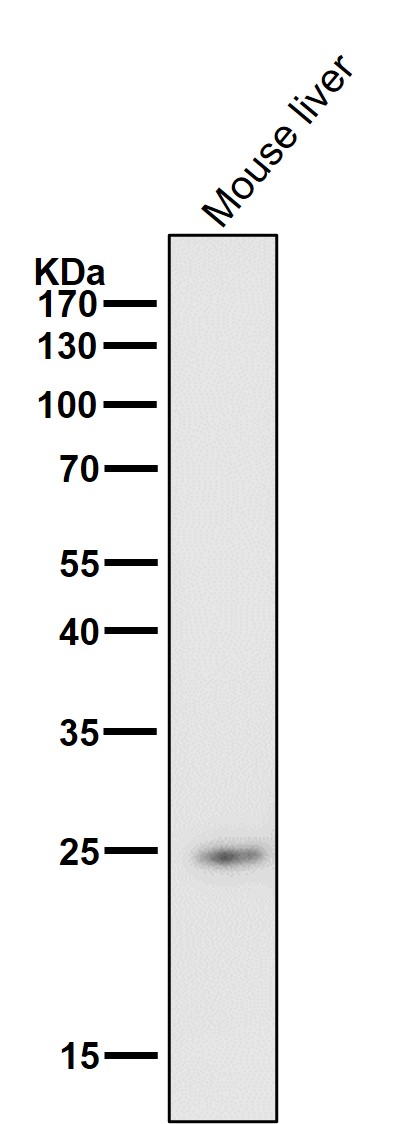
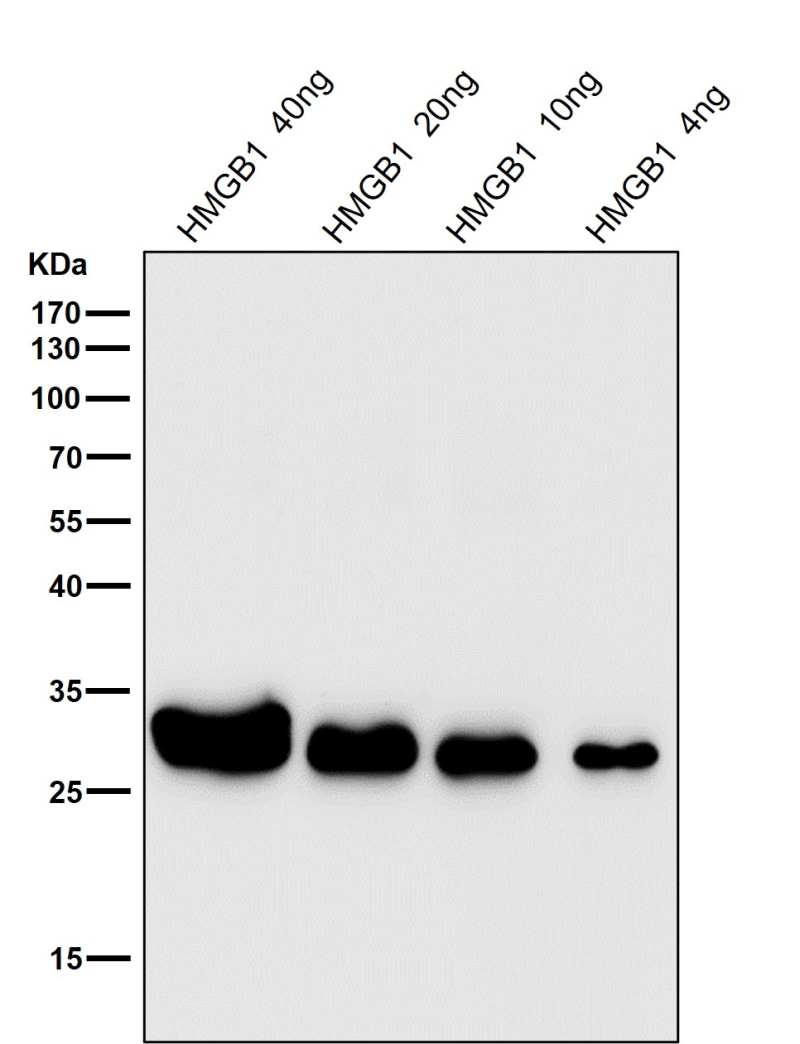
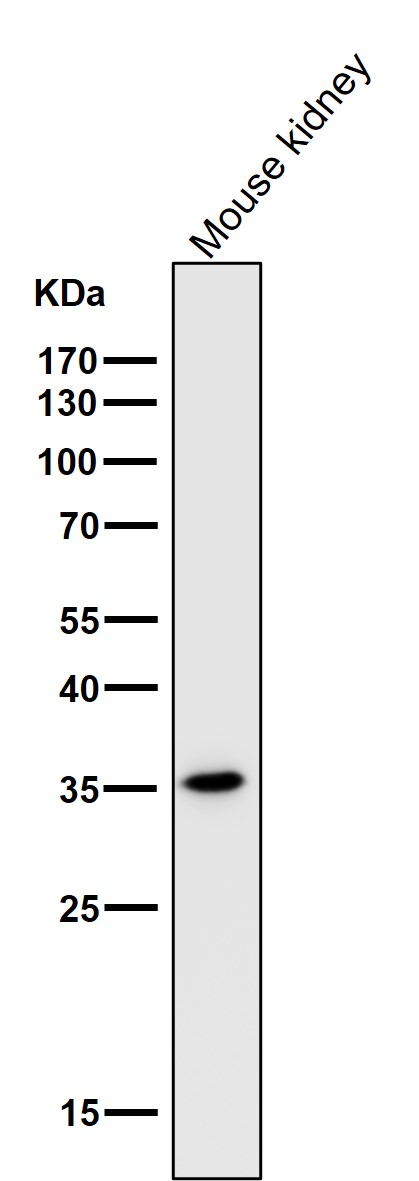
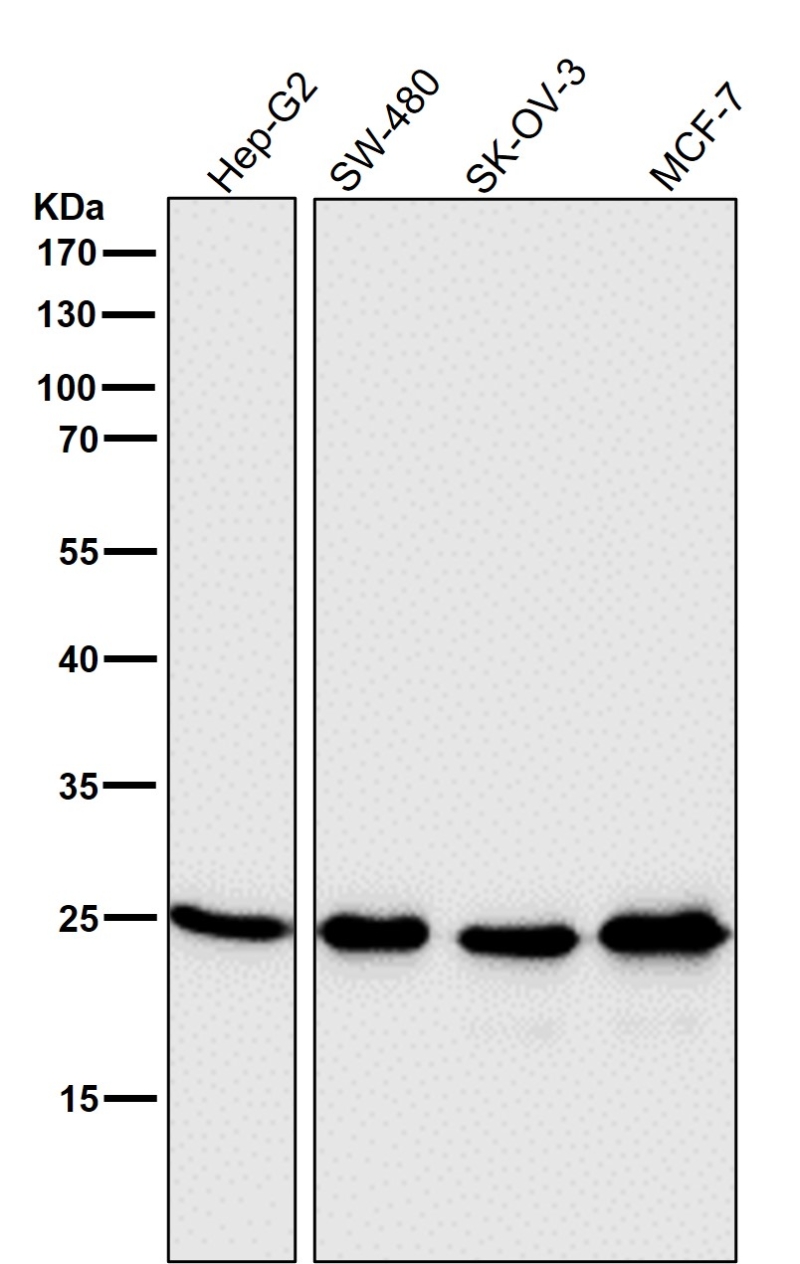
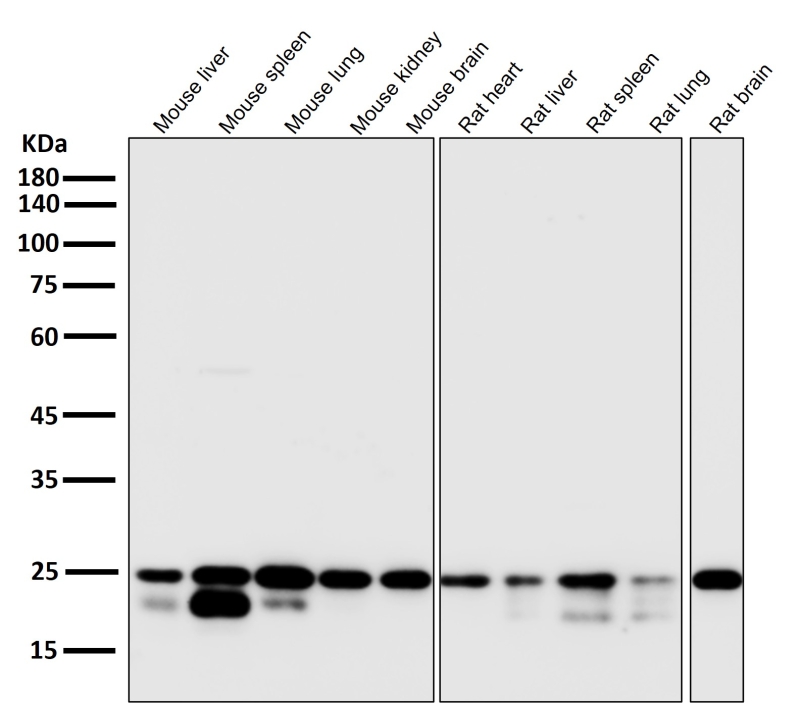

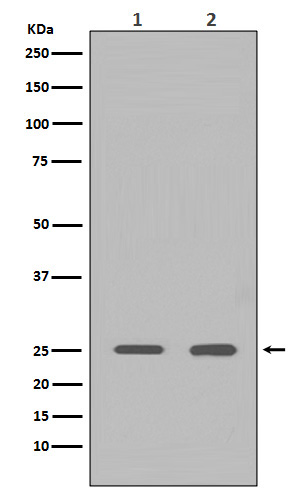
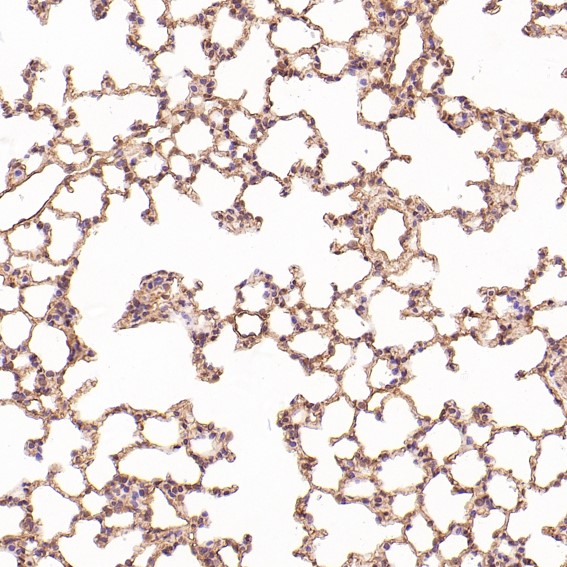
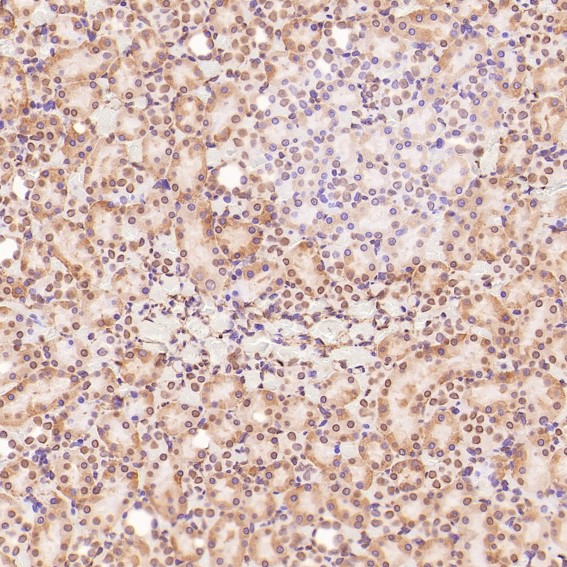
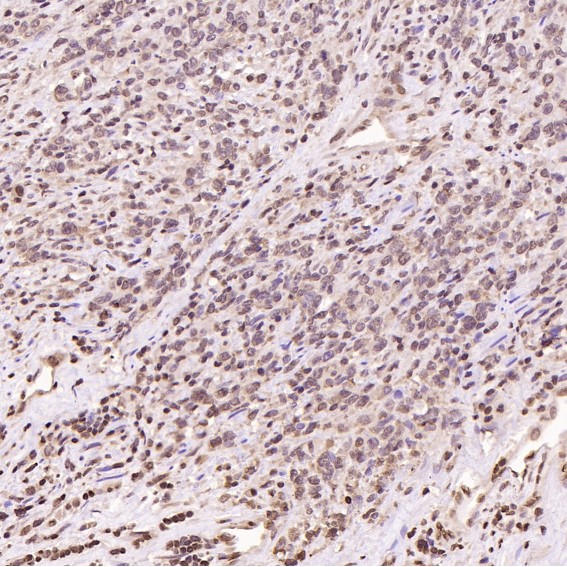
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HMGB1; HMG3; HMG1; SBP 1; Amphoterin;;HMGB1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human HMGB1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HMGB1抗体的3篇参考文献(简明格式):
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-HMGB1 monoclonal antibody ameliorates immunosuppression after systemic inflammation in mice*
