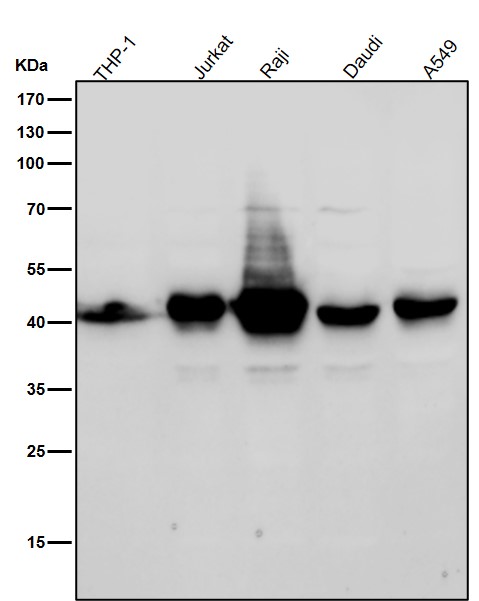
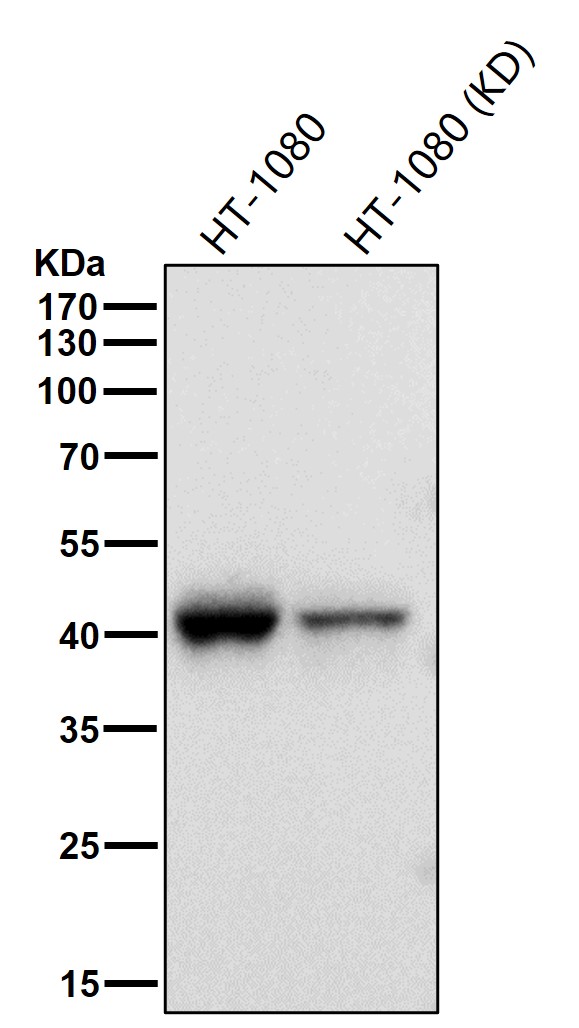
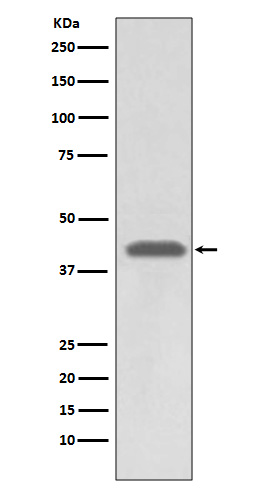
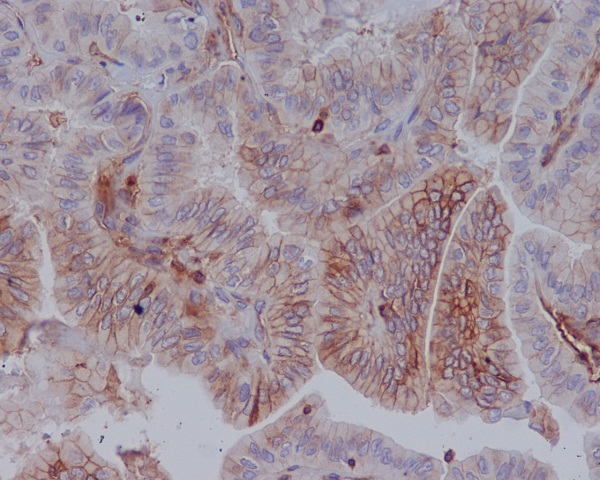
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aw-68;HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, A-28 alpha chain;MHC class I antigen A*68;HLA-A; MHC class I antigen HLA A heavy chain;;HLA A |
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human HLA A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于 **MHC class I抗体** 的参考文献,包含标题、作者和简要摘要内容:
---
1. **标题**:*Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2*
**作者**:Bjorkman, P.J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次解析了人类MHC class I分子(HLA-A2)的晶体结构,揭示了其抗原结合沟槽的构象以及与β2微球蛋白的结合方式,为后续开发特异性抗体提供了结构基础。
---
2. **标题**:*Antibody-based MHC class I manipulation drives anti-tumor immunity*
**作者**:Hansen, T.H. et al.
**摘要**:本文探讨了通过靶向MHC class I的抗体调节肿瘤细胞表面抗原呈递的机制,证明这类抗体可增强T细胞介导的肿瘤杀伤作用,为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
---
3. **标题**:*MHC class I antigen processing and presenting machinery: organization, function, and defects in tumor cells*
**作者**:Neefjes, J. et al.
**摘要**:综述了MHC class I分子从抗原加工到呈递的分子机制,并讨论了肿瘤中MHC I表达缺陷的机制,强调利用特异性抗体检测MHC I表达在临床诊断中的重要性。
---
4. **标题**:*Tapasin and other chaperones: key players in MHC class I assembly*
**作者**:Wearsch, P.A. & Cresswell, P.
**摘要**:研究了分子伴侣(如tapasin)在MHC class I分子组装中的作用,通过抗体阻断实验揭示其在抗原肽装载中的关键功能,为免疫调控研究提供工具。
---
这些文献涵盖了MHC class I的结构、功能、抗体应用及治疗潜力,可作为相关研究的参考基础。如需具体DOI或期刊信息,可进一步补充检索。
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules are cell surface proteins critical for adaptive immune responses, primarily presenting intracellular antigens to CD8+ T cells. Structurally, they consist of a polymorphic α-chain (encoded by HLA-A, HLA-B, or HLA-C genes in humans) non-covalently bound to β2-microglobulin. MHC class I is expressed on nearly all nucleated cells, enabling immune surveillance against intracellular pathogens (e.g., viruses, certain bacteria) and cancerous cells. Dysregulation of MHC class I expression is linked to immune evasion by pathogens and tumors, as well as autoimmune disorders and transplant rejection.
Antibodies targeting MHC class I are essential tools in research and clinical diagnostics. They are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to study protein expression, tissue distribution, and immune interactions. In transplantation, MHC class I antibodies help assess donor-recipient HLA compatibility, as mismatches can trigger graft rejection. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, such as those blocking MHC class I in autoimmune diseases, are under investigation. Additionally, certain viral infections (e.g., HIV, CMV) and cancers downregulate MHC class I to evade T cell detection; antibodies detecting this loss aid in prognostic evaluation. Autoantibodies against MHC class I are also observed in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, contributing to pathogenesis. Overall, MHC class I antibodies provide insights into immune regulation, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic development.
×