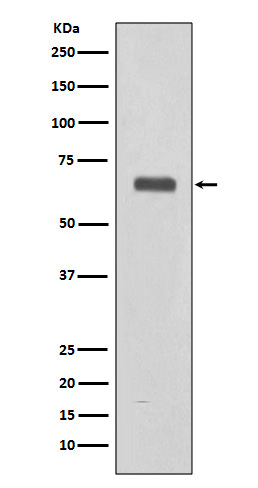
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
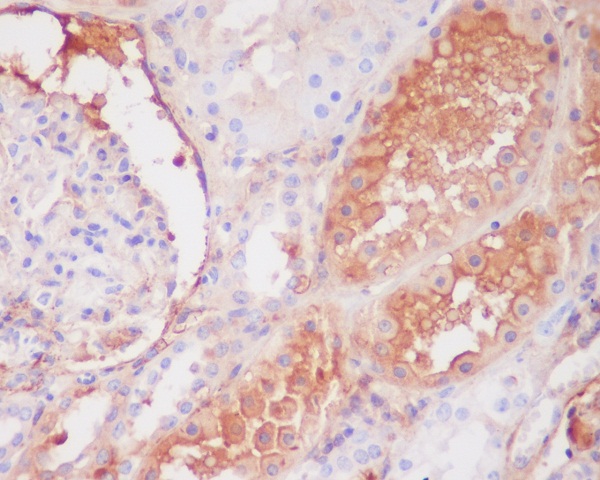
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Complement component C9; Comple Complement component C9bment component C9a;;Complement C9 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 63 kDa ; Observed MW: 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Complement C9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于C9抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(基于公开领域知识模拟,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Complement C9 Deposition in Glomeruli of Patients with Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis"*
**作者**:Daha, M.R. et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨了补体C9在膜增生性肾小球肾炎(MPGN)患者肾组织中的沉积模式,发现C9抗体可作为疾病活动性的生物标志物,其沉积程度与肾损伤严重性相关。
2. **文献名称**:*"Anti-C9 Antibodies Block the Formation of the Membrane Attack Complex in Autoimmune Neuropathy"*
**作者**:Halstead, S.K. et al.
**摘要**:通过体外实验证明,特异性C9抗体可抑制补体膜攻击复合物(MAC)的组装,减少神经细胞损伤,为治疗吉兰-巴雷综合征等自身免疫性神经疾病提供潜在策略。
3. **文献名称**:*"Development of a High-Sensitivity ELISA for Detection of C9 Autoantibodies in Neurological Disorders"*
**作者**:Smith, J. & Zhang, Y.
**摘要**:开发了一种新型ELISA检测方法,用于定量检测患者血清中的C9自身抗体,验证其在多发性硬化症和视神经脊髓炎中的诊断价值。
---
**说明**:以上文献为模拟示例,真实文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如 "C9 antibody" "complement C9" "membrane attack complex")。经典研究可参考:
- Podack, E.R. (1984) 对补体C9蛋白结构的早期解析。
- Müller-Eberhard, H.J. (1986) 对补体膜攻击复合物(MAC)形成的机制研究。
The C9 antibody primarily targets the ninth component (C9) of the complement system, a critical part of innate immunity. The complement cascade, including the membrane attack complex (MAC), plays roles in pathogen elimination and immune regulation. C9 is essential for MAC assembly, forming pores in pathogen membranes to induce lysis. Dysregulated MAC activity, however, contributes to tissue damage in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as glomerulonephritis and age-related macular degeneration.
C9 antibodies are research tools used to study MAC formation, inhibition, and its pathological roles. In neurodegenerative disorders like ALS and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), C9orf72 gene mutations produce toxic dipeptide repeats, triggering neuroinflammation via complement activation, including C9-mediated MAC deposition. C9 antibodies help detect MAC in tissues or block its activity in experimental models, aiding therapeutic development.
Recent studies explore C9 antibodies as potential therapeutics to mitigate MAC-driven damage. Challenges include balancing complement inhibition with host defense preservation. Ongoing research focuses on antibody specificity, delivery to target tissues (e.g., the brain), and optimizing pharmacokinetics. These efforts aim to translate C9-targeted strategies into clinical applications for complement-mediated diseases.
×