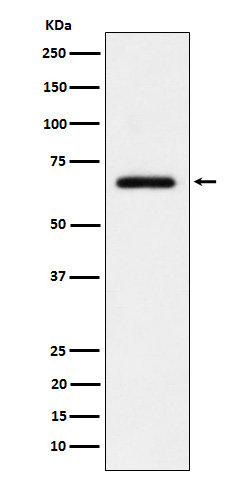
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Inactive ubiquitin specific peptidase 39; SAD1; snRNP ASSEMBLY DEFECTIVE 1; SNRNP65; Ubiquitin specific peptidase 39; USP39;;USP39 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human USP39 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于USP39抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:USP39 regulates spindle assembly checkpoint and progression of mitosis via interaction with CDC20 in hepatocellular carcinoma
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用USP39抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现USP39通过调控CDC20的稳定性影响肝癌细胞的有丝分裂进程,并揭示其作为潜在治疗靶点的作用。
2. **文献名称**:USP39 promotes breast cancer malignancy by stabilizing checkpoint kinase 1
**作者**:Zhang X, et al.
**摘要**:通过USP39抗体抑制实验,研究发现USP39通过去泛素化修饰稳定CHK1蛋白,促进乳腺癌细胞的DNA损伤修复和化疗耐药,提示其与患者预后不良相关。
3. **文献名称**:Depletion of USP39 induces glioma cell apoptosis via downregulation of β-catenin
**作者**:Wang H, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用USP39抗体敲低其表达,发现USP39通过调控β-catenin信号通路维持胶质瘤细胞存活,抑制USP39可诱导细胞凋亡,为胶质瘤治疗提供新方向。
The USP39 antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study ubiquitin-specific protease 39 (USP39), a deubiquitinating enzyme belonging to the USP family. USP39 is a 65 kDa protein involved in pre-mRNA splicing as a component of the spliceosome, particularly in the assembly and activation of the catalytic core. It plays roles in cell cycle regulation, DNA damage repair, and maintaining genomic stability. While not a direct deubiquitinase, USP39 interacts with splicing factors like SF3b and regulates spliceosome dynamics, indirectly influencing gene expression.
USP39 antibodies are commonly used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to investigate its expression, localization, and protein interactions. Studies have linked USP39 dysregulation to cancers (e.g., hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer) and neurological disorders, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. Commercial USP39 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal residues) and validated for specificity using knockdown controls. Researchers utilize these antibodies to explore USP39's molecular mechanisms in disease models and its functional interplay with pathways like p53 and PI3K/AKT. Proper validation remains critical due to occasional cross-reactivity concerns with spliceosome-related proteins.
×