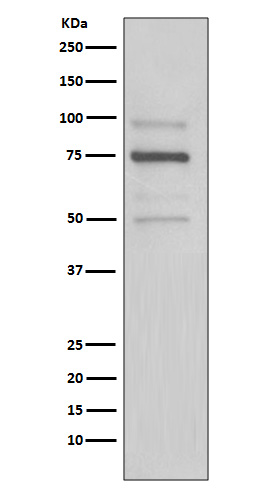
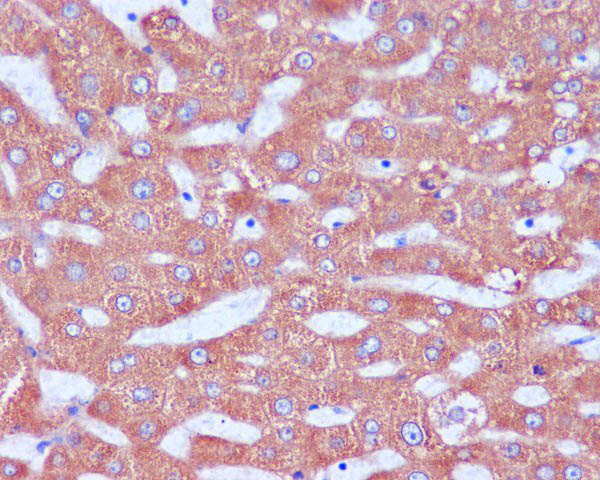
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KDEL; Lys Asp Glu Leu;;KDEL |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 25 kDa ; Observed MW: 78 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from KDEL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KDEL抗体的3篇经典参考文献及其摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins.
**作者**:Munro S, Pelham HR.
**摘要**:该研究首次提出C端KDEL序列是内质网驻留蛋白的关键信号,通过实验证明该序列可阻止溶酶体酶等蛋白分泌到细胞外,奠定了内质网蛋白定位机制的基础。
2. **文献名称**:Recycling of proteins from the Golgi compartment to the ER in yeast.
**作者**:Semenza JC, Hardwick KG, Dean N, Pelham HR.
**摘要**:揭示了KDEL受体在酵母中介导内质网蛋白从高尔基体逆向运输的机制,阐明了KDEL序列与受体结合的动态过程及其pH依赖性特点。
3. **文献名称**:Monoclonal antibody against KDEL sequence improves detection of ER stress.
**作者**:Vaux D, Tooze J, Fuller S.
**摘要**:报道了一种特异性识别KDEL序列的单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在免疫印迹和免疫荧光中检测内质网应激相关蛋白(如GRP78)的应用价值。
---
以上文献涵盖了KDEL序列的机制研究、受体功能及抗体开发应用,可作为相关领域的关键参考。
KDEL antibodies are immunological tools specifically designed to detect proteins containing the KDEL amino acid sequence, a canonical endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retention signal. The KDEL motif (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) is typically located at the C-terminus of soluble ER-resident proteins, such as chaperones (e.g., BiP/GRP78) and enzymes involved in protein folding. This sequence functions as a retrieval signal, ensuring that ER proteins escaping to the Golgi apparatus are recognized by KDEL receptors and returned to the ER via COPI-coated vesicle-mediated retrograde transport.
First described in the 1980s, KDEL antibodies were developed to study ER protein localization, trafficking, and homeostasis. They are widely used in techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunoprecipitation to visualize ER-resident proteins or monitor ER stress responses. The antibodies exhibit high specificity for the KDEL sequence, which is highly conserved across eukaryotic species, enabling cross-species applications.
In research, KDEL antibodies help investigate diseases linked to ER dysfunction, including neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and cancer. They also serve as markers for ER contamination in subcellular fractionation studies. Notably, some pathogens exploit the KDEL system to evade immune detection, making these antibodies valuable in infectious disease research. Despite their utility, interpretation requires caution, as non-ER proteins occasionally acquire KDEL-like sequences through mutation or post-translational modifications.
Overall, KDEL antibodies remain essential for probing ER biology and related pathological mechanisms.
×