**作者**:Yang H et al.
**摘要**:研究显示,抗HMGB1单克隆抗体通过阻断HMGB1与TLR4/NF-κB通路的相互作用,逆转脓毒症模型小鼠的免疫抑制状态,改善生存率。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting HMGB1 in inflammation-driven cancer progression with a neutralizing antibody*
**作者**:Tang D et al.
**摘要**:该文献证明抗HMGB1抗体可抑制慢性炎症诱导的肿瘤转移,机制涉及减少HMGB1介的肿瘤微环境中巨噬细胞极化和血管生成。
3. **文献名称**:*HMGB1-neutralizing antibody attenuates acute lung injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in mice*
**作者**:Qin S et al.
**摘要**:在小鼠肺缺血再灌注损伤模型中,抗HMGB1抗体通过抑制HMGB1释放和下游炎症因子(如TNF-α、IL-6)的产生,显著减轻肺组织病理损伤。
如需更多文献或扩展内容,可进一步补充。
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a non-histone chromatin-associated protein involved in DNA organization, transcription regulation, and cellular stress responses. Under physiological conditions, HMGB1 resides predominantly in the nucleus, stabilizing nucleosome structure and modulating gene expression. However, during cell death, injury, or stress, HMGB1 can be actively secreted by immune cells or passively released by necrotic cells into the extracellular space. Extracellular HMGB1 functions as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule, triggering inflammatory responses by binding to receptors like TLR4 and RAGE, thereby activating immune cells and amplifying cytokine release.
HMGB1 antibodies are critical tools for studying its dual roles in homeostasis and disease. In research, they are used to detect HMGB1 localization (nuclear vs. cytoplasmic/extracellular) via techniques such as Western blot, immunohistochemistry, or ELISA. Therapeutic HMGB1-neutralizing antibodies are being explored to mitigate pathological inflammation in sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, or ischemia-reperfusion injury. Conversely, HMGB1’s involvement in cancer metastasis and chemotherapy resistance has spurred interest in blocking its oncogenic signaling. Both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are available, with monoclonal antibodies offering higher specificity for epitope-targeted applications. Challenges include distinguishing between redox-modified HMGB1 isoforms (e.g., disulfide vs. fully reduced forms) and ensuring cross-reactivity validation across species. Overall, HMGB1 antibodies remain pivotal in elucidating its context-dependent roles and developing targeted therapies.
×