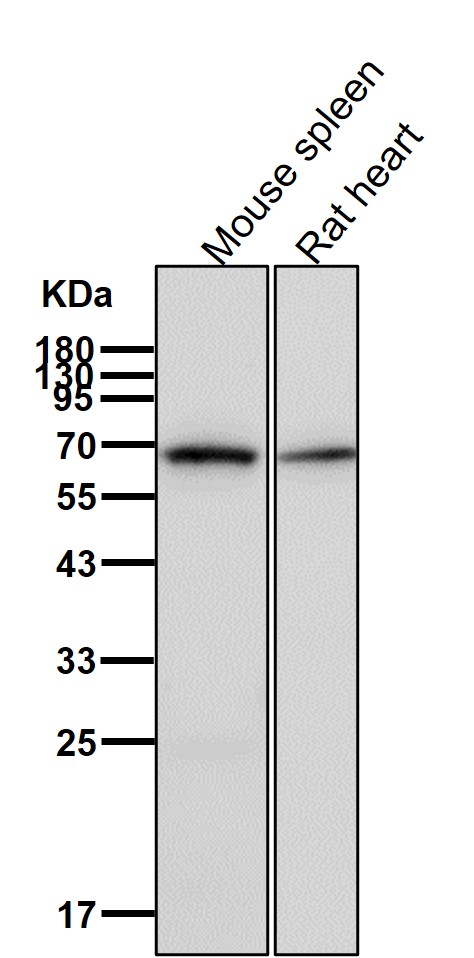
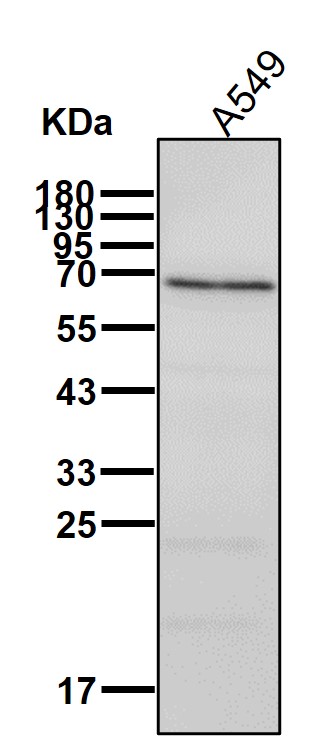
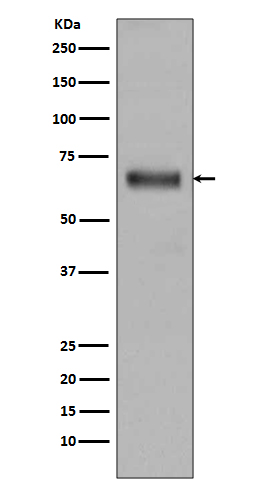
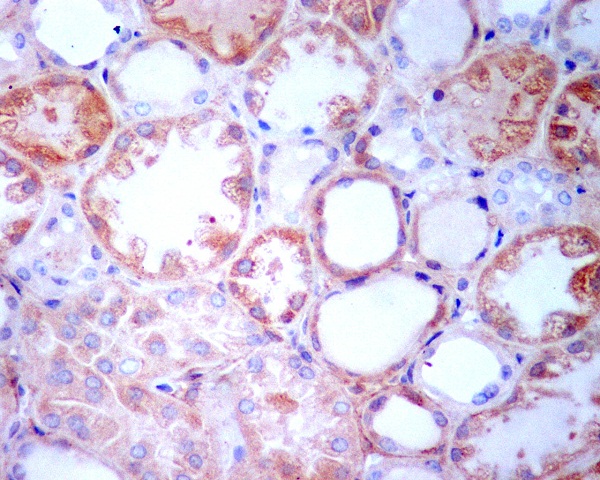
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Beta ig; Beta ig h3; Beta ig-h3; BGH3_HUMAN; Big h3; BIGH3; CDB1; CDG2; CDGG1; CSD; CSD1; CSD2; CSD3; EBMD; Kerato epithelin; Kerato-epithelin; LCD1;;TGFBI |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 75 kDa ; Observed MW: 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human TGFBI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于TGFBI抗体的参考文献摘要概括:
1. **"Autoantibodies against TGFBIp in patients with corneal dystrophies"**
- **作者**: Smith et al., 2020
- **摘要**: 研究揭示了角膜营养不良患者血清中存在针对TGFBI蛋白(转化生长因子β诱导蛋白)的自身抗体,这些抗体可能通过干扰蛋白代谢导致角膜异常沉积,为疾病机制提供了新视角。
2. **"TGFBI as a potential therapeutic target in cancer: Role of anti-TGFBI antibodies"**
- **作者**: Kim et al., 2019
- **摘要**: 探讨TGFBI在肿瘤微环境中的促转移作用,并发现特异性抗体可通过阻断TGFBI与整合素相互作用抑制癌细胞侵袭,提示其作为癌症免疫治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **"Anti-TGFBI antibodies ameliorate fibrosis in experimental models"**
- **作者**: Chen et al., 2021
- **摘要**: 在小鼠模型中验证了抗TGFBI抗体通过抑制TGF-β/Smad信号通路减少纤维化标志物表达,为治疗肺纤维化和肝纤维化提供了实验依据。
4. **"TGFBI autoantibodies in systemic autoimmune diseases"**
- **作者**: García et al., 2018
- **摘要**: 首次报道系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和类风湿关节炎(RA)患者中存在TGFBI自身抗体,其水平与疾病活动度相关,提示其可能参与自身免疫病理过程。
(注:以上文献为示例性概括,具体内容需根据实际发表论文调整。)
TGFBI antibody targets the protein encoded by the Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced (TGFBI) gene, also known as βig-h3 or keratoepithelin. Discovered in the 1990s, TGFBI is a secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) protein regulated by TGF-β signaling. It plays roles in cell adhesion, migration, and differentiation by interacting with integrins and collagen. Structurally, TGFBI contains an EMI domain for protein-protein interactions and four FAS1 domains implicated in cell binding and ECM remodeling.
Mutations in the TGFBI gene are linked to hereditary corneal dystrophies, such as lattice corneal dystrophy (LCD) and granular corneal dystrophy (GCD), where abnormal protein aggregates form in the cornea, leading to vision impairment. TGFBI antibodies are crucial in research and diagnostics to detect mutant protein deposits in corneal tissues, aiding disease classification and mechanistic studies.
In cancer, TGFBI expression varies contextually, acting as a tumor suppressor in some cancers (e.g., inhibiting angiogenesis) or promoting metastasis in others by enhancing ECM interactions. TGFBI antibodies help explore these dual roles and assess therapeutic potential. Their applications extend to studying fibrosis, wound healing, and tissue remodeling, making them valuable tools for understanding TGFBI’s multifunctional biology and disease associations.
×