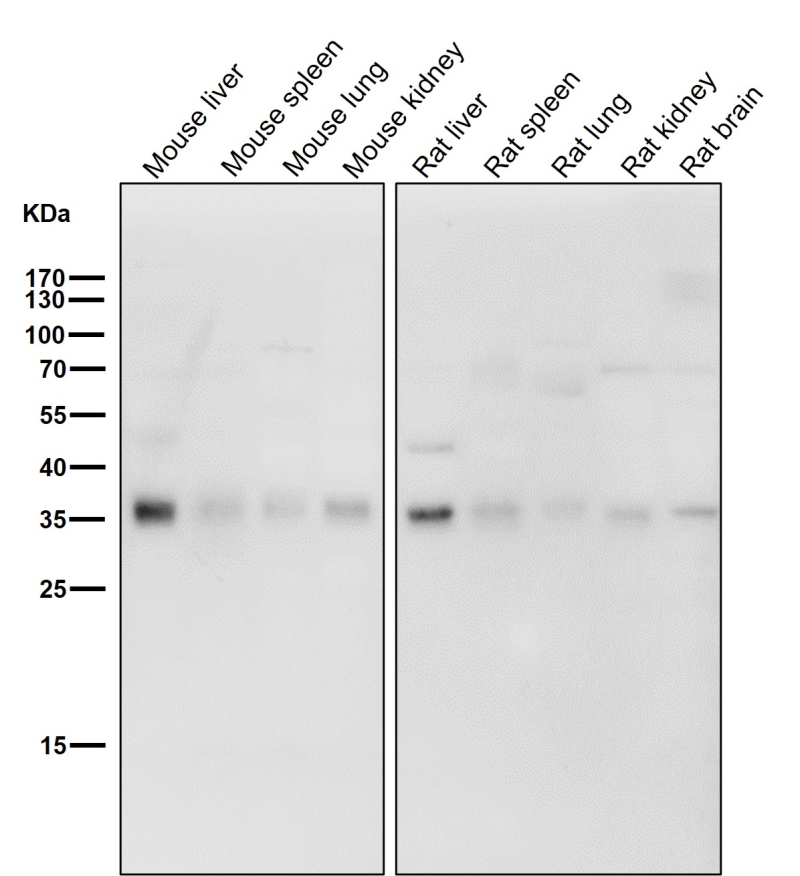
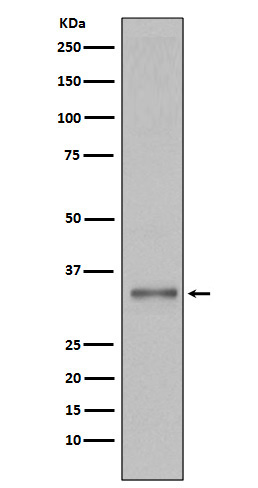
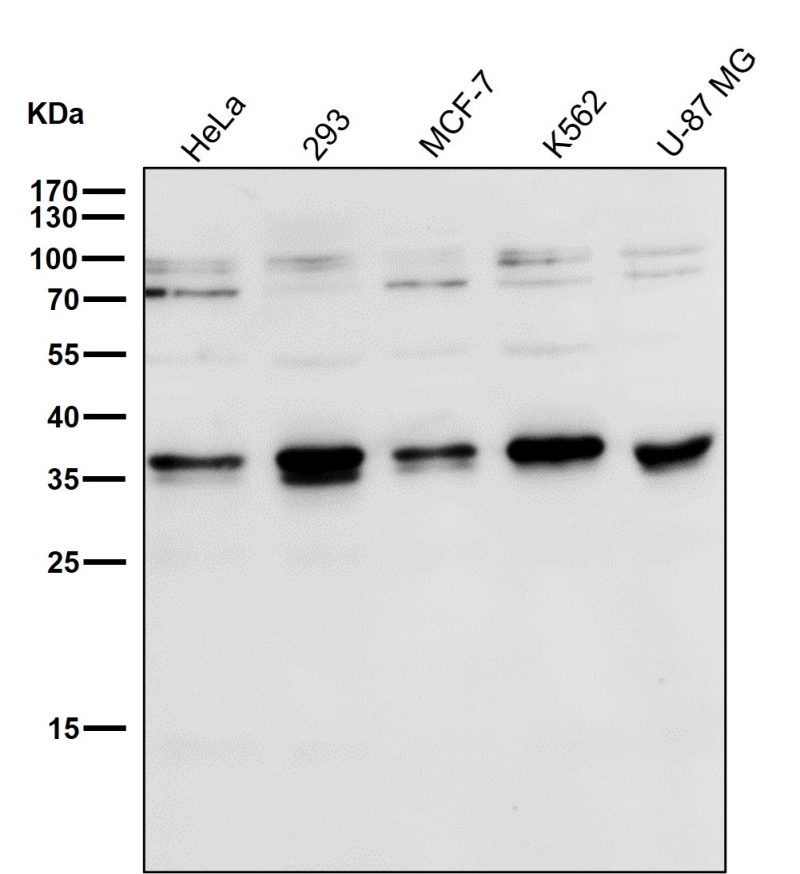
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TOR1A;DQ2; DYT1; TorsinA;;Torsin 1A |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 38 kDa ; Observed MW: 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Torsin 1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于TorsinA抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **"TorsinA and its torsion dystonia-associated mutant forms are lumenal glycoproteins that exhibit distinct subcellular localizations"**
- **作者**: Goodchild RE, Dauer WT
- **摘要**: 该研究利用TorsinA特异性抗体,通过免疫荧光和细胞分馏技术,揭示了野生型与突变型TorsinA在内质网和核膜区的差异定位,为DYT1肌张力障碍的病理机制提供了细胞学基础。
2. **"TorsinA in the nuclear envelope"**
- **作者**: Naismith TV, Heuser JE, Breakefield XO, Hanson PI
- **摘要**: 通过TorsinA抗体进行免疫电镜和Western blot分析,发现TorsinA主要定位于核膜内腔,并参与核膜相关蛋白的调控,突变体ΔE-TorsinA则形成异常聚集结构。
3. **"Dysregulation of cellular calcium homeostasis by mutant torsinA underlies neuronal dysfunction in DYT1 dystonia"**
- **作者**: Kim CE, Perez A, Perkins G, Ellisman MH, Dauer WT
- **摘要**: 研究使用TorsinA抗体检测神经元中TorsinA的表达及分布,发现突变体导致内质网钙稳态失衡,进而引发神经元功能障碍,揭示了DYT1肌张力障碍的潜在分子机制。
4. **"The role of torsinA in primary neurons: A new component of nuclear envelope architecture"**
- **作者**: Jungwirth M, Dear ML, Brown R, Holbrook K, Goodchild RE
- **摘要**: 通过TorsinA抗体的免疫组化分析,发现TorsinA缺失导致神经元核膜形态异常,表明其在维持核膜结构和神经元存活中的关键作用。
以上文献均通过TorsinA抗体开展蛋白质定位、功能及疾病相关性研究,为理解DYT1肌张力障碍提供了实验依据。
