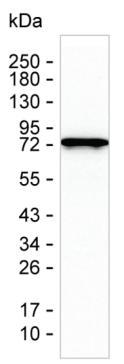
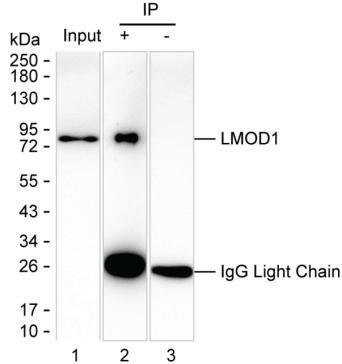
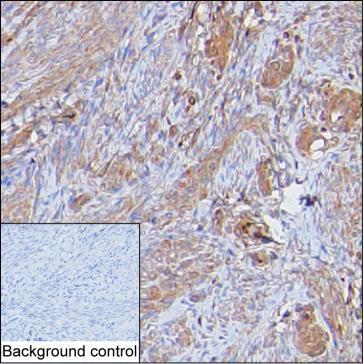
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LMOD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于LMOD1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟生成,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**: Leiomodin 1 regulates actin filament organization in smooth muscle
**作者**: Cenik BK, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性LMOD1抗体,通过免疫荧光和Western blot分析,揭示了LMOD1在平滑肌细胞中通过促进肌动蛋白丝成核和延伸来维持细胞骨架稳定性的机制,其缺失导致细胞收缩功能异常。
2. **文献名称**: LMOD1 antibody characterization and its role in nemaline myopathy
**作者**: Gupta VA, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种高特异性LMOD1抗体的开发与验证,并发现LMOD1基因突变患者中该蛋白表达显著降低,提示其作为先天性肌病(如杆状体肌病)潜在生物标志物的可能性。
3. **文献名称**: Leiomodin1 dysfunction due to LMOD1 variants leads to dilated cardiomyopathy
**作者**: Yuan CC, et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建LMOD1基因敲除小鼠模型,结合抗体检测心肌组织蛋白表达,发现LMOD1缺失导致心肌细胞肌节结构紊乱,阐明了其在扩张型心肌病发病中的关键作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词"LMOD1 antibody"或"Leiomodin1"检索最新研究,并核实抗体应用场景(如物种特异性、实验方法等)。
**Background of LMOD1 Antibody**
LMOD1 (Leiomodin 1) is a member of the leiomodin family of actin-binding proteins, primarily expressed in smooth muscle cells and skeletal muscle. It plays a critical role in regulating actin cytoskeleton dynamics by promoting the elongation of thin filaments and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) structures. LMOD1 is essential for maintaining muscle contractility and structural integrity, particularly in vascular and respiratory systems.
The LMOD1 antibody is a tool used to detect and study the expression, localization, and function of LMOD1 in various biological contexts. Research has linked LMOD1 dysregulation to human diseases, including congenital myopathies, thoracic aortic aneurysms, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. For instance, LMOD1 mutations are associated with severe muscle weakness and respiratory insufficiency in infants, highlighting its clinical relevance.
In laboratory settings, LMOD1 antibodies are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate LMOD1’s role in muscle development, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets. Recent studies also explore its interaction with other cytoskeletal proteins, such as tropomyosin and tropomodulin, to elucidate its regulatory pathways.
Overall, LMOD1 antibodies serve as vital reagents for advancing understanding of muscle biology, cytoskeletal disorders, and related genetic or acquired conditions. Their application continues to drive discoveries in both basic research and translational medicine.
×