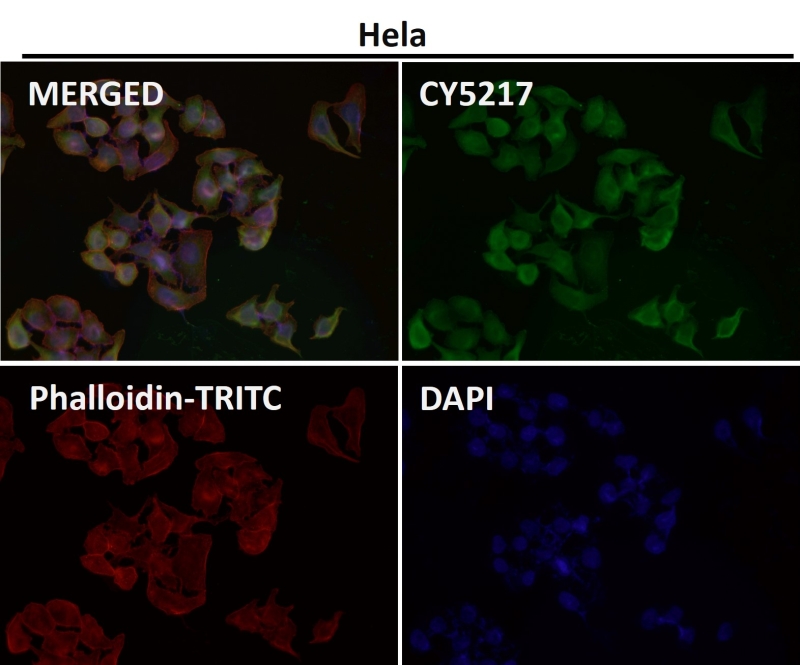
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NGF;Beta-NGF;HSAN5;MGC161426;MGC161428;NGFB;proNGF;;beta NGF |
| WB Predicted band size | 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human beta NGF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于NGF抗体的代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-NGF antibody improves pain-related behavior and reduces nerve sprouting in a canine model of chronic osteoarthritis pain*
**作者**:Lane NE et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过犬类骨关节炎模型,发现抗NGF抗体可显著缓解疼痛相关行为,并抑制感觉神经异常增生,表明其通过阻断NGF信号通路改善疼痛和神经重塑。
---
2. **文献名称**:*NGF as a therapeutic target: A double-edged sword in chronic pain and neurodegeneration?*
**作者**:Cattaneo A.
**摘要**:综述探讨NGF在慢性疼痛和神经退行性疾病中的双重作用,指出抗NGF抗体在治疗疼痛(如骨关节炎)中的潜力,但也警示其可能对神经修复产生负面影响。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Fulranumab, a humanized anti-nerve growth factor monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of chronic post-surgical pain: A randomized phase 2 trial*
**作者**:Katz N et al.
**摘要**:II期临床试验显示,抗NGF单抗Fulranumab可显著降低术后慢性疼痛患者的疼痛评分,且耐受性良好,支持进一步开展III期研究。
---
**注**:以上文献均聚焦于抗NGF抗体的作用机制或临床转化,覆盖基础研究、综述及临床试验方向。如需具体文献链接或补充其他研究,可进一步说明。
Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) antibodies are a class of biologics targeting NGF, a neurotrophic protein critical for the development, survival, and function of sensory and sympathetic neurons. Discovered in the 1950s, NGF binds to tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) and the p75 neurotrophin receptor, regulating pain signaling, inflammation, and tissue repair. Dysregulated NGF signaling is implicated in chronic pain conditions (e.g., osteoarthritis, neuropathic pain) and inflammatory diseases, driving interest in therapeutic inhibition.
NGF-blocking antibodies, such as tanezumab and fasinumab, are monoclonal antibodies designed to neutralize NGF, disrupting its interaction with receptors and downstream pain pathways. Preclinical studies show they effectively reduce hyperalgesia and inflammation. Clinical trials have demonstrated efficacy in osteoarthritis and chronic lower back pain, particularly in patients unresponsive to conventional analgesics.
However, safety concerns emerged, including reports of rapidly progressive osteoarthritis and peripheral neuropathy, leading to partial clinical holds by regulatory agencies. These adverse effects highlight the complex role of NGF in both nociception and tissue homeostasis. Ongoing research aims to refine dosing, identify patient subgroups, and mitigate risks.
Despite challenges, NGF antibodies represent a promising alternative for refractory chronic pain, offering a non-opioid mechanism. Their development underscores the importance of balancing targeted biologic therapies with safety in modulating multifaceted signaling pathways.
×