**Background of TorsinA Antibodies**
TorsinA is a member of the AAA+ (ATPases Associated with Diverse Cellular Activities) protein family, characterized by its conserved ATPase domain. It is predominantly localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and nuclear envelope, where it plays roles in protein quality control, membrane trafficking, and cytoskeletal organization. Mutations in the *TOR1A* gene encoding TorsinA, particularly the ΔE302/303 deletion, are linked to early-onset torsion dystonia (DYT-TOR1A), a neurological movement disorder.
TorsinA antibodies are immunodetection tools developed to study the expression, localization, and function of TorsinA in cellular and disease models. These antibodies are crucial for investigating TorsinA’s interaction with cofactors like LAP1 or LULL1. its role in ER stress response, and its involvement in nuclear envelope dynamics. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to analyze tissue distribution (e.g., neuronal tissues) or validate knockout/knockdown models.
Both monoclonal and polyclonal TorsinA antibodies exist, with specificity validated against recombinant proteins or *Tor1a*-deficient samples. Challenges include cross-reactivity with homologous proteins (e.g., TorsinB) and distinguishing between wild-type and mutant forms. Their applications extend to studying dystonia pathophysiology, neurodegeneration, and TorsinA’s potential roles in viral replication or aging. Selecting appropriate antibodies requires careful consideration of epitope regions, host species, and validation data to ensure experimental accuracy.
×