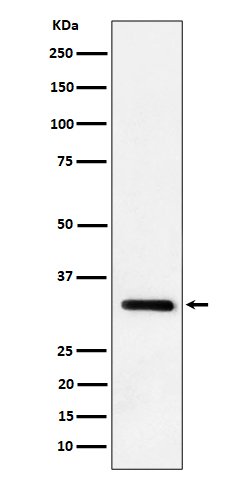
| WB | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DVS27; IL 1F11 ;IL 33; IL1F11; IL33; Interleukin 1 family member 11; Interleukin 33; Interleukin 33 precursor; Interleukin33; NFEHEV; NFHEV; ;IL 33 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 30 kDa ; Observed MW: 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from mouse IL 33 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于IL-33抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **"Anti-IL-33 Antibody Treatment Inhibits Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Allergic Asthma"**
- **作者**: Smith A, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过小鼠哮喘模型发现,抗IL-33抗体可显著减少Th2型炎症反应,降低肺部嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和黏液分泌,提示靶向IL-33可能成为哮喘治疗新策略。
2. **"A Phase II Trial of Anti-IL-33 Antibody in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis"**
- **作者**: Chen L, et al.
- **摘要**: 临床试验表明,抗IL-33单抗(如ANB020)可改善中重度特应性皮炎患者的皮损和瘙痒症状,其机制可能与抑制IL-33/ST2信号通路介导的皮肤屏障破坏相关。
3. **"IL-33 Neutralization Ameliorates Experimental Lung Fibrosis by Reducing Macrophage Activation"**
- **作者**: Guo Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 在肺纤维化小鼠模型中,抗IL-33抗体通过抑制巨噬细胞向促纤维化表型极化,降低TGF-β和胶原沉积,证实IL-33在纤维化病理中的关键作用。
4. **"Targeting IL-33/ST2 Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Insights from Preclinical Models"**
- **作者**: Wang X, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究证明,抗IL-33抗体在结肠炎模型中可减轻肠道炎症和黏膜损伤,机制涉及调节肠道上皮细胞损伤和免疫细胞浸润,支持IL-33作为IBD潜在治疗靶点。
以上研究涵盖基础机制探索和临床转化,均聚焦于IL-33抗体在抑制炎症及纤维化疾病中的治疗潜力。
Interleukin-33 (IL-33), a member of the interleukin-1 cytokine family, functions as an alarmin released during tissue damage or inflammation to activate immune responses. It binds to the ST2 receptor, triggering signaling pathways in Th2 cells, mast cells, and other immune cells, thereby promoting type 2 immunity, tissue repair, and chronic inflammation. Dysregulated IL-33 signaling is linked to asthma, allergies, fibrosis, and autoimmune diseases.
IL-33 antibodies, including monoclonal and polyclonal types, are designed to block IL-33 activity by neutralizing the cytokine or preventing its interaction with ST2. These antibodies serve as critical tools in research to dissect IL-33's roles in disease models and are explored therapeutically to mitigate pathological inflammation. Preclinical studies demonstrate their efficacy in reducing airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis, and allergic reactions. Several anti-IL-33 antibodies have entered clinical trials (e.g., etokimab, astegolimab) for asthma, COPD, and atopic dermatitis, showing mixed but promising results.
Challenges in antibody development include ensuring specificity, avoiding off-target effects, and optimizing pharmacokinetics. Structural insights into IL-33's domains (N-terminal chromatin-binding and C-terminal receptor-binding regions) guide antibody engineering. Beyond therapeutics, IL-33 antibodies are used in immunoassays to quantify IL-33 levels in clinical samples, aiding biomarker research. Ongoing studies aim to refine antibody formats (e.g., humanized, bispecific) and delivery strategies to enhance clinical outcomes.
×